Imagine this situation: there are no auxiliary parts between the engine and gearbox. They are connected directly. Do you think the car will be able to drive? Hardly. The only thing you will achieve is strange intermittent movements of the car, as well as a further complete stop of the engine. If this ever happens, your box won’t last long, and within three days it will simply break. Moreover, problems with the engines themselves will overtake you as suddenly as replacing the gearbox. The prospect is not very good, you will agree. But, fortunately, in order to avoid such embarrassment, engineers came up with a clutch.
The main purpose of this device is to smoothly connect the engine and gearbox for their further functioning. If we omit all the terminology, then the clutch is necessary in order to turn off the torque. One of the biggest advantages when using this device is that if you have it, you don’t have to worry about the transmission deforming when braking at high speed. The use of such a device allows you to avoid expensive repairs that might be necessary in its absence.
Basic clutch malfunctions
The type of clutch used is characterized by a high degree of reliability and durability, and low maintenance costs.
The following malfunctions may occur due to improper use of the clutch pedal (constant contact of the driver’s foot with the clutch pedal while driving, sudden release of the pedal or incomplete “squeezing” of the pedal), long-term operation of the car with impaired pedal travel, or natural wear and tear of parts or their damage during many years of use car.
In the latter case, the clutch must be repaired at a service station.
Nine clutch device
The clutch kit is one of the key components of the Nine transmission. This is a single-disc friction-type mechanism located between the engine and the gearbox (gearbox). The algorithm for its operation is as follows:
- Initially, the car is stationary, the engine is started, the pedal is released. The gearshift lever is in the neutral position, that is, the rotation of the input shaft is not transmitted to the secondary shaft.
- The driver is preparing to move forward. With his left foot he presses the pedal, and the mechanism disconnects the gearbox input shaft from the engine. The driver moves the lever to the first gear position, the mechanism ensures the engagement of the primary and secondary shafts of the gearbox. The car is stationary because the engine is disconnected from the transmission input shaft.
- The driver smoothly but decisively releases the pedal. The engine is connected to the input shaft, the task of which is to transmit power to the drive wheels through the secondary shaft, then the car will start moving.
- Switching from first gear to second, from second to third, and so on occurs in the same way.
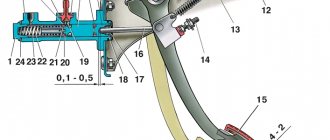
The VAZ 2109 clutch design is such that when the pedal is released, the driven disk is clamped by springs between the flywheel and the pressure plate. In this case, power is transferred to both gearbox shafts and the drive wheels. When you press the pedal, the VAZ 2109 clutch fork rotates through a special rod and presses on the levers that retract the pressure plate. The VAZ 2109 clutch driven disc is disconnected and power transmission stops. The mechanism casing is connected to the pressure plate by three pairs of elastic plates. The unit is driven by a cable, its lower tip is fixed with nuts in a bracket on the engine crankcase.
The clutch cable is connected to the clutch release fork lever.
Incomplete disengagement of the clutch (clutch “drives”)
With this malfunction, it is difficult to change forward gears, and reverse gear is engaged with noise. Causes of the malfunction and ways to eliminate it:
- large free play of the clutch release fork lever due to an increase in the gap between the clutch release bearing and the petals of the pressure spring (for a clutch with a servo mechanism). This leads to an increase in the free play of the clutch pedal (clutch release lever) and a decrease in the working stroke. Therefore, complete separation of the clutch discs does not occur. This cause of the malfunction can be eliminated by adjusting the free play of the clutch release fork lever, as indicated above;
- warping of disks. This malfunction occurs when the clutch discs overheat due to their slipping. The end runout of the driven disk should not exceed 0.5 mm. If the runout is greater, the disc should be straightened or replaced. If the pressure plate becomes warped, it is replaced as an assembly with the clutch casing and pressure spring;
- jamming of the driven disk hub on the splines of the input shaft. This malfunction may occur after prolonged or improper use of the vehicle due to contamination or wear of the splines. In the first case, it is enough to clean the shaft and hub splines and coat them with LSC-15 or Litol-24 grease; in the second case, replace worn parts;
- loosening of rivets or breakage of friction linings. It is necessary to rivet the friction linings using steel rivets. After flaring, the rivets should not have any breaks. The distance from the rivet to the surface of the friction lining must be at least 0.2 mm;
- insufficient clutch pedal travel. This malfunction occurs due to incorrect adjustment of the backlash-free drive when the pedal travel is not enough to completely disengage the clutch discs. To eliminate the malfunction, you need to correctly adjust the pedal travel within 125–130 mm;
- malfunction of the clutch cable due to damage to the cable or its sheath or other reasons causing the clutch drive to jam. It is necessary to determine the cause of the malfunction and replace damaged or worn parts.
