Clutch VAZ 2101 Zhiguli
/ VAZ/ vaz-2101/ Transmission/ Clutch/ Clutch
Clutch assembly
| 1 – bleeder fitting; 2 – clutch pressure spring; 3 – stepped pressure spring rivet; 4 – pressure disk; 5 – driven disk; 6 – flywheel; 7 – clutch housing; 8 – bolt securing the clutch housing to the flywheel; 9 – gearbox input shaft; 10 – clutch release bearing clutch; 11 – clutch release fork; 12 – ball support for the clutch release fork; | 13 – clutch release bearing; 14 – thrust flange of the pressure spring; 15 – clutch release fork cover; 16 – fork spring; 17 – support ring of the pressure spring; 18 – clutch casing; 19 – clutch release fork pusher; 20 – adjusting nut; 21 – lock nut; 22 – protective cap; 23 – clutch release cylinder (working cylinder); 24 – fork release spring; 25 – tension spring bracket |
Clutch pedal and master cylinder
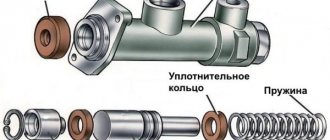
| 1 – plug; 2 – main cylinder body; 3 – bypass (compensation) hole; 4 – fitting gasket; 5 – fitting; 6 – lock spring washer; 7 – piston of the main cylinder; 8 – sealing ring; 9 – pusher piston; 10 – hook; 11 – bracket for clutch and brake pedals; 12 – clutch pedal servo spring; | 13 – clutch pedal release spring; 14 – clutch pedal travel limiter; 15 – clutch pedal; 16 – piston pusher; 17 – protective cap; 18 – retaining ring; 19 – inlet; 20 – sealing ring (ring valve); 21 – piston bypass hole; 22 – working cavity of the cylinder; 23 – spring; 24 – gasket |
Slave cylinder and clutch release fork
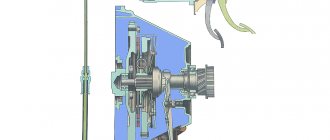
| 1 – clutch release bearing; 2 – ball joint; 3 – clutch release fork; 4 – pusher; 5 – adjusting nut; 6 – lock nut; 7 – tension spring; 8 – housing plug; 9 – fitting for bleeding; | 10 – cylinder body; 11 – sealing ring; 12 – protective cap; 13 – piston; 14 – seal; 15 – plate; 16 – spring; 17 – support washer; 18 – retaining ring |
The car has a single-disc, dry, permanently closed clutch, with a central pressure diaphragm spring and a torsional vibration damper on the driven disc.
The leading part of the clutch is a non-separable unit, includes a clutch housing 18 (see Fig. Clutch assembly ), pressure plate 4 and diaphragm pressure spring 2. The clutch housing is attached to the flywheel with 6 dowel pins and bolts 8. Pressure disk 4 is connected to the housing 18 by three pairs of steel plates, each of which is riveted at one end to the casing and the other to the pressure plate. Through the clamps, the pressure disk is connected to the outer edge of the diaphragm spring 2, which rests on two O-rings 17, fixedly fixed to the casing with stepped rivets 3.
Driven disk 5 is made of steel, has radial slots that divide it into twelve sectors, bent in different directions. Friction linings are rivet-fastened to the disk sectors, independently of each other. To dampen torsional vibrations, the driven disk is connected to the hub using a torsional vibration damper (damper).
The clutch release drive is hydraulic. It consists of master cylinder 2 (see Fig. Clutch pedal and master cylinder ), clutch release cylinder 10 (see Fig. Slave cylinder and clutch release fork ), fork 3 and clutch release bearing 1, reserve tank and clutch pedal with servo spring. The tank and drive cylinders are connected to each other by pipelines.
From June 1972 to November 1978, the vehicles described were equipped with a clutch and brake pedal bracket manufactured specifically for these models. Since December 1978, a bracket has been installed, unified at the mounting location, for cars with and without a vacuum booster. The clutch pedal from a VAZ 2103 is installed on standardized brackets.
Comments
No comments yet
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Replacing the VAZ clutch cable
VAZ-produced cars come in both front-wheel drive and rear-wheel drive, and they also have different clutch drives. If all VAZ classic cars have a hydraulic drive, then in many front-wheel drive cars (2108-2115) the release is controlled by mechanics, and the control element is a cable. Like all parts, the clutch cable (TC) wears out over time and therefore needs to be replaced periodically. The reasons for vehicle failure are:
- jamming of the cable itself in the “jacket”;
- breakage of the remaining threads of the vehicle;
- break of the cable itself.
If the vehicle itself is intact, but the clutch has become difficult to squeeze out, you can try to lubricate the cable. Litol or other grease is suitable as a lubricant, but it should be noted that this is a temporary measure, and you still need to prepare to replace the VAZ clutch cable. Changing the vehicle on a Zhiguli 2108-2115 is very simple:
- We disconnect one end of it from the pedal;
- unscrew the cable fastening nuts on the gearbox bracket (in Figures 1 and 2);
- disconnect the vehicle from the plug on the gearbox.
In order to remove the vehicle, we pull it out into the engine compartment, then install a new part, and use the nuts on the bracket to adjust the cable tension.
Replacing a VAZ clutch disc
On VAZ models, replacement of the drive (basket) or driven clutch disc is periodically required; repairs to the vehicle are necessary in case of wear or breakage of parts. The main malfunctions of the clutch basket (CB) are:
- grinding the petals 2108-15 (they are erased by the release bearing);
- breakdown of the “spider” 2101-07;
- wear of the KS plate;
- breaking off steel petals.
The main malfunctions of the clutch driven disc (DC) are:
- grinding off friction linings;
- weakening or wear of damper springs;
- DS hub breakage.
