The durable metal surface of new or old cars is coated with special anti-corrosion agents. This allows, under conditions of constant use, to extend the service life of the car body for a long time.
The production volumes of anti-corrosion coatings continue to grow because all means cannot protect even the highest quality car from the oxidative effects of air, water and time. With a skillful approach and regular care of the condition of the car, when applying an anti-corrosion coating to the car, careful car owners can manage to keep the car untouched by rust for a significant period of time.
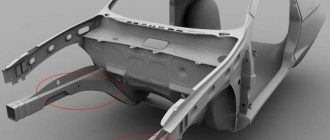
The most vulnerable places
Corrosion is the process of destruction of metals. Oxidation occurs due to electrochemical, physicochemical and/or chemical interaction with other substances in the external environment - oxygen and water. The most vulnerable areas of a car to rust are those that are under constant and long-term exposure to external factors.
The open surfaces of the car are subject to mechanical stress and are constantly in contact with atmospheric air containing oxygen. Hard-to-reach areas of the car body cannot always dry quickly after moisture enters, and therefore are also subject to the destructive effects of oxidizing processes.
The most vulnerable places for corrosion in a car are the following:
There are always microcracks in places where car body parts are welded. They are the initial sources of corrosion, especially in the presence of high levels of humidity. In this case, water turns into ice in winter and, increasing in volume, contributes to the appearance of a crack in the seam and its subsequent increase and cracking.
- The underbody of the car, the surfaces of the wheel arches, the exhaust pipe, the muffler, the wheel arches, the sills.
The bottom, lower part of the doors and other parts of the car into which crushed stone and other debris flies from the road are constantly exposed to increased exposure to streams of dirt and sand quickly moving from under the wheels, which enhances the corrosive effect. These places primarily need anti-corrosion treatment.
- Engine and exhaust system.
In conditions of constant operation of the car engine and the exhaust system, which is closely connected with it, permanent conditions of elevated temperatures and high humidity are created, so corrosion also occurs in this part of the car.
The car interior and internal cavities remain wet and dirty even after several short trips around the city.
It is worth noting that despite similar processes occurring during vehicle operation, vulnerable areas are treated with different solutions. Since the nature and intensity of pollution is heterogeneous, each detail requires an individual approach.
Hidden and hard-to-reach car cavities are treated with liquid oils, wax-containing and paraffin-containing elastic automotive products. Oily car products fill cracks, displace moisture, periodically moving along the surface as the car moves. Substances with a high content of paraffin and wax contain a solvent that gradually evaporates and an inhibitor remaining on the surface, that is, a corrosion retardant.
External surfaces need to be treated with hardening compounds, and internal, hard-to-reach places - on the contrary, with liquid, non-hardening substances.
Anticorrosive treatment. Quality criteria:
As is known, all protective coatings have their own critical thickness, below which long-term protective properties decrease. The physical characteristics of the materials and equipment must ensure that the required thickness of the coating is applied.
The complexity of the body structure with an abundance of hidden cavities requires anti-corrosion materials to have special properties such as penetrating ability and moisture displacement. So, the protective properties of the coating are ensured by applying a film layer of at least a critical thickness.
Penetrating ability is ensured by the penetration of the material into micro-gaps to an effective depth and height in the required quantity. The moisture-displacing ability is ensured by the distribution of the film over the entire area of the wet surface.
All cavities are treated from the outside through small technological openings using spray nozzles in the absence of visual control. Consequently, the equipment and fixtures used must guarantee the application of anti-corrosion compounds within the normal film thickness and in the proper volume. Good command of the spraying technique combined with knowledge of the structure of the hidden cavities of the body is a mandatory requirement for a specialist in anti-corrosion treatment; pay attention to this point if you decide to do the anti-corrosion treatment yourself.
Make anticorrosive with your own hands. Features of materials:
Professional anti-corrosion compounds must have good thixotropy (the ability to remain in a horizontal position), i.e. After applying the coating to the surface, the film thickness should not decrease below a critical level due to runoff, dripping under the influence of temperature or vibration.