Vendettax7 › Blog › When to change and how to check the clutch
Will you be upset or not when you find out that the manufacturer does not indicate specific figures for clutch life
. If, for example, in the brake system, it is clearly stated that the thickness of the brake disc should be such and such, then why is this not applicable to the clutch?
The fact is that clutch wear depends on many reasons.
, and first of all, of course, on how the driver changes gears and in what mode he uses the clutch.
And while clutch disc thickness cannot be measured the same way brake disc thickness can be measured with a caliper, there are ways to measure it. There are two of them. The first way
to measure the thickness of the clutch disc is with a special measuring gauge.
This method does not require dismantling the clutch; it is performed on a lift. But you are unlikely to use it. The second method
is simpler to implement and allows you to determine the wear of the clutch disc in order to replace it.
Replacing the driven disk is a procedure provided by the manufacturer, because The driven disk is a consumable part. The check is carried out as follows: with the engine running, you need to put it in high gear, accelerate it, and if the car does not stall, this means that the driven disk is worn out and requires replacement
.
It must be remembered that such a check of the thickness of the clutch disc is not technologically correct, but it is effective and allows you to determine the condition of the disc extremely accurately. As already mentioned, the life of any clutch is determined by its operating conditions. Without going into technical details of the interaction of clutch parts, you should understand that basically the life of the clutch and the wear rate of the discs depend only on the driver. A clutch of the same quality and manufacturer can last 5,000 km for one driver, and 100,000 for another. Participation in drag racing, frequent slipping, abrupt starting at high speeds, ingress of foreign liquids and objects, unqualified installation and adjustment clutch - all this reduces the life of the clutch. How to check the clutch?
The clutch is checked using already proven and reliable folk methods, and only by them. Naturally, in addition to disassembling the clutch. We are talking about how you can check the clutch of your car yourself, and then decide whether you need a more in-depth diagnostic with dismantling the clutch mechanism.
Incomplete engagement of the clutch (clutch “slips”)
Signs of this malfunction:
- insufficient acceleration of the car when the throttle control pedal is sharply pressed, a loss of power is felt when driving uphill, fuel consumption increases, the engine overheats, a specific smell is felt from the burning of the driven disk linings. Causes of the malfunction and methods for its elimination: there is no free play of the clutch release fork lever. In this case, it is possible that the clutch release bearing constantly acts on the petals of the pressure spring c. force at which the driven disk will not be clamped with sufficient force, which will lead to its slipping. This cause of the malfunction can be eliminated by adjusting the free play of the clutch release fork lever, as indicated above;
- Friction linings are worn out or burnt. In this case, it is necessary to rivet or replace the driven disk;
- Clutch discs are oily. This is possible when the gearbox seals are worn. To replace them, you should contact a service station, as this involves complete disassembly of the gearbox;
- jamming in the clutch release drive. This is possible if the cable or its sheath is damaged (kinks, chafing) and can be eliminated. Replacing the cable with subsequent adjustment of the clutch drive.
The procedure for replacing the VAZ 2109 clutch
1. Remove the gearbox.
2. Insert the mandrel into the pressure plate hole. If there is no mandrel, then when removing the clutch, you need to hold the driven disk so that it does not fall out of the casing. You can use the old input shaft as a frame.
3. Lock the flywheel with a screwdriver and remove the six bolts that secure the housing to the flywheel.
4. Remove the casing along with the driven disk - do this carefully.
Now take a close look at the driven disk and its elements. There should be no cracks on them. Friction linings must not be worn out.
- rivet heads have a depth of less than 0.2 mm;
- there is oil on the surface of the friction linings;
- rivet joints are weak
- damper springs in the disc hub sockets are broken;
- if there is warping on the disk and the runout value exceeds 0.5 mm...
... then you need to replace the driven disk.
5. Now inspect the flywheel and pressure plate, especially where they touch each other. They should not have:
- deep marks;
- scuffing;
- nick;
- clearly visible signs of wear and overheating.
In addition, the rivet connections of the pressure plate parts must not be loosened.
If you find any of the above flaws, then the pressure plate or flywheel needs to be replaced.
You only need to check and inspect the clutch parts in one case: if you are not going to change the entire clutch, but only the worn parts. But VAZ 2109 owners with experience say that it is better to change it as a kit. The most expensive, but high-quality, products are considered to be from the following companies: Valeo and Sachs.