In any case, replacing a disk on VAZ cars involves removing and installing the power transmission.
Why it stalls - reasons and their elimination
The clutch usually slips due to the following:
- There is no gap between the pressure bearing and the fifth basket;
- the clutch drive is not adjusted;
- oil gets on the discs;
Depending on the cause of this problem, the repair progress is determined. If the problem is with the diaphragm spring, it will have to be replaced with another one. When the friction linings wear out, the driven disk is replaced. When repairing/removing linings, the gaskets are checked. If they are in poor condition, they are also replaced with new ones. If oil gets on the driven disc, you will need to treat it with kerosene and clean it with fine sandpaper.
Disc oiling
Grease may get on any side of the flywheel and pressure plate due to an increased oil level in the gearbox housing or a leak in the rear crankshaft bearing. To solve the problem, diagnostics are performed and the cause of the leak is eliminated - the seals are replaced, then the spare parts are cleaned.
Read, it may come in handy: How to check the condition of the VAZ-2107 steering on your own
The free stroke according to technical conditions is 30-35 mm, the full stroke is 140 mm. Any deviation from the norm is associated with a malfunction of the transmission and requires adjustment work. The parameter is checked using a ruler. To do this, determine the distance from the pedal to the center of the platform. The adjustment is made on a pit or lift using open-end wrenches 13 by 17 mm and 17 by 19 mm. We clean the adjusting rod and nuts with a brush and treat them with WD-40. Next, the lock nut is loosened, and by rotating the adjusting nut we change the gap. If the free play needs to be reduced, we lengthen the thrust; if it is increased, we shorten it. After completing the work, tighten the locknut.
Damaged release clutch
Replacing the VAZ 2107 clutch
All cars of the VAZ-classic family have almost identical power units and transmissions. The engines are very similar in appearance, they differ only in cylinder capacity and fuel system. Manual transmissions on the “Classic” differ only in the number of gears – there are 4-speed gearboxes. and 5-st. Manual transmission. All clutch baskets 2101-07 are the same, only the DS differs - the “penny” discs (2101) have friction linings that are smaller in diameter than the DS 2106.
Replacing the VAZ 2107 clutch is done in exactly the same way as on 2106 models.
Replacing the working cylinder on a VAZ 2101
Clutch slave cylinder - not all people know what it is, but you still have to replace it from time to time, but how can you replace it if not everyone knows what it is? In short. In the car we are currently considering a classic, there are two clutch cylinders, one of which is the main one and the other is the worker. They perform almost the same function; when you press the clutch pedal, the piston (indicated by a green arrow) which is located inside the clutch master cylinder moves and thereby pushes the brake fluid further.
At this time, the brake fluid continues its path and thereby rests against the same piston (Indicated by a blue arrow), only which is already located in the clutch working cylinder, and after the brake fluid rests, it begins to push the piston and therefore it moves to the front and there, by pressing the fork, the clutch in the car disengages.
In general, we understand that there must always be brake fluid in both cylinders, but why is it needed, some of you may ask? The thing is that brake fluid is not compressible, and therefore it is used both in the brake system and in the clutch drive, in general, let's get back closer to the topic. To replace the clutch slave cylinder with a new one, you will need to stock up on: A basic set of wrenches, as well as pliers, and you may also need about 1 or 2 liters of new brake fluid!
Where is the clutch slave cylinder located?
It is located next to the box, and to be more precise, it is secured with two bolts on the clutch housing itself, so you will only be able to see it unobstructed if you are under the bottom of the car, or if you look deep into the engine compartment, For more details on its location, see the photo below, it is indicated by an arrow:
When should you replace the clutch slave cylinder?
As we already understood, inside the working cylinder there is brake fluid due to which the clutch is disengaged in the car, but it happens that over time this cylinder becomes unusable and cracks begin to appear in its body and thereby the liquid that is in it gradually begins to come out of it be, it is very easy to understand if you visually look at it, and you can also understand it without looking at it at all, but how to do this you ask?
The thing is that if the cylinder becomes unusable and brake fluid begins to come out of it, then the first thing that will happen to the clutch pedal is that it will become very easy to press, that is, the system will not be airtight, so to speak, and if the system is not is sealed, then the clutch will practically not work, that is, you press the pedal, it is pressed very lightly and the clutch does not engage, this is perhaps one of the most common problems that happens when the clutch slave cylinder fails.
Removal
1) To remove, first you will need to stock up on a wrench and, using the wrench, loosen the nut that secures the hose to the cylinder.
2) Then put the wrench aside, and then use pliers to pull back and then completely remove the release spring from the cylinder.
3) Next, without removing the pliers, straighten and then remove the cotter pin from the hole located in the tip of the pusher of this cylinder.
4) Next, using a wrench, remove the two bolts that secure the cylinder to the clutch housing of the gearbox.
5) Now disconnect the bracket from the cylinder, which was also bolted together with the cylinder itself and which serves to secure the tension spring.
6) Then, grasping the working cylinder with your hand, carefully remove it, while removing the pusher, which is indicated by the arrow, from the hole located in the fork.
7) And then completely unscrew the nut that secures the hose to the cylinder, and then completely remove the cylinder from the car.
Replacing the VAZ 2106 clutch
On a VAZ classic, the clutch can fail for various reasons, and the problem may not necessarily lie in the basket or disc; often the cause of the breakdown is the clutch slave or master cylinder (MCC). Signs of a faulty GCS:
- the clutch does not appear the first time, you have to press the pedal several times;
- The pedal squeeze is “waddly.”
A defective cylinder head can be identified by external inspection; if the cylinder is faulty, it begins to leak. Clutch 2106 is replaced on a car lift or pit, the gearbox is dismantled, and then the disc and basket are removed.