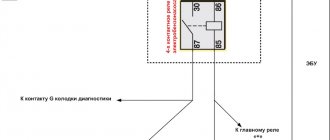
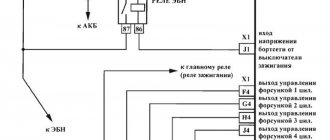
How's the warranty?
Against the background of such an attitude towards the consumer, the position taken by the Kia concern causes a sharply negative attitude. Until the beginning of 2021, in the service book of cars of this brand there was an inscription that the warranty for the catalytic converter extends up to 1 (!) thousand kilometers. Roughly speaking, two refuelings, and then “bad Russian gasoline” can damage the catalytic converter, but the company is no longer responsible for this. True, from 2021 the warranty on the catalytic converter has been extended to 150 thousand km.
In the author's opinion, the warranty on the catalytic converter should be at least as long as that on the car.
Now let’s take a closer look at what a car owner should and shouldn’t do to ensure that the neutralizer serves a long and happy life.
Causes of catalytic converter failure:
- Poor quality fuel - most often with a low octane number. The engine management system switches to late ignition. This causes the mixture to burn out at the outlet and an increase in the temperature of the exhaust gases.
Incorrect operation of the ignition system (misfire). Fuel that is not burned in one cylinder is immediately ignited and burns in the neutralizer.
From personal experience
Second half of the nineties. I worked as a fleet manager for a commercial company. The boss calls and says: We will sell Karina (Toyota Carina E). Go to the car wash and let your engine shine like...
Toyota Carina E
In general, it burned and stopped. I returned to the car, opened the hood, opened the distributor cap, and there was a swamp. He wiped away the moisture, dried it and finally made it to the office. Now answer the question: where do you think the fuel burned?
What if it’s the end?
Not everyone can or will want to replace a failed catalytic converter on an out-of-warranty car with an original one. Before _
rogo it. What are the options for the development of events?
- Just knock the filling out of the neutralizer. This requires reflashing the control unit so that it “turns a blind eye” to the signal from the second oxygen sensor, or installing a mechanical or electronic switch. The mechanical one is a bushing in which a piece of the catalytic converter is fixed, and the electronic one simply simulates the correct signal from the oxygen sensor.
- Knock out the filling and install a flame arrester in its place. It consists of several chambers with holes that serve to reduce the temperature and pressure of gases. This somewhat reduces noise and facilitates the operation of other elements of the exhaust system. The “brains” of the car must be deceived, as described above.
- Install a universal repair catalytic converter instead of the ceramic block. Most often on a metal rather than ceramic base. The degree of cleaning will be slightly lower, but you will not feel like “pests”.
Tell us, how did you communicate with the “monster under the bottom” - the catalytic converter: does it work, was cut out, replaced?
You can get acquainted with the “illness histories” of cars of past generations by following the link.
Installing a flame arrester instead of a catalyst
By and large, the process of installing a flame arrester can be divided into three main stages:
- Removing the catalyst or alternative mechanism;
- Installation of a flame arrester;
- Installing new firmware.
The failed neutralizer must be removed from the system and a new flame arrester welded in its place. Then the technician must install special oxygen sensor decoys. After all, if this is not done, the car system will constantly issue a “CHECK” error signal.
Removing the Lada Granta catalytic converter
Tools:
- Ratchet wrench
- Extension
- 8 mm head
- 13 mm head
- Open-end wrench 10 mm
- Open-end wrench 22 mm
- 13 mm straight box spanner
- Pliers
- Chisel
- Hammer medium
- Medium Phillips screwdriver
Parts and consumables:
- Aerosol lubricant such as WD-40 or similar
- Gasket of catalytic collector and inlet pipe
- A set of nuts securing the catalytic collector to the cylinder block
- Graphite grease
- Rags
Notes:
Carry out the work when replacing the gasket in the connection between the catalytic converter and the intake pipe with the cylinder head or when removing the cylinder head. The junction of the catalytic collector and the intake pipe with the mating plane of the cylinder head is sealed with a metal gasket. In the event that the gasket is burnt out or the nuts securing the catalytic converter and intake pipe are loose, exhaust gases can escape through this connection to the outside, which is accompanied by a characteristic sound. If tightening the nuts securing the intake pipe and catalytic collector cannot eliminate the defect, it is necessary to replace the gasket.