It is a fallacy to say that a material should not change its initial properties over time. According to the laws of physics and chemistry, this is impossible; changes inevitably occur. The best materials are distinguished by the fact that their protective properties change slowly and evenly. Thus, periodic renewal of the protective coating and additional anti-corrosive treatment are necessary.
The car body has hidden cavities of various configurations and sizes, located in different places. Accordingly, these cavities have different microclimates - humidity, temperature, electrolyte concentration. Some areas of the body, due to their aggressive microclimate, are more susceptible to corrosion. Such areas are called critical. Examples of such areas are cavities with an abundance of microgaps and welds. The lower they are located and the closer to the engine compartment, the higher the corrosion rate.
This happens for the following reasons:
- in microgaps the electrolyte lasts longer than in open areas;
- water from the road constantly gets onto the lower part of the body;
- areas near the engine compartment become hot.
Another example is box sections designed without regard to corrosion resistance requirements. Such sections retain water and are exposed to high humidity for a long time, and in winter they are subject to the forces of freezing water increasing in volume.
Thus, effective protection is ensured by paying special attention to critical areas. The mere presence of anti-corrosion material in hidden cavities is not enough for a high rating of vehicle treatment. In order to evaluate the quality of processing, it is necessary to ensure that the material is present in critical areas, and that the film thickness and volume of the composition will provide reliable protection for the longest possible period of operation.
How to protect your car from corrosion
Anti-corrosion treatment of a machine requires the use of several substances and technologies. During the complete rust treatment procedure, the following types of protection are used:
Protective anti-corrosion substances that actively interact with the surface of the machine and repel moisture, for example, Movil with a corrosion inhibitor.
Refers to mechanical methods of protection. Substances are also used that, after applying a thick layer to the surface of the car, completely isolate the car from corrosion or external influences of sand and gravel. For example, mastics have good protective properties against mechanical damage and corrosion.
Products that transform the surface of a car that has already begun to rust. They cover up rust on the body.
They combine several substances into a single complex.
The first type of anti-corrosion treatment for a car is done with your own hands to prevent corrosion on the bottom of the car. To provide passive protection to the underbody, it is carefully covered with a special material, thus preventing the lower surface from getting destructive fractions from the outside.
Barrier protection and galvanizing method
Anti-corrosion protection of the car body by galvanizing is carried out at the factory. To protect against corrosion, the machine body is dipped into a special bath of molten zinc, as a result of which a strong ferro-zinc (Fe + Zn) alloy with a layer thickness of 0.8-2 microns is formed on the treated surface. In this case, the distribution of zinc throughout the metal of the body is as follows: in the depth of the anti-corrosion protection there is about 70% of zinc and only closer to the surface the zinc content increases to almost 100%.
After properly galvanizing, the machine is closed to corrosion barrier and electrochemically. The car body is also protected by attaching shields, hood spoilers made of plastic material or leather, as well as lockers, that is, plastic fender liners, linings, covers for the sills and the lower part of the doors.
Body lamination
Lamination is the covering of a car body with a special polyurethane, vinyl, anti-gravel film using special tools. This anti-corrosion film not only acts as a barrier to small fractions (pebbles) falling on the car, from scratches, chips and other minor damage, but also prevents sunlight from spoiling the color saturation of your car. This type of protection of the car body from corrosion does not damage the varnish (paint) and does not enter into a chemical reaction with the paintwork, so it can be easily removed when worn. Properly glued film lasts about five to seven years.
Cathodic protection
The effect of anti-corrosion protection when using cathodic protection devices is compared with galvanizing. The principle of operation is the polarization of the metal during the creation of a galvanic couple: the electrode and the protected surface. During the application of cathodic protection, a negative potential of the desired limit value is produced, which prevents oxidation.
The peculiarity of this method is that it protects the car from corrosion even in hard-to-reach places. Moreover, restoration of car parts already affected by corrosion becomes available. Cathodic anti-corrosion protection is also actively used to protect the trunk of a car from external influences.
