Sometimes the very first signs of an adsorber malfunction can be completely unnoticeable, and sometimes they remind you of themselves with very characteristic symptoms. How can you tell if your car's adsorber has become damaged and requires repair? After reading our material, you will know more about adsorbers than ever before.
Signs of a malfunctioning adsorber are a “dark horse” for another reason. Even beginners know where the oil filter, carburetor, and battery are located in the car. But what is an adsorber? Where did this part come from, what role does it play in a modern car? After all, if you take into account domestic cars of previous years, they did not have any trace of adsorbers.
That’s right - the adsorber in the Soviet Union was a real curiosity. Today, with the advent of the Euro 3 standard, they began to install it on all modern cars. The basic task of the device is to retain the vapors of consumed fuel and do everything possible to ensure that as little harmful exhaust as possible enters the atmosphere. The rules of the standard are unshakable, so fulfilling it is an obligatory task for every car enthusiast. In connection with this fact, the adsorber began to be installed on foreign and domestic cars.
By the way, in some sources you can also find the name absorber. We are talking about the same device.
The appearance of the adsorber is somewhat reminiscent of an opaque jar. It is small in size and gases are adsorbed inside. The main adsorbent is coal, but some other substances can also be used. The spare part also has an electric valve. When working, it makes very characteristic sounds. When you warm up the engine, it begins to make a very characteristic clattering noise.
If we talk about adsorber malfunctions, they do not happen so rarely. Like any other part, the adsorber can become clogged with harmful impurities and become unusable. Other flaws are associated with minor or more serious mechanical damage, natural wear, and contamination of the gas-absorbing element.
Problem #1
– there is too much pressure in the gas tank. In fact, this is one of the main symptoms that something is wrong with your car's canister. The vapors have nowhere to go, so they begin to accumulate and put pressure on the gas tank. Even when the engine is not running, they do not want to escape through the adsorber. It is not difficult to verify the presence of strong pressure. Open the gas tank cap. If you hear a hissing sound, there is indeed a lot of vapor accumulated in the gas tank, which can be harmful to the atmosphere.
Naturally, you shouldn’t take every hissing sound as a serious problem. A light, barely noticeable hiss can still be taken as normal. According to modern environmental requirements, fuel systems must be strictly sealed. This allows you to minimize the release of vapors into the atmosphere.
Problem #2
– a sharp drop in speed. This happens if you start warming up the engine at 60 degrees, and it mercilessly stalls. In this situation, we can only advise one thing - check your adsorber again. It is possible that it is he who “spoils the weather.” To do this, disconnect the small hose that goes to the valve from the manifold. You will need to muffle it - for example, using a tie or plug. Start the engine again. If it continues to operate sluggishly and unstably, the adsorber is clogged.
Principle of operation
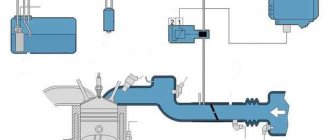
The adsorber itself allows fuel vapors to accumulate in a special place - the separator. As a result, gasoline turns into condensate and goes back to the tank. Vapors that have not undergone treatment go through double valves of the system, one of which prevents fuel from spilling out during an emergency (for example, a coup), and the second “is engaged” in regulating the pressure in the tank. The adsorber purge valve is located under the hood, and the adsorber itself is located on the tank. The control unit ensures the normal operation of the entire system: it ventilates and removes condensation.
How to disable or remove the adsorber on a car and do you need to reflash the ECU?
You need to understand that when the adsorber is removed, the solenoid valve is turned off, which is directly connected to the controller and controlled by the latter.
This will lead to error p0443, which we already mentioned above. The tubes are also silenced, in particular the one that goes to the intake manifold.
What is the disadvantage of such a shutdown?
The fact is that through the tube that goes to the intake manifold, air is constantly sucked in; even in idle mode, the so-called small purge of the adsorber occurs. At high speeds from 1500 – 2000 and above there is a lot of blowing.
In the ECU firmware, constant air leaks and the flow of fuel vapor are taken into account when forming the air-fuel mixture, despite the fact that all this goes past the mass air flow sensor, the causes of the malfunction of which can be found out by clicking on the link.
If you plug the pipe, which many people do, a certain amount of air will not flow into the intake manifold bypassing the ECU, but the latter still takes them into account.
That is, the controller takes into account one volume of air, but another (smaller) one actually enters. As a result, the amount of fuel is generated by the ECU based on more air than is supplied. This leads to an over-enrichment of the air-fuel mixture.