Carry out the work on an inspection hole or overpass. To avoid burns, it is recommended to start work after the exhaust system has cooled down.
1. Disconnect the manifold flange from the additional muffler pipe flange, as written here.
2. Remove the intake manifold/throttle assembly as described here.
3. Disconnect the oxygen concentration sensor (OC) wire connectors from the engine management system wiring harness connectors and remove these sensors as described here (control DC) and here (diagnostic DC).
4. Using a 13 mm socket, unscrew the two bolts securing the catalytic collector to the cylinder block bracket.
5. Using a 13 mm socket, unscrew the bolts securing the bracket to the cylinder block.
6. Using an 8 mm socket, unscrew the two bolts (see first photo), and with a 10 mm wrench, unscrew the nut (see second photo) securing the heat shield of the inner CV joint of the right wheel drive to the rear support bracket of the power unit.
7. Remove the heat shield along with the brackets.
8. Slide the cathode manifold along the cylinder head studs and lift it up.
9. Remove the metal gasket of the catalytic converter and inlet pipe.
10. Before installing the catalytic converter and intake pipe, clean the mating surfaces of the cylinder head, catalytic converter and intake pipe from carbon deposits with a rag and install a new gasket.
11. Before installing new nuts, apply graphite lubricant to the cylinder head studs.
12. Tighten the fastening nuts to the prescribed torque.
Notes:
Before installing the heat shield, it must be assembled with the collector brackets, but the nut securing the heat shield to the bracket must not be tightened, and the bolts connecting both brackets must not be tightened.
After installing the heat shield with brackets in its original place, you must check that all holes in the screen and brackets coincide with the holes for the fastening bolts. After the bolts are installed, it is necessary to check that the entire structure of these parts is in a free state. After this, you can gradually, step by step, evenly tighten the fastening bolts, while simultaneously checking that there is no distortion of the parts.
13. Install all removed parts in the reverse order of removal.
The article is missing:
- Photo of the instrument
- Photos of parts and consumables
Technology for changing the catalytic converter to the 4-2-1 insert
To work, you need to prepare a set of keys for 13, 17, 19 and 22, you also need a socket head for 13 and a screwdriver with a flat blade. Parts you should purchase are two bolts with springs, a graphite connecting ring, an extension for the sensor, and a manifold gasket. Since the spider with tubes is longer than the standard neutralizer, it would not hurt to purchase a corrugation with double or triple braiding 200 mm long.
You must first remove the negative terminal from the battery. The further process of dismantling the standard part continues according to the following diagram:
- Remove the intake module using a 13mm socket, disconnect the injector wiring harness and the fuel supply hose.
- Unscrew the nuts securing the flanges of the intake pipe and catalytic converter, and then remove the pipe flange from the converter studs.
- Disconnect the oxygen sensor connectors and disconnect the wiring harness from the heat insulation shield.
- Unscrew the two nuts securing the catalytic converter bracket and remove the clamp.
To finally replace the standard catalyst on Kalina 8 valves with a modified spider, all that remains is to slide the flange off the studs and pull the assembly down. The head gasket seating areas should be cleaned.
The flange is cut off from the old catenary collector with a grinder and welded to a section of the pipe with corrugation. A snag is screwed into the sensor hole or the ECU is subsequently reflashed. These measures will get rid of the Check-Engine, and will also be cheaper than buying a new converter.
Removing the catalyst. Pros and cons, consumption, firmware - we reveal all the secrets
Often my blog (and my channel) receives a lot of questions regarding the catalyst, and some readers still have many misconceptions in their heads. One of them (for example) is that if you remove this part of the muffler, then it will be VERY bad for the car, it will literally stand up and refuse to go! I decided to answer all the questions at once, so today we will talk: - is it worth removing it or not (what are the pros and cons of such manipulation), what will be the consumption after cutting it out, is it necessary to flash the ECU (and what are the risks), and well a few words about “deception”. In general, it will be interesting, as usual, the video version at the end...
