Clutch VAZ 2107
The vehicle's handling largely depends on the serviceability of the VAZ 2107 clutch mechanism. How often this mechanism will have to be repaired is influenced by the quality of the roads and the driver’s experience. For beginners, as a rule, the clutch fails quite quickly, and repairing and replacing the unit is quite labor-intensive.
Purpose of the clutch
The main task of the clutch is to transmit torque from the engine to the drive wheels of the car.
The clutch serves to transmit torque from the engine to the main gear and protect the transmission from dynamic loads
Initially, it was intended for short-term separation of the engine and the main gear during smooth starting and gear shifting. The VAZ 2107 clutch has the following characteristic properties:
- has the smallest permissible moment of inertia of the driven disk;
- removes heat from rubbing surfaces;
- protects the transmission from dynamic overloads;
- does not require a lot of pressure on the pedal when controlling the clutch;
- It is compact, maintainable, quiet, easy to maintain and maintain.
The design and principle of operation of the VAZ 2107 clutch
Clutch VAZ 2107:
- mechanical (driven by mechanical forces);
- frictional and dry (torque is transmitted due to dry friction);
- single-disk (one slave disk is used);
- closed type (the clutch is constantly on).
When you press the pedal, the force is transmitted hydraulically to the pressure bearing, which releases the driven disc.
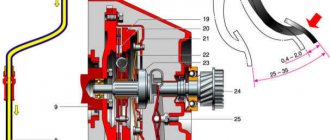
Cohesion can be roughly represented in the form of four components:
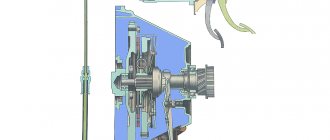
- driving or active part (crankshaft flywheel 6, basket with casing 8 and steel pressure disk 7);
- driven or passive part (slave or passive disk 1);
- inclusion elements (springs 3);
- shutdown elements (levers 9, fork 10 and pressure bearing 4).
The basket casing 8 is bolted to the flywheel, connected by damper plates 2 to the pressure disk 7. This creates conditions for transmitting constant torque from the flywheel through the casing to the pressure disk, and also ensures that the latter moves along the axis when the clutch is turned on and off. The driving part rotates constantly when the engine is running. The passive disk moves freely along the splines of the input shaft 12 of the gearbox. The hub is connected to the driven disk through damper springs 3 and due to this has the possibility of a certain elastic rotation. This connection dampens torsional vibrations that occur in the transmission due to engine operation at different speeds and corresponding dynamic loads.
When the pedal 5 is depressed, the passive disk 1, with the help of springs 3, is clamped between the flywheel 6 and the pressure disk 7. The clutch is engaged and rotates together with the crankshaft as a single unit. The rotational force is transmitted from the active to the passive part due to the friction that occurs on the surface of the friction linings of the driven disc, flywheel and pressure plate.
When pedal 5 is pressed, the hydraulic fork moves the clutch with the pressure bearing towards the crankshaft. Levers 9 are pressed inward and pull pressure plate 7 away from driven disk 1. Springs 3 are compressed. The active rotating part is disconnected from the passive one, no torque is transmitted, and the clutch is disengaged.
When the clutch is engaged, the driven disc slips relative to the smooth surfaces of the flywheel and pressure plate, so the torque increases gradually. This allows the car to move away smoothly and protects transmission components during overloads.
Clutch hydraulic drive device
The transmission of torque from the engine to the drive wheels is carried out using a hydraulic drive.
The clutch hydraulic drive transmits force from the pedal to the clutch fork.
The hydraulic drive plays an important role when starting the vehicle and changing gears. It includes:
- pedal;
- master and slave cylinders;
- pipeline and hose;
- pusher;
- clutch engagement and release fork.
The hydraulic drive allows you to smoothly engage and disengage the clutch without exerting much effort when pressing the pedal.
Clutch master cylinder
The clutch master cylinder (MCC) increases the pressure of the working fluid when you press the pedal. Due to this pressure, the clutch fork rod moves.
The clutch master cylinder converts the force from pressing the pedal into working fluid pressure, which moves the clutch on/off fork rod
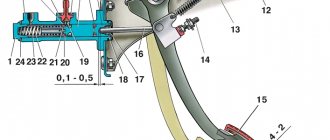
The pusher piston 3 and the master cylinder piston 5 are located in the main cylinder body. The use of an additional pusher piston reduces the radial force on the main cylinder piston when the pedal is pressed. In this case, the sealing ring 4 is pressed against the walls of the cylinder mirror and improves the sealing of the pistons. To ensure tightness inside the cylinder, there is an o-ring 12 located in the groove of the piston 5.