As a result, the engine does not work correctly, because the mixture is constantly over-enriched where it is and is not needed, and fuel consumption increases.
It is also worth talking about the transient mode of operation of the engine, which can manifest itself when approaching an intersection, a traffic light, lying to a policeman, at the moment when the gas is released.
At this moment, a failure may occur - a decrease in speed below idle. The engine seems to choke, it doesn’t have enough air, the reason is an over-enriched mixture. After a few seconds, the situation is resolved electronically.
Therefore, it would be correct to disable the adsorber in the following ways:
After removing the device, install a nozzle with a diameter of 1 mm into the tube that goes directly past the mass air flow sensor. This will, at least partially, solve the problem, since only air without gasoline vapors will be supplied in doses.
- The ECU is re-queried (difficult). If it is impossible to remove the Check error, you may need engine chip tuning, which is expensive.
- Dismantling the entire system except the solenoid valve, which operates idle.
- By installing a resistor (valve emulation) in the electrical circuit at 200 - 250 Ohms and 2 watts. To do this, bend the legs of the resistor and insert them into the valve chip. We secure everything with electrical tape. But this doesn't always help.
How to disable the adsorber on a VAZ 2110, 2112, 2114
Taking into account the recommendations above, we do the following:
- Disconnect the power connector from the valve.
- Disconnect all pipes from the adsorber and remove the latter along with the mount.
- We fix the valve in a place where the plug with wires and pipes will reach.
- Connect a hose with a fuel filter to the lower fitting (see photo below).
- To the upper end fitting we connect the pipe going to the intake manifold.
- We put another filter on the pipe going into the tank, similar to the first one.
With this scheme, when the valve opens, clean air enters the system, albeit without gasoline vapors.
We exclude the valve
This method is even simpler. We dismantle everything, including the valve. We put a fuel filter on the pipe coming from the gas tank, and we plug the pipe going to the intake manifold with a bolt and clamp.
The consequences of this method are described above, but this method also has the right to life. As for Priora, Granta, Lada Largus, Gazelle and other cars, the absorber is turned off in similar ways as described above.
Toyota Chaser
It is worth considering one of the foreign cars, for example, the Toyota Chaser.
The shutdown principle is similar to the previous ones:
- Locate the canister valve. It is located near the mass air flow sensor on the air filter housing.
- Disconnect the chip with wires and all pipes from it (Check may light up on the instrument panel).
- Find the adsorber, disconnect the pipes from it and plug it.
- Disconnect the pipe going to the valve from the throttle assembly and plug it with a bolt and clamp.
- Place a fuel filter from a carburetor VAZ on the pipe going to the tank.
What's the catch in flashing from Euro 4 to Euro 2?
Many people change the ECU from Euro-4 to Euro-2, as a rule, they do this when removing the catalyst and installing a blende. At this moment, the canister valve may turn off (on purpose or accidentally), and the ECU does not control the latter and does not control it in any way.
As a result, if the valve malfunctions, the engine will run intermittently, and the error will not be displayed on the instrument panel. To make sure of this, turn off the valve and observe the operation of the motor.
If the version is confirmed, plug the canister pipes and turn off the valve; the controller still does not control it.
Design and operation of the adsorber purge valve
The KPA is an electromagnetic locking device that operates from the vehicle’s on-board network. The valve consists of:
- plastic case;
- valve with spring;
- windings;
- metal core;
- connector
When the vehicle's engine is turned off, no voltage is supplied to the valve and it remains in the closed position. That is, on the motor side, the system that captures vapors is blocked. At the same time, the adsorber begins to “collect” vapors. When the power unit starts, voltage is applied to the valve, causing it to open and fuel vapors to enter the intake manifold. As soon as the ignition is turned off, the control unit is de-energized and the pipeline is closed: no vapors enter the receiver.
What is an adsorber and what is it for?
What does the adsorber look like?
The adsorption process is the absorption of gaseous media by bodies of solid or liquid consistency. Accordingly, the main task of the adsorber is to absorb gases, preventing them from entering the environment. However, these are not exhaust gases, but gasoline vapors emanating from the cavity of the fuel tank. When the car engine is running, the trapped vapors are transferred to the intake manifold; while parked, gasoline vapors are neutralized inside the adsorber.