What will you need for the job?
To protect the underbody of a car from corrosion with anticorrosion, you can use various preservatives for hidden cavities, anti-gravel coatings, compounds for the underbody, materials for arches and the inner parts of the wings. All of them are needed to prevent premature rust formation.
For the bottom
Anticorrosive for the bottom
The price of anti-corrosion agent for the bottom of a car is not very high, but these compounds form an elastic, high-strength and thick enough film to protect surfaces from negative influences. The materials must be applied to a cleaned and pre-primed surface. Anticorrosive contains special fillers, for example, tiny aluminum powder. Also, the composition always contains corrosion inhibitors that slow down its formation.
At home, anticorrosive coating can be applied with an ordinary brush, and as for domestically produced materials, the most affordable and widespread are bitumen mastics with rubber crumbs.
Another task that mastic copes with is increasing the vibroacoustic characteristics of the body. This is what crumb rubber is designed for.
Anticorrosive for arches
Anticorrosive for arches
Special anti-corrosion compounds for arches have the same properties as the above-mentioned materials, but there is one feature. Arches have less protection against abrasive wear than the bottom. They are constantly exposed to snow, wet mud, sand, ice and stones that fly out of the wheels and hit the surfaces of the arches. If you do not protect them, corrosion will inevitably begin to form within a few years, even on a new car.
You can insert plastic fender liners into the wheel arches, which will solve the problem, but you can also purchase a special Liquid Locker, which is a high-strength elastic material. When applied to the surface of the arches, a layer is formed that protects the metal from abrasive wear.
If you wish, you can apply an anti-corrosion agent for the bottom to the inner parts of the wheel arches yourself, but do it in two layers. Similar to underbody compounds, arch materials contain corrosion inhibitors.
For hidden cavities
Every car has numerous hidden cavities:
- racks;
- thresholds;
- spars;
- trunk reinforcements;
- floor enhancers.
Rust Stop
They can only be accessed through special technological openings. So-called cavity preservatives are low-viscosity liquid materials, similar to motor oil, containing corrosion inhibitors. They form a semi-drying film on the walls of cavities, have a unique penetrating ability and are able to displace moisture from metal surfaces.
The most famous domestic preservative for cavities is Movil. It has been produced for several decades and still remains relevant. The non-ecological composition provides reliable anti-corrosion protection for the bottom of the car.
We also do not recommend buying products from the Waxoil company, since it contains only 13 percent solids, and the remaining 87 are solvents. The absence of odor indicates a high degree of purification of the solvents, but this is not the most important thing if you want to make anti-corrosion bottoms with your own hands. There is also a composition of the Rust Stop brand, which is created on the basis of mineral oil. It is very hygroscopic, so it is better to treat hidden cavities with it at least once every two years, otherwise you will get the opposite effect: excess moisture will stimulate the development of rust.
How are the external surfaces of the body and muffler treated?
According to the variety of compositions of various means for treating a car body against corrosion with your own hands, you can select the following substances:
- Anti-corrosion mastic for cars.
Various tread or protective preparations, which are made on the basis of bitumen, epoxy or synthetic resin, sometimes with the addition of rubber, are applied to almost any part of the body. They have sound insulating properties, dampening resonant vibrations of the body. Mastics are applied mainly in a warm, heated form.
It is used as a protective agent with high permanent elasticity, however, such mastic does not protect against impacts and sudden movements of the machine.
- Bitumen mastic or bitumen-rubber.
A preventive agent for treating the car body against corrosion, which contains special inhibitors.
Suitable not only for anti-corrosion treatment of external parts of the car, but also for coating the bottom of the car.
Contains elements of different types of mastic and can withstand air temperatures reduced to -60 C.
Polymer liquid anti-corrosion materials (sometimes phosphate), applied to the surface being treated, consist of substances based on polyvinyl chloride or rubber. This anti-corrosion treatment for cars has good adhesion, that is, excellent and durable adhesion to the surface. Apply on a pre-coated primer.