Pros and cons of deletion
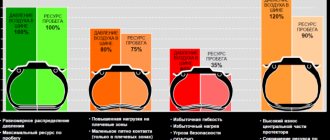
I have prepared a small sign with the pros and cons of what will happen if you remove the catalyst
| MINUSES | PROS |
| Increase in harmful substances in the exhaust, decrease in the environmental component | There is no need to buy a new catalyst, because it is very expensive |
| The smell of the exhaust becomes much more toxic, sometimes this exhaust penetrates into the car (it smells unpleasant) | A small increase in power (really small in terms of error, about 3%) |
| Exhaust sound. After knocking out the catalyst honeycomb, it is advisable to install a flame arrester, otherwise there will be a ringing sound from the empty “can” (especially at high speeds) | You can install a 4-2-1 or 4-1 spider , plus more power (which is said out of the blue) |
| You need to install either a fake or new firmware for EURO2 | Reduced fuel consumption (also about 3%) |
| Increasing the life of the power unit, because ceramic dust can get into the combustion chambers and wear it out prematurely |
As you can see, there are a few more advantages, the most significant is the price of this whole rework (removing it will cost several times, if not dozens of times, cheaper).
Now let's watch the video version.
In conclusion, I would like to say that removing the catalyst is NOT CORRECT AT ALL from an ECOLOGICAL point of view. After all, our planet is already polluted, and in this way you are making it even dirtier!
This is where I end, I think this material will help you make the right choice. Sincerely yours, AUTOBLOGGER.
( 56 votes, average: 4.50 out of 5)
Removing the catalyst on a VAZ Granta is a responsible job that requires special knowledge and extensive experience. If you want to avoid problems in the future, contact RamFlow Exhaust Center. We carry out physical and programmatic removal of catalytic converters, installing “bleeders” and flame arresters instead. This approach to work eliminates the activation of the Check Engine light and the engine going into emergency mode.
Before knocking out, removing or cutting out the catalyst, technicians analyze on-board errors. Identifying the cause of the problem will help you avoid more serious problems in the future. The service includes:
- software shutdown of the catalyst;
- physical block removal;
- performing firmware of the electronic control unit;
- installation of a fake oxygen sensor.
If necessary, a flame arrester can be installed after removing the catalyst. Come to our auto repair shop from 9:00 to 22:00 at the address: Moscow, Beregovoi Ave., 2, building 7. We are open 7 days a week.
Why do you need a catalyst?
I already have an article - what is it , I won’t repeat it. You need to understand that a catalyst (and scientifically, a catalytic converter) is needed only to clean the car's exhaust from harmful emissions and make them less harmful.
In simple words, it purifies harmful gases (while glowing almost “red hot”) and “almost” harmless CO2 and N2, O2 emerge from harmful CO, CH and other compounds. This way we save the environment at least a little.
Its structure is quite simple - it is a thickened pipe, which inside has something like a honeycomb, only long and hollow. They are usually made of ceramic elements coated with noble metals (usually platinum group metals are used - iridium, rhodium, palladium).
It is because of this that it costs, to put it mildly, quite a bit, from 30 to 150,000 rubles, it all depends on the class of the car and its volume.
In order for gases to transform from toxic to less harmful, the temperature of the catalyst must be about 750 degrees Celsius, otherwise the chemical reaction will not occur. The gases that come out of a car engine have a temperature of approximately 500 - 550 degrees Celsius (which is not enough), when they pass through the catalyst, a chemical reaction occurs with the release of heat, thus heating just the right amount (750 - 900 degrees).
Diagnostics
Checking the condition of the catalytic converter is possible without the use of specialized tools used at service stations. However, the result is not 100% reliable. If the efficiency of the catalyst is difficult to assess without testing for CO-CH at a service station, its throughput can also be measured in a garage.
To check, you will need a regular pressure gauge and a hose for it with an adapter for the thread of the oxygen sensor installed in front of the catalyst. Unscrew the sensor, connect the pressure gauge, start the engine and give 3-4 thousand revolutions. The pressure should not rise above 0.3-0.4 kg/cm3.
For cars with EURO-4 standards and higher, you can check the pressure after the catalyst by unscrewing the control sensor. The difference in readings before and after the neutralizer should not exceed 20-30%.
Together with other symptoms of a clogged catalyst described in the previous paragraph, this method provides almost one hundred percent reliability of the test results.
The catalytic converter is knocked out, is this bad for the car?
As I wrote above, this is simply an environmental system, and if it is not there, then the car, on the contrary, will improve its characteristics (power, consumption). To put it simply, the engine doesn’t care about this converter, whether it is there or not.