Thus, the adsorber does not allow gasoline vapors to penetrate into the environment, which is required by modern environmental standards, and also does not allow them to enter the cabin. In addition, delaying, condensing vapors and returning gasoline back to the fuel system provides additional savings.
We recommend: How to change the heater radiator on a Lada Kalina
It should also be noted that the function performed by the adsorber is complex ventilation of the fuel tank. When fuel is consumed, the freed space is filled with air, which is supplied through the adsorber. Here the air is filtered and dried, which has a positive effect on the operation of the engine as a whole.
The key basis for dividing adsorbers into separate classes is its filling. Currently the following options are used:
- granular adsorbent in a stationary state;
- granular adsorbent capable of moving in the cavity of the device;
- fine-grained filling with a boiling bottom layer.
Adsorbers with static coarse-grain filling show maximum efficiency. Its main advantage is protection from partial or complete loss of the active substance along with fuel vapors.
Signs of a malfunction of the control unit
First, start the engine: at idle or in cold weather, you will hear a characteristic, barely audible chirping sound. It indicates that the valve is working properly. In order not to confuse this sound with the noise from a working timing belt, sharply press the gas. The character of the chatter should not change. The following signs indicate a malfunction of the control unit:
- lighting of the CHECK signal on the instrument panel;
- determination of error PO441 during testing;
- increased gasoline consumption;
- unstable operation of the power unit when driving;
- unstable idle;
- increase in CO2 content;
- a hissing sound when unscrewing the tank lid (a vacuum has appeared);
- the appearance of a fuel smell in the cabin.
What is an adsorber in a car, how long does it last, signs of malfunction, how to replace it
The issue of ecology has long been an issue for major car manufacturers, and the result is achieved through many innovations. Among them is installing an adsorber in a car.
What functions does this device have? Where is it located? What are the advantages and disadvantages? These and a number of other issues require consideration in more detail.
What is an adsorber in a car, why is it needed and where is it located?
Today, the European environmental standard “Euro-3” is in force, according to which the emission into the atmosphere of hydrocarbon vapors resulting from the combustion of fuel is prohibited. To implement this task, a special device was developed - an adsorber.
The name of the device comes from the word adsorbent (absorbent composition). The unit is mounted in the fuel system of a vehicle in order to absorb harmful vapors arising during the evaporation of fuel.
The absorbent is activated carbon, which fills the tank. It is this that absorbs harmful substances when the engine is not running. Otherwise, the vapors are sucked into the intake pipe and burned in the engine along with the combustible mixture.
This feature helps to increase the efficiency of the car. The result is a double effect: fewer harmful vapors enter the atmosphere and the combustible mixture is saved.
An adsorber is a filter element that becomes dirty over time and its effectiveness decreases.
The main sign of a malfunction is a “hissing” sound when the fuel tank cap is unscrewed. This happens due to the fact that fuel vapors have nowhere to go, and they “rush” out with all their might.
The location of the adsorber varies depending on the make and model of the car. So, in VAZ cars the device takes the form of a black can with a cylindrical shape. The device is often located on the right side in the direction of travel, in the near corner (near the headlight).
But for each model, the manufacturer determines the location of the device individually.
For example, in the VAZ 21099 the absorbent injector is located like this.
From what Euro standards is it established?
According to international requirements, the installation of an adsorber is mandatory on cars with Euro-2 standards and higher. As for the standard known in Russia (Russia-83), there is no installation of an adsorber here.
So, in VAZ-2108 cars there is no adsorber. Here the separator and the fuel tank are connected to each other using a drain tube.
During operation, condensation occurs and returns to the fuel tank.
In addition, the separator interacts with the atmosphere using a 2-way valve, which does not allow the pressure in the tank to increase or decrease.
The connection between the tank and the neck occurs using a gasoline-resistant tube, fixed with clamps. It turns out that when the pressure in the tank decreases (increases), fuel vapors escape into the atmosphere.
The system is organized differently in VAZ Priora cars. Here, the fuel vapors that entered the separator from the fuel container condense. The condensate then accumulates and returns to the tank.
A gravity valve is mounted in the upper part of the separator, which prevents the fuel mixture from leaking out of the tank if the machine overturns.
If the engine is started, the vapors of the fuel mixture are mixed with air masses and discharged through the throttle assembly into the intake pipe - to the cylinders of the power unit.
It turns out that fuel vapors in a stationary position of the car accumulate in the adsorber, and if the car is moving, they are purged by the valve and sent to the receiver and to the engine for afterburning.