For additional sealing of the piston, an axial hole is drilled in its guide part 9, connected to the ring groove by 12 radial channels. As the pressure in the working space of the GCS increases, it reaches the inner part of the ring 12 and expands it. Due to this, the tightness of the master cylinder piston increases. At the same time, ring 12 acts as a bypass valve, through which the working part of the cylinder is connected to the reservoir with the working fluid. When the pistons reach their extreme position at the plug 11, the sealing ring 12 opens the compensation hole.
Through this hole, when the clutch is engaged (when the RCS piston creates excess back pressure), part of the fluid passes into the reservoir. The pistons are returned to their original position by a spring 10, which at one end presses on the plug 11, and with the other on the guide 9 of the piston 5. All internal parts of the GCS are fixed with a retaining ring 2. On the mounting side, a protective cover is put on the GCS, protecting the working part of the cylinder from dirt. .
Most often, the o-rings on the master cylinder wear out. They can always be replaced from the repair kit. In case of more serious malfunctions, the GCS changes entirely.
If the compensation hole becomes clogged, excess pressure will be created inside the drive system, which will not allow the clutch to fully engage. She will slip.
Clutch slave cylinder
The clutch slave cylinder (CLC) is attached with two bolts to the gearbox housing in the area of the clutch housing. This arrangement of the RCS leads to the fact that dirt, water, and stones often get on it from the road. As a result, the protective cap is destroyed and wear of the O-rings is accelerated.
The slave cylinder is secured with two bolts to the gearbox
When you press the pedal, pressure is created in the clutch hydraulic drive, which is transmitted to piston 6. The piston, moving inside the cylinder, moves the pusher 12, which, in turn, turns the clutch engagement and release fork on a ball joint.
It is very important to observe the dimensions of the internal mirror of the main and working cylinders. When factory assembled, they are equal to each other - 19.05+0.025–0.015 mm. Therefore, the sealing rings on the pistons of both cylinders are completely interchangeable. If you need to make the clutch pedal softer, you need to buy a foreign analogue of the working cylinder with a smaller diameter of the working cavity. If the diameter is larger, then the pressure on it will be less. Therefore, in order to overcome the elastic force of the basket friction springs, greater force must be applied. Therefore the pedal will be tighter.
Composition of the VAZ 2107 clutch kit
The VAZ 2107 clutch kit consists of:
- baskets;
- driven disk;
- pressure bearing.
According to VAZ regulations, these elements are not repaired, but are immediately replaced with new ones.
Read how to bleed the clutch on a VAZ 2106: https://bumper.guru/klassicheskie-modeli-vaz/stseplenie/kak-prokachat-stseplenie-na-vaz-2106.html
Basket
The basket has the most complex device in the clutch kit. It consists of many parts that require correct and precise assembly. The basket is assembled only in factory conditions and is not repaired even in specialized car repair shops. If wear or serious defects are detected, the basket is replaced with a new one. Main cart malfunctions:
- loss of elasticity due to sagging springs;
- mechanical damage and fracture of damper plates;
- the appearance of wear marks on the surface of the pressure plate;
- kinks and cracks in the basket casing;
- other.
Usually the entire clutch is replaced, so the replacement kit includes a driven disc, pressure plate and pressure bearing
The service life of the clutch is determined by the life of the basket, driven disk or pressure bearing. Therefore, to avoid the cost of repeated repairs, the coupling is always replaced as a set.
Driven disk
The driven disk is designed to transmit torque from the engine flywheel to the transmission input shaft and can briefly disconnect the gearbox from the engine. The technology for manufacturing such disks is quite complex and requires the use of special equipment. Therefore, it is impossible to repair the disk yourself. It is replaced with a new one when:
- wear of friction linings;
- wear of the internal splines of the hub;
- detecting defects in damper springs;
- loosening the sockets under the springs.
Pressure bearing
The pressure bearing is designed to retract the pressure plate from the driven one and is activated when the clutch pedal is pressed. Its malfunctions are usually accompanied by whistling, knocking and other sounds. When the rollers jam, the supporting working surface or the seat in the cup wears out, the pressure bearing assembly is replaced.
Clutch slave cylinder maintenance
From time to time, the clutch drive circuit may become airy. To remove accumulated air, a system bleed valve is provided in the working cylinder.
To remove air you need to:
- Place a rubber hose onto the valve.
- Place the end of the tube into a container filled with liquid.
- Unscrew the valve nut.
- Press the clutch pedal all the way down several times. Monitor the level of working fluid in the tank.
- Once pumping is complete, tighten the nut back, remove the hose and refill the fluid in the reservoir.
Another important aspect of cylinder maintenance is the timely replacement of damaged seals.
Clutch slave cylinder seals.
Rubber elements wear out from exposure to working fluid and low temperatures. If you turn a blind eye to cracked or worn seals, dust and dirt will damage the cylinder mirror. All necessary components can be found in the repair kit.