But why on many cars, if this unit fails (say, melted, clogged or crumbled), the CHECK ENGINE and the car begins to behave abnormally, traction disappears, sometimes it trots a little, and simply may not start at all.
And here, friends, everything is simple. If the catalyst is melted or clogged, then the exhaust gases cannot pass through it normally, which means that some returns back into the combustion chamber and makes the newly introduced combustible mixture less efficient. The motor is choking itself.
If there is no melting, but the “CHECK” light comes on, then perhaps it has simply worn out due to high mileage. In modern cars there are so-called oxygen sensors (lambda umbrellas), one is located in front of the catalyst, the other after and detects the presence of harmful compounds; if their percentage has increased, then the second (or also called the lower “lambda”) gives a signal that the converter is not working ( or it doesn’t do its job as it should) AND IT NEEDS TO BE REPLACED. By the way, some cars may not even start (a tribute to the environment).
Thus, by knocking out or removing it, you simply free the car’s exhaust tract from the obstacle in the form of a filter and lower its environmental standards. BUT AGAIN - THIS DOES NOT AFFECT THE RESOURCE OF THE POWER UNIT !
BUT in order for your car to drive normally, you need to upgrade to a lower environmental class (usually EURO2) or install a fake one. Otherwise, the program in the ECU will not allow you to drive normally.
Increase in oil intake
There is an opinion that after removing the catalyst, engine oil consumption increases. They are mainly removed at 150-200 thousand km. At this time, there are already scuffs in the cylinders, and oil burn is inevitable in any case at this mileage. If the removal is done on a new car, there will be no oil consumption, you can check.
They also say that oil is being thrown into the corrugation and the air filter. I specially removed the corrugation and decided to take a look.
I didn't see any signs of abandonment. This myth is unfounded. The mileage is already 1000 km, and if there was something, I would see it.
Firmware for EURO2 and snag – what does this mean?
As I wrote above, the second oxygen sensor (lower lambda) controls harmful emissions. Their number is now strictly regulated by European standards, which are called “EURO”; I will not talk about EURO “0-1” now; we are interested in the second generation.
So, what is EURO2 ? It was introduced a long time ago, namely in 1996. AT that time, the cars received an innovative system, namely a catalyst. As we all know, over time it can become clogged, and the fuel then was not the same as now, it had a lot of sulfur, which contributed to the honeycombs clogging much faster, and as you and I know, the car began to choke itself. Then the engineers installed an oxygen sensor, there was only one, and it was needed to capture CO2 in the chamber in front of the catalytic converter.
If the CO2 level increased, this indirectly indicated that the catalyst was clogged (that is, a backpressure effect was manifested); the sensor sent this information to the ECU and the ignition was adjusted, namely, a decrease in the supply of the fuel mixture. Thus, the power dropped significantly, the car did not drive and the owner “willy-nilly” had to go to a service station and change this spare part.
BUT, as you and I know, the price tag is, to put it mildly, HIGH, so many owners simply removed these honeycombs and the POWER RESTORED!
But how? YES, everything is simple, the CO2 level in the chamber in front of the neutralizer dropped significantly, the oxygen sensor recorded this (that everything is in order) and the car drove cheerfully and without constraint. This suited everyone, BUT NOT ECOLOGISTS! Therefore, they introduced the EURO3 standard (now the EURO5 standard already exists). What has changed is that a second oxygen sensor (lower lambda) just appeared behind the catalyst. The principle of operation here is this : the first lambda (before the filter) records the level of harmful substances, the second (after it) should record a much lower level, because the harmful substances have decomposed.
If you remove the catalyst cells , then both sensors will record the same values (“the second one” supplies information to the ECU), thus, CHECK ENGINE will light up, the power will drop, and the car will not drive. Now this doesn't solve the problem.
What is done with firmware for EURO2? The firmware in the ECU is changed, instead of EURO3.4 standards, EURO2 standards are installed. The essence of all these actions is banal - we simply turn off the second lower lambda (only the upper one remains), the car begins to drive as expected, without underestimating the power.
But such interventions in the firmware are not entirely good. The whole point is that they don’t produce them themselves, okay, the second “lambda” is simply turned off, that is, they simply adjust the readings. Or maybe this programmer will want to put some incomprehensible algorithms into the ECU, the engine will definitely not benefit from this. You need to be very careful here.
