A hot top and cold bottom of a car radiator is a normal condition only for cold engine after launch. If the engine has been running for several minutes, during which the coolant temperature has already reached 80–90 degrees (depending on the model), and the upper radiator pipe is hot and the lower one is cold, this is sign of trouble in the cooling system. However, there are exceptions to this rule.
The main reasons why the lower radiator hose is cold after warming up are a malfunction of the thermostat or pump , or a clogged radiator . This article will tell you how to determine the specific cause of the problem and what to do in this case.
What can cause the lower radiator hose to be cold and the upper hose to be hot?
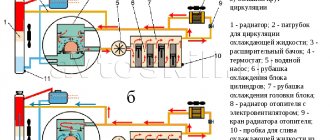
Coolant circulation diagram: Click to enlarge.
Whether the lower radiator hose should be cold depends on the path of antifreeze.
After starting the engine, it first circulates in a small circle, bypassing the radiator, and after reaching a temperature of about 85 ° C , at which the thermostat partially opens, it goes to a large one.
In most models, coolant enters the radiator through the upper pipe, after which it is pumped down and returns through the lower pipe to the engine cooling jacket.
In those models where the thermostat blocks the flow of antifreeze from the radiator (for example, VAZ 2109), the lower pipe may be cold while the upper pipe is hot and before the engine warms up. If both channels or the radiator inlet are blocked (as on the Lada Granta), when the upper pipe warms up, both the radiator and the lower outlet should quickly warm up.
With a working cooling system, the bottom of the car radiator is cold and the top is hot only at the moment when the thermostat has already opened slightly, but the antifreeze has not yet reached the lower pipe. When the air temperature is low and the interior heater is on in winter, it takes longer for the coolant to warm up. In this case, the thermostat opens 10 minutes or more after the start of movement. At low air temperatures, it often happens that a car’s radiator is hot on top and warm on the bottom, since antifreeze quickly cools down as it passes through it.
Diesel engines warm up much slower than gasoline engines. Some cars with a diesel engine in winter can only fully use the large circle when driving at high speed (over 100 km/h) and during long periods of “taffy” in traffic jams.
You need to figure out why the lower radiator hose is not heating up and solve the problem in the following situations:
- the upper pipe is hot, and the lower one remains cold even after high-speed driving in warm weather;
- the radiator warms up only at the top, remaining cold at the bottom;
- coolant temperature readings on the dashboard go into the “red zone” ( more than 100–110 degrees );
- Antifreeze is boiling in the expansion tank.
The main reasons why the upper radiator pipe heats up and the lower one is cold:
Why does an air lock appear in the cooling system: video
- Thermostat is stuck in the closed or half-closed position.
- cooling pump is worn out and cannot create the required pressure.
- radiator channels with deposits.
- An air lock has formed in the cooling system.
Cooling system malfunctions are not always reflected in sensor readings. The coolant temperature sensor (coolant temperature sensor) may not be in contact with the overheated liquid and show a normal temperature. For the same reason, the radiator fan may not turn on in a timely manner.
Computer diagnostics only help identify problems with an electronically controlled thermostat. A problem with a mechanical valve is indirectly indicated by the non-corresponding readings of the DTOZ located on the block, in the cylinder head or in the area of the thermostat.
You cannot operate the car if the car is heating up and the lower radiator pipe is cold! This is fraught with a breakthrough of the gasket between the head and the block, failure and damage to the cooling system pipes, misalignment of the cylinder head, scuffing and wedge of the engine CPG due to overheating!
Procedure for checking the Lada cooling system
1. Check the coolant level in the expansion tank; it should be between the “MIN” and “MAX” marks. If antifreeze has to be added periodically, then the system is not sealed (we check the integrity of: hoses, radiator drain holes, cylinder block, sensor installation locations, expansion tank housing, pump and its connections, engine and heater radiators).
2. Check the thermostat. We warm up the engine to 85-92C and check the lower radiator hose leading from the radiator (in diagram No. 10), if it is cold, it means the coolant is circulating only in a small circle, the thermostat is faulty and should be replaced.
3. Check the circulation of antifreeze in the cooling system. Open the cap of the expansion tank and monitor the flow of antifreeze into the tank. Attention, the cooling system is under pressure, and the antifreeze in the system may be hot; open the expansion tank cap very carefully. Poor circulation of antifreeze indicates a malfunction of the water pump (pump), or the cooling system is clogged (needs to be cleaned).
How to determine the reason why the lower radiator hose is cold and the upper one is hot
The lower radiator hose is slightly cooler than the upper one, since the antifreeze coming from above cools down as it passes through the radiator. But, as a rule, we are talking about a relatively small temperature difference. When the outlet pipe/hose from the radiator does not warm up at all, this indicates a violation of the coolant circulation and heat exchange in the internal combustion engine.