The service also includes replacing the brake fluid in the hydraulic drive. Over time, it accumulates moisture, which leads to corrosion on metal and rubber elements. Replacing consumables will extend the life of important components of your car.
Clutch faults VAZ 2107
The main signs of a faulty VAZ 2107 clutch are:
- it is difficult to change gears;
- the driven disk slips;
- vibration appears;
- The pressure bearing whistles;
- the clutch is hard to disengage;
- The pedal does not return from the lower position.
Destruction of the pressure plate and basket casing can lead to very serious consequences
Almost any malfunction is accompanied by extraneous sounds - noise, knocking, whistling, etc.
Find out why a car can jerk when starting from a stop: https://bumper.guru/klassicheskie-modeli-vaz/hodovaya-chast/pri-troganii-s-mesta-mashina-dergaetsya.html
Gears won't shift
If the gears are difficult to shift, an experienced driver will immediately tell that the clutch is moving. In other words, the clutch does not disengage completely. As a result, when starting from a stop, it is difficult to engage first gear, and when the pedal is pressed, the car moves slowly. The reasons for this situation may be:
- Increased distance between the thrust bearing support surface and the heel of the basket. It must be set within 4–5 mm, changing the length of the working cylinder rod.
- The spring sectors of the driven disk are warped. The disk needs to be replaced with a new one.
- The thickness of the driven disk has increased due to the stretching of the rivets securing the friction linings. The disk needs to be replaced with a new one.
- Jamming of the driven disk on the splines of the gearbox drive shaft. Both parts are defective and, if necessary, replaced with new ones.
- Lack of brake fluid in the master cylinder reservoir or accumulation of air bubbles in the hydraulic drive system. The working fluid is added to the required level, and the clutch hydraulics are pumped.
The clutch is slipping
The clutch may start to slip for the following reasons:
- there is no gap between the pressure bearing and the fifth basket;
- the clutch drive is not adjusted;
- oil got on the rubbing surfaces;
Oil getting on the driven disc can cause the clutch to slip and operate jerkily. - the bypass channel in the main cylinder body is clogged;
- The clutch pedal does not return to its original position.
Such malfunctions are eliminated by adjusting the drive, replacing oil seals, cleaning the channel with wire, and identifying and correcting the causes of pedal sticking.
Clutch is jerky
If the clutch starts to jerk, it may be caused by the following:
- the driven disk is jammed on the splines of the gearbox drive shaft;
- oily areas have formed on the friction linings;
- the clutch hydraulic drive is not adjusted;
- the steel disk of the basket is warped, some friction springs have lost their elasticity;
- The driven disk is faulty.
In such situations, a complete clutch replacement is most often required.
Noise when engaging clutch
The appearance of grinding and rattling noises when releasing the clutch pedal may be due to the following:
- the pressure bearing is jammed due to lack of lubrication;
- The gearbox drive shaft bearing is jammed in the flywheel.
In both cases, the problem is solved by replacing the bearing.
Noise when disengaging the clutch
When you press the clutch pedal, you hear a knocking, clanging, rattling sound, and you can feel vibration on the gear lever. The reasons may be the following:
- the damper part of the driven disk (springs, sockets) is faulty;
If the driven disk has worn splines, broken or loose damper springs, it must be replaced - The splined connection of the driven disk and the gearbox drive shaft is badly worn;
- the return spring of the clutch fork has become detached, lost its elasticity or broken.
In all cases, worn elements should be replaced with new ones.
The pedal returns but the clutch does not work
Sometimes it happens that the clutch does not work, but the pedal returns to its original position. This may be due to the following situations:
- air entering the hydraulic drive system;
- wear of the sealing rings of the main and working cylinders;
- lack of working fluid in the tank.
In these cases, you should bleed the hydraulic drive, replace the rubber rings with new ones and add working fluid to the reservoir.
Find out when you need to change tires to summer ones: https://bumper.guru/klassicheskie-modeli-vaz/poleznoe/kogda-menyat-rezinu-na-letnyuyu-2019.html
Tight grip
The softness of the clutch is determined by the force of pressure on the heel of the basket to retract the pressure plate. The magnitude of the force depends on the elasticity of the damper springs. Baskets from many manufacturers, including foreign ones, are suitable for the VAZ 2107 clutch. A tight pedal signals to the driver that the basket's life is coming to an end.
The pedal disengages the clutch at the beginning/end of its stroke
When you press the pedal, the clutch may disengage at the very beginning or, conversely, at the very end. In such situations, adjustment of the free and working travel of the pedal will be required. The free stroke is regulated by changing the length of the pedal limit screw, and the working stroke is regulated by changing the length of the working cylinder rod. In addition, increased free play may be a consequence of wear on the driven disk linings.