Therefore, we found a second solution, and I think it is more correct - installing a blende. What is a snag - essentially it is a “spacer” in front of the second oxygen sensor, it seems to move it a greater distance from the exhaust gases, it detects more oxygen and starts working normally.
Now there are several options for deception:
- Empty . It's just a tube with a very thin hole at the end (the part that screws into the muffler), and an oxygen sensor is screwed into the other side. A limited amount of harmful substances from the exhaust passes through it, there are no excesses and therefore CHECK does not burn.
- With a mini-catalyst inside . That is, right in the “spacer” there are, as it were, mini honeycombs, which also clean the exhaust precisely to record normal values.
- Angular . These are both of the types described above, only they are made at an angle of 90 degrees; they are needed for difficult places.
Inspection of LADA Granta without catalyst: Changes for 2021
Inspection of LADA Granta without catalyst: Changes for 2021
On March 1, 2021, a new procedure for passing technical inspection was supposed to come into force in Russia, but at the last moment the government once again moved the deadline to October 1. Be that as it may, the question remains relevant: is it possible to undergo maintenance without a catalyst? Let's look into everything in more detail.
Why do they get rid of catalysts?
Many owners of LADA Granta and other models cut out catalysts. There are several explanations for this. Firstly, power increases while fuel consumption decreases.
Secondly, a faulty catalytic converter has a detrimental effect on the engine. Exhaust gases return to the combustion chamber, which leads to rapid engine failure.
Finally, you can make good money by selling the catalyst. The fact is that it contains non-ferrous metals, which are then reused.
However, it is worth considering that when cutting out a filter device, several rules should be followed. Safe removal of the LADA Granta catalyst will help not only save money, but also not kill the car.
Lack of catalyst and technical inspection
In this regard, not everything is so simple. We should start with the fact that there is an official List of faults with which it will be problematic to undergo maintenance. However, there is no reference to the presence or absence of a catalyst.
But there is another point. Clause 32 of the mentioned document states that the emission level must comply with the Technical Regulations of the Customs Union for the vehicle. Simply put, we are talking about Euro-4 and Euro-5 standards.
The catalytic converter is largely responsible for meeting emissions regulations. Therefore, in its absence, a technical inspection can lead to problems. Moreover, in many cases, after removing the component in question, the engine electronics are “flashed” for Euro-2.
Therefore, if a gas analyzer is present at the service station, then you can forget about the diagnostic card without a catalyst.
Possible changes in legislation
In the time remaining before the introduction of new technical inspection rules, a lot may change in regulatory documents. Therefore, vehicle owners should be on their guard.
However, that's not all. The Ministry of Internal Affairs plans to prepare a new List of faults in which the operation of vehicles is prohibited. It is expected that it should come into force on June 1 of this year. Clause 8.4 of the project also mentions the absence of a catalytic converter.
And if nothing changes before the final version of the document is adopted, then driving without a catalyst will result in liability under Part 1 of Art. 12.5 Code of Administrative Offences. It provides for a warning or a fine of 500 rubles.
As a result, we can say that today it will be extremely problematic to pass a technical inspection without a catalyst.
On March 1, 2021, a new procedure for passing technical inspection was supposed to come into force in Russia, but at the last moment the government once again moved the deadline to October 1. Be that as it may, the question remains relevant: is it possible to undergo maintenance without a catalyst? Let's look into everything in more detail.
Why do they get rid of catalysts?
Many owners of LADA Granta and other models cut out catalysts. There are several explanations for this. Firstly, power increases while fuel consumption decreases.
Secondly, a faulty catalytic converter has a detrimental effect on the engine. Exhaust gases return to the combustion chamber, which leads to rapid engine failure.
Finally, you can make good money by selling the catalyst. The fact is that it contains non-ferrous metals, which are then reused.
However, it is worth considering that when cutting out a filter device, several rules should be followed. Safe removal of the LADA Granta catalyst will help not only save money, but also not kill the car.
Lack of catalyst and technical inspection
In this regard, not everything is so simple. We should start with the fact that there is an official List of faults with which it will be problematic to undergo maintenance. However, there is no reference to the presence or absence of a catalyst.