According to Euro-2 requirements, the fuel tank ventilation must not come into contact with ambient air, and vapors must be collected and directed to the engine (or adsorbed by the device in question).
As for the Russia-83 standards, contact between the atmosphere and ventilation of the fuel bank is not prohibited.
The adsorber device, together with which devices it works
The device for absorbing harmful vapors of the fuel mixture consists of the following components:
- adsorbent composition (activated carbon);
- gravity (electromagnetic) valve;
- separator;
- purge valve;
- fuel drain pipes;
- steam hose.
The basis of the design is the adsorber, whose task is to collect harmful vapors that come from the fuel tank and prevent them from entering the atmosphere.
In this case, the adsorber will combine with:
- Fuel tank;
- Intake manifold;
- Atmosphere (through a separate valve installed on the air filter or at the inlet to the device).
The system valve is an actuator that combines the adsorber and the intake manifold.
Pros and cons of the device
Like any other unit, the adsorber has its own positive and negative qualities that the car enthusiast should know about:
1. Advantages:
- No harmful fuel vapors enter the atmosphere.
- Fuel is saved because the vapors do not escape into the atmosphere, but return back to the engine for combustion.
- The unpleasant smell of gasoline disappears from the passenger compartment (this effect does not always occur).
2. Disadvantages:
- The adsorber has a substantial size, so it takes up a certain space under the hood.
- The engine operates unstably, and “swimming” occurs at idle (one of the main signs of a failed adsorber).
- High price. Installing an adsorber increases the cost of the car.
- Risk of the tank cap “shooting out”. This is possible in the event of a breakdown of the adsorber and prolonged accumulation of fuel gases in a confined space.
- Risk of deformation of the fuel pump. Ignoring the failure of the device also leads to this problem.
- Risk of accumulation of a flammable mixture in the intake manifold due to the inability of the adsorber to perform its functions. As a result, the stability of the motor is disrupted.
Valve check on site
You will need a tester (voltmeter, multimeter) and a screwdriver. The KPA itself is installed on the radiator frame. The device can be recognized by seeing two tubes approaching it, through which the evaporation moves. Further:
- disconnect the electrical connector from the control unit by releasing the block lock;
- using a multimeter, check for the presence of voltage by touching the negative (black) probe of the device to ground, and the red probe to “A” (the letter on the block connector);
- turn on the ignition: the multimeter should show the vehicle's on-board voltage. If not, check the wiring.
Checking the functionality of the adsorber
To make sure that the malfunction is related specifically to the valve of this element, you can send the car for a full diagnosis. But this is expensive, so let’s first try to identify possible problems ourselves.
First of all, you need to see if the controller is generating errors, for example, “open circuit control.” If everything is fine, then it will use a manual check. To do this, just prepare a multimeter, a screwdriver and several wires. After this you need to follow a few simple steps:
- Raise the hood of the car and find the valve you need.
- Disconnect the wiring harness from this element. To do this, you must first release the special lock that secures the pad.
- Check if there is voltage going to the valve. To do this, you need to turn on the multimeter and switch it to voltmeter mode. After this, the black probe of the device is connected to the ground of the car, and the red probe is connected to the connector marked “A”, which is located on the wiring harness. The next step is to start the engine and see what readings the device gives. The voltage should be the same as the battery. If it is not there at all or is too small, then you will probably have to look for a more serious problem. If everything is fine with the voltage, then you can move on to the next step.
- Remove the purge valve. To remove it you need to use a screwdriver to slightly loosen the clamps. After this, you can easily move the valve slightly up and smoothly pull it out along a small bracket. After this, the device must be connected directly to the battery terminals. One wire goes to the purge valve (to “+”), and the second is connected to “minus”. After this, both conductors are connected to the corresponding battery terminals. If there is no click, then the valve is completely out of order and it is best to replace it.
We recommend: Installation and replacement of the fuel pump relay
How to check the adsorber valve removed from the car
You need to take a medical syringe of suitable volume, simply pull out the piston 2-3 cm and connect it to the outlet fitting. If you press on the piston, it will move with difficulty, which indicates that there is pressure in the valve. Now connect the battery to the electrical part of the control unit and press the piston again: the resistance should disappear. If this does not happen, you will have to buy a new valve.