It is a polymer plastic material that is used to treat the most vulnerable areas for corrosion on a car. These are wheel arches, sills, the edge of the hood; liquid plastics are considered additional protection.
The anti-corrosion agent is designed to protect joints, seams and surfaces of the car body. After application and drying, it forms a waxy protective anti-corrosion layer.
Next you need to figure out how to paint the muffler. Protective body painting will help you in this matter. Such protection against car corrosion prevents rust and aging of the metal material. It is advisable to paint the muffler using heat-resistant paint so that the car can be used in hot and cold weather.
The highest temperature point at which protective paint performs its functions is 400 C. To increase the protective and repellent properties of the coating applied to the muffler, you can also choose paint with the addition of silicone.
Anti-corrosion agents for the muffler and other car parts require drying or heat treatment, that is, measures that increase the tightness and strength of metal parts.
Now you have learned how to protect your car from corrosion. To do this, use special car products and films glued to the body.
An article about how to properly perform anti-corrosion treatment of a car body. Step-by-step algorithm of work, necessary materials. At the end of the article there is an interesting video about anti-corrosion treatment of the car body.
However, while rejoicing at your new “iron friend,” you should not forget that this “friend” is far from eternal and is very vulnerable. Especially the body, which is the first to be hit by thousands of misfortunes. And the very first enemy of the body is corrosion.
You shouldn’t rely on the manufacturer and think that the factory took care of your psyche and applied a reliable anti-corrosion coating to the body of the car you bought. It’s possible that they did... And if not?
It will be a shame if over time the body begins to be corroded by rust in the most unexpected places. Therefore, you should not expect favors from the manufacturer, but rather insure yourself.
Types of anticorrosives
The modern market offers hundreds of products for treating metal body parts against premature corrosion. Various classes of anticorrosives are used for internal and external surfaces. Compositions for internal bottom pockets, side members, and struts displace moisture from a closed cavity and have a high elasticity index.
The materials do not harden and cover the inner surface with a protective film. Treatment is carried out using a pneumatic gun, if the product is in a jar, or with an aerosol can, the anticorrosive agent is poured into the cavity through a technical hole. The main components in the production of such protection remain paraffin, oil, and silicone.
Anti-corrosion agents for external body treatment: the bottom, wheel arches, the outer part of the threshold have a dense composition, the material used is bitumen mastic, rubber base, organic and synthetic resins.
The composition creates a dense elastic film with a thickness of 1 cm, which prevents the penetration of salt reagents, protects the bottom and sills from mechanical damage from flying gravel during movement.
Why is anti-corrosion treatment needed?
Natural causes
The most vulnerable point of any car body is its bottom. It is constantly bombarded with sand, gravel, asphalt chips and other road debris that can fly out from under the wheels.
In addition, the protective coating of the bottom can be destroyed by snow, salt, ice, acidic dirt and other aggressive environments. As a result, the paint peels off, chips and microcracks appear - and that’s what moisture needs to get inside and cause corrosion.
Therefore, sometimes such an unpleasant paradox arises: the layer of paint is absolutely intact, but since it has lagged behind the metal surface, the body underneath begins to rust inexorably. Moisture under peeling paint occurs as a result of condensation from temperature changes.
New Russian car and used foreign car
The listed nuances already give rise to anti-corrosion treatment of the body. But this applies more to used foreign cars, as well as new domestic cars. Russian car factories do not carry out anti-corrosion treatment at all. And if you bought a domestic car, anti-corrosion treatment must be carried out without fail.
But used foreign cars must be carefully inspected on the overpass, because it is impossible to predict in advance how the previous owner cared for the car.
Metal fatigue
The next reason for anti-corrosion treatment is the so-called “fatigue” of the metal. That is, during long-term use, the metal becomes less durable and therefore more prone to oxidation and corrosion, which in such a situation do not take long to occur.
Financial return
Carrying out anti-corrosion treatment is also financially beneficial. As practice shows, repairing a neglected body can cost almost the same amount as you bought a used car for. Therefore, you should not wait for ventilation from the holes that appear as a result of corrosion - they will not bring you any benefit.