All common reasons why a cold lower radiator pipe does not heat up normally are collected in the table.
| Possible reason | Consequence | How to understand/define it |
| The thermostat is stuck in the closed or half-closed position. | The coolant circulates in a small circle and does not cool. |
|
| The expansion tank cap valve is faulty. | The pressure in the circuit is not automatically regulated, which may cause air pockets. |
|
| The radiator channels (lines) are clogged. | Antifreeze does not pass through the radiator and circulates mainly in a small circle. |
|
| The water pump impeller is worn out. | The pump cannot create the required pressure, which causes the coolant circulation and heat transfer from the engine to the radiator to deteriorate. |
|
| There is an air lock in the cooling circuit. | Coolant circulation deteriorates, heat exchange is disrupted, and pipes may swell and rupture. |
|
Improved cooling of VAZ-1118 “Kalina”
To reduce the likelihood of airing of the SOD due to jamming of the compensation valve of the expansion tank cap, readers suggested removing the valve from it as a temporary measure. We cannot recommend this method, because the risk of boiling and overheating of the engine increases. But if you decide to go this route, in order to prevent the antifreeze from boiling away at atmospheric pressure, we lower the fan start temperature to 98 degrees programmatically, or we cut an adapter into the radiator inlet pipe for sensor .
A more correct upgrade option has been tested several times and has shown its performance on cars with a cable-operated throttle. We put a plug in the pipe connecting the large cooling circle to the expansion tank;
- We connect the freed fitting to the lower heater hose through the tee from 2110;
- We plug the thin outlet hose (distant, if you look from the front of the car) of the throttle heating.
- We connect the free fitting through a tube of the appropriate diameter to the expansion tank. To do this, we cut an additional nipple into the upper plane, or connect through a tee to a thin input. Thus, we transfer the steam outlet to a small circle, while taking the liquid with air bubbles at the top point of the system.
Thus, we transfer the steam outlet to a small circle, while taking the liquid with air bubbles at the top point of the system. On a car with an electronic pedal (e-gas), we do the same.
- We connect the thin fitting of the thermostat to the upper part of the expansion tank (via a tee or an additional fitting). We turn off the standard thin tube from the thermostat.
- Disconnect and turn off the lower extension hose. tank, in the vacant space we connect a homemade line from a tee embedded in the “return” of the heater.
The problem of air removal is solved once and for all.
We wish our readers warmth in the cabin and stable engine temperature!
Cars that most often have heat transfer problems
On some cars, the situation where the upper radiator hose is hot and the lower hose is cold is more common than others. Such models and their “childhood diseases” are collected in the table below.
| Brand, model | Cause of the problem | How can I fix it? |
| VAZ 2106, 2101 and other “Classics” | Low quality of original components, in particular the thermostats themselves, which jam. | Instead of the original VAZ thermostat valve, use parts from other companies: Metal Incar, Finwhale, Vernet. |
| The cold bottom of the radiator in a VAZ “Classic” with high mileage is a consequence of corrosion of parts and clogging of the radiator channels. | Flush the radiator using a special fluid or, if that doesn’t help, replace it. | |
| VAZ 2108-21099, 2113-2115, Kalina | A faulty expansion tank cap valve does not allow maintaining operating pressure in the cooling system, which disrupts coolant circulation and causes the heater to heat poorly. | Replace the expansion tank cap. |
| VAZ 2110 – 2112, Lada Priora | On the VAZ 2110-2112, the lower pipe is cold, and the heater blows cold due to the predisposition to the formation of traffic jams and disruption of coolant circulation. | Monitor the condition of the cooling circuit, remove plugs, especially when replacing antifreeze. As a radical solution, you can replace the thermostat with a “six-hole” one (art. 21082-1306010) or from Lada Granta (21900-1306010), adapting the circuit to it. |
| The upper pipe is heated, and the lower pipe is cold, due to exhaustion and lack of pump performance. | Install an improved pump, like the Luzar Turbo. | |
| Skoda Octavia | On the Skoda Octavia, the lower radiator pipe is cold, and the engine begins to overheat due to a faulty oil heat exchanger gasket. | Replace the oil heat exchanger gasket. |
| Daewoo lanos, Sens, ZAZ Chance | Cold lower pipe and radiator, a consequence of early opening or jamming of the thermostat. | Replace the thermostat with a better one that opens at 87 degrees. |
| Ford Focus | On a Ford Focus, the bottom of the radiator is cold and the top is hot, usually due to a stuck thermostat. | Replace the faulty thermostat. |
| Mazda 3 | On a Mazda 3, the lower pipe is cold, usually due to a faulty thermostat. | |
| Volkswagen Passat | With high mileage, the pump and thermostat fail. | Replace the pump or thermostat. |
| Suzuki Grand Vitara | Airing of the cooling system due to pressure failure. | Remove air pockets. Replace the expansion tank cap, which often becomes clogged or, on the contrary, does not hold pressure. |
If your car begins to overheat frequently, there may be several reasons for this:
- Thermostat. It is very simple to check its performance: on a warm engine, touch the lower and upper radiator hoses with your hand. If the latter turns out to be cold, and the lower one is barely warm, then, most likely, the thermostat is jammed, and the antifreeze circulates only in a small circle. In this case, the solution to the problem will be to install a new device in the car.
- Clogged radiator honeycomb. This is also one of the common causes of malfunctions in the cooling system. It occurs especially often in late May - early June, when annoying poplar fluff flies along the street. The solution to the problem is to clean the outer part of the radiator. This work often causes difficulties for car enthusiasts, but no other methods have yet been invented to solve clogged honeycombs. Therefore, everything is cleaned by hand.
- Faulty fan. If you notice that when the coolant heating level increases, this part does not turn on, you should check the temperature sensor, wiring and relay.
- Air in the cooling system. "Kalina", like any other car, is not immune to an airlock inside the SOD. And if in all previous cases the problem was solved very quickly, or at least clearly, then here car enthusiasts often have problems. Therefore, in order to fully explain the picture, below we will look at how such breakdowns are eliminated.