A specific question is: how to check the operation of the adsorber valve? This device is found on many new cars. It is designed to absorb excess carbon gases from the car's gas tank. Thus, this mechanism prevents the release of gases into the atmosphere. It was necessary to use a device of this type after the introduction of new restrictive Euro-3 and higher standards. When working properly, the car has a low level of pollutant gases in the exhaust, and there is also a slight reduction in fuel consumption. However, like any device, this engine element also tends to break. Failure can occur due to clogging of the adsorbent inside the absorber, as well as due to direct mechanical impact on the absorber body. In any case, problems begin when the engine operates...
CONTENTS OF THE ARTICLE
First, a little definition.
Priora adsorber valve: repair and replacement
A car today is a high-tech and rather complex device. It is extremely difficult and almost impossible for a simple car enthusiast to understand all the intricacies of its arrangement.
But it is still necessary to at least have some understanding of the operation of cars. This will allow you to identify possible technical problems in a timely manner and call for the help of specialists to fix them.
In the article, we will look at such, on the one hand, a minor part as the solenoid valve for purge of the Priora adsorber, we will analyze the reasons for its failure, and we will also talk about the main points that you should pay attention to when replacing it.
The concept of an adsorber valve in a car, its appearance and purpose
This device is installed on all injection engines. The Priora is also equipped with the same engine. The adsorber valve is mounted in the device itself, which looks like a can filled with activated carbon. It is installed next to the gas tank and absorbs the emitted gasoline vapors.
And now in more detail
How can I check the functionality of this device? An important element in the absorber is the valve. To understand the function, let's look at how the adsorber works. When the car is parked, a large amount of gasoline vapor can accumulate in its tank. Some of the vapor is caught by the recuperator, and the rest settles back into the tank. The part that was caught is sent to the adsorber. When the engine is running, the absorber valve closes and interrupts the access of vapors, now they are sent into the combustion chamber. Why is this necessary? When you start the car, our device prevents vapors from entering the exhaust manifold, thereby reducing the amount of harmful substances in the gas.
Device
Engines with distributed fuel injection first appeared on front-wheel drive Ladas, starting with the 2111 model. They differ greatly from their carburetor predecessors in a more complex power system design. It consists of 2 subsystems: fuel supply to the fuel rail and gasoline vapor recovery. One of the components of the latter is the adsorber in the VAZ-2114.
A solenoid valve is placed on top of the plastic cylinder and is controlled by the engine control unit. This part is removable and secured with plastic latches. The valve body is rectangular, and there are 2 fittings (inlet and outlet) and a connector for connecting the ECU.
The hoses are secured to the fittings using clamps. The incoming one is connected to the gravity valve and then to the separator and the gasoline tank. The outlet is connected to the throttle valve assembly.
How to identify a problem at work?
The most common symptoms of malfunction include:
1) Sometimes the engine starts to run unstable at idle speed;
2) If clogged, you may feel a slight increase in fuel consumption;
3) The car engine does not start the first time when hot;
4) A noticeable loss of traction at low speeds. At higher speeds, the loss of torque is less sensitive.
Another common malfunction is the appearance of cracks in rubber plugs. Through these cracks (holes), additional air is sucked in, and as a result, leads to problems with the engine.
There are problems, but everything is whole
Having the above symptoms, and having checked the integrity of the hoses, we move on to the adsorber valve. How to check it?
1) First of all, disconnect the negative terminal from the battery;
2) Remove the absorber (in most cases it is located on the right side of the engine near the car’s air system);
3) Now turn off the electrical power to the valve itself;
4) Remove the hoses (inlet and outlet);
5) Then we try to blow air into the system through the valve (into the holes for the hoses);
6) If it is working, then when the power is removed from it, it will be blocked, i.e. You won't be able to blow it out;
7) Check further. We connect two wires from the battery to the power contacts on the valve. At the same time, you should hear an opening sound (click);
8) When connected to the source, we try to blow air into it. It should work without problems, if not, then it is closed;
9) Reset the power, if it closes again, then it is 100% working.
By checking the adsorber valve in this way, you can determine its performance at almost 100%. Of course, there may be nuances in which this will be more difficult, but the principle is the same everywhere. Thus, we have described in detail how to check this device.
If it is faulty, then you need to buy a new one - the cost is about 2000 rubles, so before you immediately change it, check it. If the problems lie in the operation of the electronic control unit, then this is a completely different story and everything becomes much more complicated.
Now a short video of a VAZ engine.
I’ll finish here, read our AUTOBLOG.
Similar news
- How to bead a wheel?
- What are stabilizer bars used for?
- Blue smoke from the exhaust pipe