We carry out anti-corrosion treatment with our own hands
If you don’t have time to spare, and also want the body of your car to serve you for as long as possible, then it’s best to do the anti-corrosion treatment with your own hands - it will be more reliable. After all, by performing this procedure yourself, you will do it conscientiously, and besides, you yourself will have information about the condition of your body.
It is worth being well prepared for the anti-corrosion treatment procedure. Start by preparing your funds.
Types of drugs
Based on their content, such materials can be divided into two types:
- wax-based mixtures;
- bitumen-based mixtures.
Regarding their application, anti-corrosion materials also have two varieties:
Products for protecting hard-to-reach internal surfaces
2. Preparations for protecting external surfaces
Anti-corrosion
Any metal part can sooner or later begin to rust. Moreover, the wheel arches, which take mechanical damage from small stones and sand while driving. And in winter, it contributes to the deterioration and failure of coatings - the mixture that is sprinkled on our roads during slippery seasons. Therefore, treating the wheel arches of a car with anti-gravel is one of the most optimal ways out of the situation.
Of course, you can contact the service to resolve the issue. But you can try to do a similar procedure yourself, saving a certain amount of money. And besides, you will be as sure as possible that everything was done according to the rules, because you processed the details yourself.
{banner_content}
Algorithm for anti-corrosion treatment of wheel arches and underbody
If you carry out anti-corrosion treatment yourself and do it correctly, you will significantly increase the life of your car. But to really do it right, become familiar with the necessary order of sequential actions.
Step by Step Operations
- Place the machine on an overpass or inspection pit. If there is neither one nor the other, under no circumstances should you jack up the car or place it on random supports - this can be dangerous. In this case, use a reliable lifting mechanism.
- Remove dirt from the entire surface of the bottom and then degrease this surface. Do this carefully, conscientiously, because the mastic has reliable adhesion only to a clean surface. We wash the bottom with powerful water pressure from a hose, using special cleaning compounds. After you thoroughly wash the bottom, you need to dry it equally well. Try not to leave wet areas at all. For these purposes, you can use a compressor for purging.
- Carefully inspect the paintwork of the bottom in order to find and remove all peeling of the coating, its swelling and cracked areas. For these purposes, use metal brushes, a chisel, a sander and coarse sandpaper. If you find rust, sand the area to a mirror shine and then apply a rust converter.
- After the preparatory work is left behind, it is necessary to degrease the bottom again. This can be done with white spirit, gasoline or acetone.
- The degreased surface of the bottom must be dried and then coated with a zinc-containing primer. Dry again.
- Apply mastic to the bottom in several layers, but not all at once. Each layer must be dried for at least six hours. The air temperature during the entire procedure should not be lower than +16 C. The end result of your work should be a total layer of protective coating from 1.5 to 2 mm. In total, you will spend about 5 kg of mastic on the coating. If you have aerosol cans with anti-corrosion in your arsenal, use them to cover small areas - these cans are too expensive and it is unprofitable to use them on large areas.
- In order to process the wheel arches, you need to remove the wheels and carry out the same actions that were performed to process the bottom. But keep in mind that the arches are much more susceptible to bombardment by gravel and sand than the bottom, and therefore it is advisable to install plastic fender liners there.
How to treat the bottom of a car with mastic at home
Anti-corrosion treatment of the underbody of a car requires preparation and strict adherence to the instructions; when choosing a composition, the following is taken into account:
- Liquid plastic mastic is used as the main remedy against gravel damage and as an additional anti-corrosion agent.
- Rubber mastic provides the greatest protection for the metal, the waterproofing of the bottom is close to 100%, and due to its elasticity, the material easily penetrates into closed cavities.
- Bitumen mastic is applied in a layer of up to 0.4 mm. In addition to protecting against corrosion, the material prevents the appearance of marks from impacts with gravel.
When independently spraying anticorrosive on the bottom, use the following operating algorithm:
- The car should be treated indoors at a temperature of +10…+25 degrees.