Video: main clutch problems and their solution
Why it stalls - reasons and their elimination
The clutch usually slips due to the following:
- There is no gap between the pressure bearing and the fifth basket;
- the clutch drive is not adjusted;
- oil gets on the discs;
Depending on the cause of this problem, the repair progress is determined. If the problem is with the diaphragm spring, it will have to be replaced with another one. When the friction linings wear out, the driven disk is replaced. When repairing/removing linings, the gaskets are checked. If they are in poor condition, they are also replaced with new ones. If oil gets on the driven disc, you will need to treat it with kerosene and clean it with fine sandpaper.
Disc oiling
Grease may get on any side of the flywheel and pressure plate due to an increased oil level in the gearbox housing or a leak in the rear crankshaft bearing. To solve the problem, diagnostics are performed and the cause of the leak is eliminated - the seals are replaced, then the spare parts are cleaned.
Read, it might come in handy: Which shock absorbers to choose for a car?
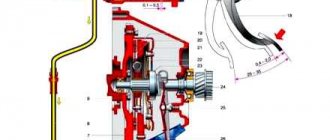
The free stroke according to technical conditions is 30-35 mm, the full stroke is 140 mm. Any deviation from the norm is associated with a malfunction of the transmission and requires adjustment work. The parameter is checked using a ruler. To do this, determine the distance from the pedal to the center of the platform. The adjustment is made on a pit or lift using open-end wrenches 13 by 17 mm and 17 by 19 mm. We clean the adjusting rod and nuts with a brush and treat them with WD-40. Next, the lock nut is loosened, and by rotating the adjusting nut we change the gap. If the free play needs to be reduced, we lengthen the thrust; if it is increased, we shorten it. After completing the work, tighten the locknut.
Damaged release clutch
Clutch selection
The manufacturer installed carburetor (2103 with a volume of 1.5 l) and injection (2106 with a volume of 1.6 l) engines on different VAZ 2107 models. Despite the external similarity, the clutch of these models has certain differences. The diameter of the basket pressure plate in both cases is 200 mm. But for the basket for 2103 the width of the pressure plate is 29 mm, and for 2106 it is 35 mm. Accordingly, the diameter of the driven disk for 2103 is 140 mm, and for 2106 - 130 mm.
Some car owners install a VAZ 2121 clutch on their VAZ 2107, which is noticeably stiffer and more reliable than the original one.
Clutches for the VAZ 2107 are produced by both domestic and foreign manufacturers
All VAZ models with rear wheel drive are suitable for clutch kits from classic cars of famous brands.
Table: clutch manufacturers for VAZ 2107
| A country | Manufacturer's brand | Advantages and disadvantages of clutch | Weight, kg | Price, rub |
| Germany | SACHS | Reinforced, so a little tough. Reviews are excellent | 4,982 | 2600 |
| France | VALEO | Great reviews, very popular | 4,322 | 2710 |
| Russia, Tolyatti | VAZInterService | Installed on the assembly line, good reviews | 4,200 | 1940 |
| Germany | LUK | There are dampers on the pressure and driven disks. Reviews are good | 5,503 | 2180 |
| Netherlands | HOLA | Noisy, short-lived, many negative reviews | 4,810 | 2060 |
| Germany | KRAFT | Soft, reliable. Reviews are good (many fakes) | 4, 684 | 1740 |
| Russia | TRIAL | Excessively hard. Reviews 50/50 | 4,790 | 1670 |
| Belarus | FENOX | Difficult, bad reviews | 6, 376 | 1910 |
| Türkiye | MAPA | Medium hardness, reviews 60/40 | 5,370 | 1640 |
| China | AUTOTECHNIK | Difficult, reviews are not very good | 7,196 | 2060 |
Clutch adjustment
Clutch adjustment is necessary after its repair or replacement, as well as after bleeding the hydraulic drive. To do this you will need:
- open-end wrenches for 8, 10, 13 and 17;
- ruler with divisions;
- pliers.
Adjusting the pedal free play
The pedal free play should be 0.5–2.0 mm. Its value is measured inside the car with a ruler and, if necessary, adjusted by changing the length of the pedal travel limiting screw.
Adjusting the working cylinder rod
The working cylinder rod is adjusted from the inspection hole or on a platform. In this case, it is necessary to achieve a clutch play value (the distance between the end of the pressure bearing and the fifth basket) within 4–5 mm. Adjustment is carried out by changing the length of the working cylinder rod.
After both adjustments have been made, the clutch operation is checked. To do this, on a warm engine with the pedal depressed, try to engage all gears, including reverse gear. There should be no noise, the speed lever should move easily, without jamming. Starting off should be smooth.