But there is another point. Clause 32 of the mentioned document states that the emission level must comply with the Technical Regulations of the Customs Union for the vehicle. Simply put, we are talking about Euro-4 and Euro-5 standards.
The catalytic converter is largely responsible for meeting emissions regulations. Therefore, in its absence, a technical inspection can lead to problems. Moreover, in many cases, after removing the component in question, the engine electronics are “flashed” for Euro-2.
Therefore, if a gas analyzer is present at the service station, then you can forget about the diagnostic card without a catalyst.
Possible changes in legislation
In the time remaining before the introduction of new technical inspection rules, a lot may change in regulatory documents. Therefore, vehicle owners should be on their guard.
However, that's not all. The Ministry of Internal Affairs plans to prepare a new List of faults in which the operation of vehicles is prohibited. It is expected that it should come into force on June 1 of this year. Clause 8.4 of the project also mentions the absence of a catalytic converter.
And if nothing changes before the final version of the document is adopted, then driving without a catalyst will result in liability under Part 1 of Art. 12.5 Code of Administrative Offences. It provides for a warning or a fine of 500 rubles.
As a result, we can say that today it will be extremely problematic to pass a technical inspection without a catalyst.
Fuel consumption
After you have removed this filter, many are tormented by the question of fuel consumption - will it increase or not? Of course, he will fall (so I think), no matter what anyone says. Let's think logically - if there is this filter element, it represents an obstacle that the exhaust gases need to overcome, and accordingly the engine will spend more effort to push them through (consumption increases slightly). If this element is NOT present, then the “working out” will be much easier - fuel will be saved.
Of course, you shouldn’t expect any global savings, usually it’s about 3% (maximum), but it’s worth noting that consumption will drop slightly.
Replacing the Lada Granta catalyst
The people's car Lada Granta was first introduced in 2011.
Designed to replace the outdated Lada Kalina, as well as the entire Samara family. This is a typical front-wheel drive sedan with an engine capacity of 1.6 liters. Three years after the presentation, a five-door liftback rolls off the assembly line. The models are in great demand among the population. It was originally planned to call the car “Low cost”, which means “low cost”. The price segment should not exceed more than 200,000 rubles. But it happened the way it happened. The cost is slightly higher than expected. Despite this, most reviews about the car are positive. As for complaints about breakdowns, the list of them is standard for the entire Lada family: transmission, chassis, thin metal, weak body part, significant power take-off from the standard catalyst. Among all the above breakdowns, the greatest resonance is caused by the failure of the catalytic filler. Read below on how to fix this.
The concept of a catalyst, its types and functions
The catalyst is a standard unit in the exhaust system of a car. In addition to the specified component, a muffler, resonator, and exhaust manifold are preinstalled. In the Lada Granta, the standard “cleaner” is installed in a single copy and it is located in the exhaust manifold housing. The material for production is metal, stainless steel. The shape of the equipment can be very diverse: rectangular, oval, cylindrical. The last type is the most popular due to its practicality. The Lada Granta has a cylindrical catalyst installed. There are two noise-insulating chambers with catalytic filler installed inside. It enters into a chemical reaction with gases, thereby reducing their toxicity level. A pipe with a perforated surface runs through the center of the product for additional filtration of gases.
The operating principle is to filter exhaust, reduce temperature and noise levels. During the passage of the perforated mesh, large particles are eliminated and settle to the bottom. Next, the flow passes into the cavity of the resonator, muffler. At each of the subsequent stages, additional cleaning and reduction in temperature occurs.
What is a flame arrester and its purpose on the Lada Granta?
A flame arrester is a metal or stainless steel product installed in the exhaust system of a car.
The shape of the part is very diverse, depending on the technical characteristics and specifications of the technical product. The internal cavity is filled with basalt filler to absorb noise, and a perforated pipe is installed. The filtration procedure is similar to the catalyst, with only one difference: the flame arrester does not have the function of reducing toxicity levels. Because of this, it is prohibited for installation in a number of countries of the European Union. In other words, it reduces the temperature of gases, their noise level, and partially filters, but does not reduce the toxicity indicator.