- The protection must be applied slowly and in an even layer up to 2 mm. It will shrink as it dries.
- It is recommended to apply anticorrosive only to the treated surface; the rust must be cleaned off and the metal sanded.
- Do not allow the product to come into contact with the exhaust system, engine, brake elements or moving parts of the vehicle.
- Protection must be applied in the following order: underbody, hidden cavities, wheel arches. At home, use a sprayer and use a soft brush to apply the anticorrosive agent into the hidden cavities of the bottom.
Even if the manufacturer indicates that its anticorrosive agent dries after 12 hours, auto mechanics do not recommend starting the car for at least 24 hours after treatment.
The independent process of applying the product does not require additional skills, but if the garage does not have a convenient pit or lift, it is recommended to contact the service.
Possible mistakes
Knowing about the most common mistakes that car enthusiasts sometimes make when doing anti-corrosion treatment on their own, it is easy to prevent these mistakes.
The most “popular” mistake is applying too thick a layer of mastic, as well as skipping untreated areas. Try to distribute the anti-corrosion material evenly and monitor the thickness of the coating.
It is undesirable to carry out anti-corrosion treatment with materials that are not intended for this purpose: waste oil, simple bitumen, lard, etc. These products do not contain ingredients that inhibit the corrosion process. Moreover, they may create a greenhouse effect, as a result of which the paintwork will begin to peel off.
Body reworking
It is useless to carry out repeated treatment with the same materials used for the initial anti-corrosion treatment. The thing is that the new layer of anti-corrosion agent will not be able to reach the affected area located under the old layer.
Therefore, for these purposes, oil-based anti-corrosion preparations are used, which dissolve the previous protective layer and successfully act on rust. Therefore, there is no need to specially prepare the bottom for such processing.
Now you can successfully carry out anti-corrosion treatment of the body of your car, and it will thank you with reliable operation over a long period of time.
Health to your car, and success and a safe road to you!
Video about anti-corrosion treatment of a car body:
Any material undergoes a change in its structure due to combination with various aggressive substances. For metal, the aggressive substance is oxygen (O2), upon contact with which the structure of the metal is destroyed. They are now trying to protect car bodies as much as possible from the formation of corrosion centers, the so-called metal blooming.
Anti-corrosion treatment: what is it and what is it for?
To extend the service life and beautiful appearance of your favorite car (covered with stickerbombing), there are special means and technologies that should be done with your own hands or by specialists.
There are places in the car that corrode faster, rust and rot. This is, first of all, the bottom of the car. The bottom of the car is exposed to impacts from pebbles, gravel, sand, water, snow, and reagents. The primer and paint itself could protect against salt and reagents, but with mechanical impact, stones, the paint cracks and the aggressive environment penetrates the metal surface itself.
It happens even worse when the paint remains intact, but has peeled off. In this case, the formation of corrosion centers occurs much faster, since the surface is not ventilated and is constantly in a wet state.
Comparison of bodies of a new Russian car and a foreign car
Both new cars and used foreign or domestic cars are exposed to the above factors of corrosion formation. Domestic automobile factories do not treat their products with anti-corrosion agents. Therefore, after purchasing a Russian car, it is imperative to treat the underbody, wing arches and other invisible areas that are significantly exposed to aggressive substances. As for foreign cars, the body of foreign cars is processed by the plant itself; they have production facilities for this. Processing is carried out by anodizing and zinc coating. Factory anticorrosive easily protects the car body for up to 5 years. Of course, it depends on what climate zone the car was operated in, humid near the sea or dry.
If a dent appears on the body, there is a new Pops a Dent dent removal device that even a beginner can use.
Many people are mistaken that all used foreign cars are well protected from corrosion. Of course, there are foreign passenger cars that are 30 years old and don’t even “bloom.” Therefore, when buying a used foreign car, you should inspect the car completely, on an overpass, from where you can clearly see the condition of the bottom and wing arches of the body.
Types of material
There are 3 types of mastic for treating the underbody of a car:
Experts decided to determine the quality of processing and protection of the underbody of the car with each of these means. To do this, they conducted a test using a sandblasting machine that operates under high pressure (9 atmospheres). It is calculated that a minute of exposure is equivalent to 20 thousand kilometers .
As a result of the test, the mastic with the addition of rubber began to deteriorate after the 4th minute, and after 8 minutes there was no trace of it left. Thus, this variety will withstand up to 80 thousand kilometers under ideal road surface conditions and careful operation.
The polymer mastic began to deteriorate after 2 minutes of operation of the device, and completely disappeared from the surface in 5 minutes, which is equivalent to 40 thousand kilometers. This result is 2 times worse. However, it must be taken into account that such a mixture is more elastic when temperature changes .
Treatment of wheel arches and the bottom of the vehicle with mastic
According to the test results, the epoxy mixture performed best when sandblasted. It began to collapse after 7 minutes (equivalent to 140 thousand kilometers), and completely disappeared from the surface in 15 . However, when choosing it, it is worth considering that when the temperature drops to low, it may peel off or crack, since epoxy resins are not elastic enough.
How to do anti-corrosion treatment with your own hands?
Doing anti-corrosion treatment of the body yourself is not so difficult and, perhaps, the work will be done much better than by a hired specialist.
Types of metal processing products.
Classification of means for treating metal against corrosion:
- wax-based substances;
- bitumen-based substances.
Classification of anticorrosives by method of application:
- Products for treating hard-to-reach places:
- Non-drying anticorrosive. The name fits because this substance does not dry out at all. Its liquid state allows it to constantly fill new microcracks that appear due to mechanical or temperature influences.
- Paraffin anticorrosives on a wax base. This type of anticorrosive agent creates a paraffin protective film, which also protects against contact of the metal with oxygen, water and other substances. Paraffin film is resistant to temperature changes.
- Products for protecting exposed surfaces.
- Bitumen mastic in synthesis with synthetic oils. Treatment with this product will create double protection: against corrosion and against mechanical influences (gravel, sand, etc.). The layer thickness should be from 0.25 to 0.4 mm. One of the means of protecting the body from mechanical shocks from small stones, etc., is gravitex, which can be painted, but sometimes does not need to be painted.
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) mastic on a rubber base. This substance is superior in strength to others. Lasts a long time. It is used, as a rule, in factories, because its application requires special technology.
- Liquid plastic. This form of plastic only protects against contact with water, salts, reagents, and oxygen. Liquid plastic is not suitable as protection against mechanical contact. Used as an additional layer for both cosmetic and partial processing.
Differences in the formation of corrosion in open and closed areas of the car body: open areas rust from mechanical damage, and closed areas rust from chemicals (salts, acids, oxygen).
Which method to choose
There are several ways to protect arches from the negative effects of water, dirt and stones. These surfaces are covered with fender liners, but even they cannot provide 100% protection of the arches from dirt and corrosion. Treatment with special compounds is required, the choice of which depends on the preferences of the car owner and his willingness to incur financial expenses.
How to treat car arches:
- Spillage of used oil. If you do it yourself, this method doesn’t cost a penny, but instead you have to pay for it in terms of lost time. To ensure protection against rust, you have to add oil 2-4 times a year. The disadvantage of this method is that used oil contains toxic substances that, when evaporated, have a harmful effect on the driver and passengers.
- Lubrication with inexpensive domestic products. They are made on the basis of bitumen, lithol, motor oils, kerosene, drying oil, and anti-corrosion additives. Treatment frequency is once a year. This costs more than used oil, but takes less time and effort.
- Use of expensive imported products. Experienced car enthusiasts believe that the only difference between such compounds is that they require updating less often. Fundamentally, they are no different in any way - they simply protect the metal from corrosion. But no anticorrosion agents will remove existing rust, and they will not repair holes in the metal.
Wheel arches in European cars begin to deteriorate after 3-4 years of operation, in Chinese cars - after 1-2 years.