Replacing a Lada Granta catalyst with a flame arrester in a car service center
Replacing the catalyst with a flame arrester is as follows:
- The only and main catalyst is installed in the engine compartment, directly on the exhaust manifold, as mentioned above. There are two oxygen sensors screwed into the manifold body itself. One of them is diagnostic, the second is control. They must be unscrewed with a key to “19”. They are located at different heights from each other. Often referred to as upstream and downstream oxygen sensors.
- Unscrew the fastening nuts of the manifold body. At this point, the work in the engine compartment is completed; we lift the car on an electric lift;
- We give the flange connection of the rear part of the manifold shank and the receiving pipe of the resonator.
- Disconnect the second lambda probe and remove the equipment from under the car.
Dismantling is completed. We are preparing a new Interlock type flame arrester with a two-layer stainless steel system. We will install it by cutting off the protective metal body of the collector and welding it inside. Which is what we do. Old catalytic fill must be removed using a screwdriver, as its physical state is solid. After packing the flame arrester into the new housing, we screw two oxygen sensors into their original places. We treat the welding areas with heat-resistant paint. We begin installing the equipment in place. We screw the tail section, then lower the car and finish the work in the engine compartment.
Do-it-yourself catalyst removal
Motorists often ask the question: is it necessary to remove the catalyst? Some drivers believe that making a hole in the KN ceramics adds power to the engine and improves the dynamics of the car. These arguments are incorrect - only the faulty catalyst needs to be removed, if the CO level is normal, it is better not to touch the KN.
You can remove the catalyst yourself, but to complete the work you will need welding equipment and a grinder.
On many modern cars, the main catalyst is welded to the exhaust manifold and is an integral part of it. To remove ceramics from such a CN, you must:
- disconnect the exhaust pipe of the muffler;
- remove the exhaust manifold;
- use a grinder to cut the neutralizer body;
- remove all the insides from the jar;
- weld the housing, install the manifold in place.
It should be taken into account that this measure is temporary; for normal engine operation it is necessary to install a flame arrester, or even better, a new catalyst.
Replacing the Lada Granta catalyst: prerequisites
If you recognize at least one of the reasons listed below, then most likely the failure and further replacement of the catalyst will not keep you waiting.
The main reasons leading to the need to replace the catalyst are:
- Low quality fuel used to fuel the car. This leads to incomplete combustion of the combustible mixture, increasing the release of soot and fossils. The obstacles created negatively affect the performance of the entire system, which leads to frequent repairs and preventive maintenance.
- Late technical inspection and long service life of equipment without replacement and prevention. Burning out the mechanisms inside contributes to the release of toxic waste outside, which is extremely undesirable.
- Installation of low-quality or non-original parts.
- Loose connection at the joints of flange connections.
- Damage to the metal casing due to collision with fencing products, as a result of which a hole appears in the housing and gas leakage occurs.
Signs of a catalyst malfunction are as follows:
- the error indicator in the operation of the exhaust gas system systematically lights up on the instrument panel;
- fuel consumption increased for no reason;
- the car's power has decreased;
- the accelerator pedal has ceased to be responsive, the response is passive;
- there is a burning smell in the cabin;
- When idling, the engine is unstable.
How does the breakdown manifest itself?
Today there is no such part in the Lada Grant device that would not be subject to wear. The flame arrester is also no exception. Long-term operation in harsh conditions negatively affects the body and filling of the device.
In addition, this unit is also adversely affected by external factors, namely corrosion and salt solutions, which our road workers like to sprinkle on snow-covered roads. All this significantly reduces the service life of this device. A breakdown of the flame arrester is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- An extraneous sound is heard coming from the location of the device;
- Engine power has noticeably decreased;
- Excessive heating of the flame arrester body, as well as parts adjacent to it, is observed.
Maintenance tips and tricks
Try to refuel only with high-quality fuel, which is provided and recommended in the operating instructions. Adhere to the timing of the technical inspection, because the condition of all other units and the degree of their wear depend on this. Observe the speed limit for this brand of vehicle. Use the machine as recommended.
Sources:
https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5bd0053b3d9f5100afac7552/5dbd0f4dbc251400ae423424 https://www.zr.ru/content/articles/905991-kataliticheskij-nejtralizator/ https://carpedia.club/Sniatie-katkollektora-Lada -Granta https://avto-blogger.ru/glush/udalenie-katalizatora.html https://euro-glush.ru/remont-vyhlopnoj-sistemy/zamena-katalizatora-lada-granta.html