How to treat wheel arches and underbody:
In order to carry out high-quality body treatment, it is necessary to observe the proportions of substances and the sequence of work.
Sequence of work
- Place the car on an overpass or inspection hole.
- Clean the bottom: remove dirt, wash, degrease. The quality of this work is very important. If the metal surface is greasy or dirty, the substance will not adhere tightly to the metal. After washing, preferably with high pressure from a hose, it is necessary to dry it with a compressor.
- Inspect the paint coating (LPC) of the bottom. If bubbles or cracks are found, clean them with a metal brush, chisel, knife, or sander with coarse sandpaper. Clean to a shine and treat with a rust converter.
- When the bottom is completely cleaned, you need to degrease it again. For this you can use white spirit, gasoline, alcohol, acetone.
- After degreasing, the surface must be dried completely.
- Next, apply zinc primer. A high-quality zinc primer (a small metal bucket) costs approximately 6,000 rubles.
- After priming it should be dried again.
- Now it's time to apply the mastic. It should be applied in layers, not all at once. Before applying the next layer, the previous one must be kept for about 6 hours. The drying temperature should not be lower than +16 degrees. The thickness of all applied layers should be within 1.5-2 mm. The mastic consumption will be approximately 5 kg. If you have aerosol cans, to save money you can use them for small areas; for large areas their use will be expensive.
- The wheel arches are processed in the same sequence, only the wheels must be removed first. Wheel arches are most susceptible to impacts from pebbles and other hard substances, so after processing the metal, it would be good to install protective plastic fender liners.
Recommendation: to create reliable protection for the metal surface of the body, it is better to use rubber-bitumen mastic. The rubber layer provides better protection against stones and is a good soundproofing barrier. Such rubber-bitumen mastics are produced, for example, by the following companies:
BODY
Waxoyl (Vaksoil)
MOVILLE
Dinitrol (Dinitrol)
Before use, the mastic must be stirred well until a homogeneous mass is formed. If it is thick, then it should be diluted with turpentine, solvent or xylene.
Anti-gravel protection
Anti-gravel is used to treat spoilers (lower part), sills, and bottom of doors. The anti-gravel agent consists of:
Processing hidden areas
To treat hard-to-reach hidden places against corrosion, you need to use a special long bendable nozzle. The tube is inserted into special holes for fastening. If they are not there, you can drill them, but plug them after processing.
To treat the internal surfaces of the metal car body, you need to insert and slowly pull out the long nozzle, while spraying the substance. For example, you can use a Walmec pistol. This gun has a long tube for spraying the substance into hard-to-reach places.
Anticorrosive agents for treating internal surfaces: Rast Stop A, Testyl Zinc ML. They have a pungent odor that will dissipate in a week.
Application technology
If you don’t know how best to treat the bottom of your car at home, follow this algorithm:
- Wash the bottom of the car from dirt, remove the anti-corrosion coating, if any;
- drive the car into the inspection pit in order to remove its wheels. Cover the brake system components with film;
- Use a brush or sandpaper to sand off any rust spots. If necessary, apply a converter to the corrosion to form a protective film instead of rusty spots;
- Make sure the bottom is clean and dry again;
Mistakes in corrosion protection
To avoid mistakes during metal body processing, you need to know them. So, popular common mistakes:
- applying a thick layer;
- skipping sections;
- The layer thickness is too thick or too thin.
Do not use materials that are not intended for such work. This is, for example: used oil (waste oil), ordinary bitumen, etc. Such substances do not contain elements that slow down the formation of corrosion. Such products can even cause harm by creating a greenhouse effect, which causes paint to peel off.
Do I need to process the body a second time?
Useful information - for re-treatment to be beneficial, it must be done with preparations that were not used to protect the first layer. The second layer should penetrate through the first layer. If their composition is the same, then it will not be able to reach the metal surface.
For the second and subsequent treatments, oil-based anti-corrosion agents are used. They dissolve the first layer and penetrate to the source of corrosion. Based on this, there is no need to prepare the underbody of the car as before applying the first layer.