The clutch is assembled and put into place in the reverse order. Just remember to center it.
On January 31, 2014, the following trouble happened: I went to the grocery store, I was standing at the traffic light, the light turned green - I put it in gear, but the car didn’t move. What is it, everything seemed to be fine. You turn on the gear, release the clutch - the VAZ 2109 barely moves. Moreover, accelerate or don’t accelerate - the speed does not change. You engage second and third gear and it doesn’t move at all. I somehow drove through the intersection (pushing through would have been faster) and stopped in the parking lot, fortunately it started 50 meters from the traffic light. I open the hood: it’s working properly, the gears are engaged, but the car doesn’t drive. The clutch of the VAZ 2109 has failed. In first gear and at about a thousand rpm, it travels at a maximum speed of 5 kilometers per hour. It also drives in reverse gear, even in reverse it goes a little faster than in first. In other gears it doesn't move at all. A couple of days before, I noticed that the clutch of my VAZ 2109 began to slip. You start, drive, everything seems to be fine. When you try to accelerate sharply, the VAZ 2109 engine gains speed, but this does not make the car go any faster. I thought it was freezing (it was -20 degrees outside), maybe it was frozen. However, it turned out that the clutch of the VAZ 2109, which was slowly getting worse, gave me a gift; it broke on December 31 at two o’clock in the afternoon. I didn’t have time to drive far from home, I turned on the emergency lights and slowly, at walking speed, drove home. On the way, I prayed that the clutch would not completely fall apart along the way. I arrived home, parked the car and walked to the store, simultaneously wondering what could have gone wrong in the clutch. I came and went online. I started reading materials about replacing the VAZ 2109 clutch. I immediately didn’t like the fact that replacing the clutch is a time-consuming and labor-intensive thing: you have to disconnect the CV joints and remove the gearbox. It's frosty outside, I don't have a garage with a pit, this clutch couldn't break in the summer. But, what can you do, you need to drive, so right after the holidays I went and bought a complete VAZ 2109 clutch kit. Of course, knowing that it was faulty, you could buy something specific: either a clutch disc, or a basket, or a release bearing. However, until you disassemble the VAZ 2109 clutch, you will not know what has gone wrong. Yes, it’s safer to change the clutch completely and not mess around with it anymore. The cost of a VAZ 2109 clutch kit starts from $50, which in principle is not very expensive; it is much more difficult to change it.
The clutch kit also included a small bag of lubricant for the input shaft of the VAZ 2109 gearbox, which is inserted into the clutch disc. There was also an instruction with brief hardware on the operation of the clutch of VAZ models with mechanical and hydraulic drive.
This kind of work cannot be done alone, so I asked a neighbor with a garage for help. When we got to the VAZ 2109 clutch, we saw that the clutch disc on the car was completely without lining and was polished to a shine. The condition of the VAZ 2109 clutch basket also leaves much to be desired. At this point, I was very glad that I immediately bought a clutch kit, and not a separate clutch disc, for example.
After putting everything back together, I immediately noticed that before the clutch would engage at the very end of releasing the pedal, but now, as soon as you start to release the pedal, the VAZ 2109 immediately starts moving. This is due to the fact that the friction linings on the old clutch were completely worn out, and on the new one, the disc with the linings is much thicker. Therefore, when you drive a VAZ 2109 and notice that the clutch grabs further than usual, it means that the friction linings of the VAZ 2109 clutch disc are worn out. It’s very unusual when you’re used to starting off with the old clutch, but with the new one the car starts off completely differently. Therefore, the first couple of days I had to get used to it and start moving more smoothly.
VAZ 2109 is the legendary “nine”. The front-wheel drive five-door hatchback was serially produced at the Volzhsky Automobile Plant from 1987 to 2004. From 2004 to the end of 2011, the VAZ 21093 modification was assembled in Zaporozhye.
Many car owners try to maintain their personal car themselves and know how to do it correctly, since they carefully study the operation of the main components and leading modules. The list of routine maintenance includes periodic adjustment of the VAZ 2109 clutch. This task is quite simple if you familiarize yourself with the operation algorithm in advance.
What causes the clutch to slip?
The most well-known causes of car slipping:
- the pedal does not move freely;
- friction linings are worn out;
- rubber parts are swollen.
In order to eliminate or prevent clutch slipping, you first need to check the clutch pedal travel. If necessary, it is adjusted.
Friction linings worn down to rivets
VAZ 2109 clutch slips
The reasons for this problem may be:
- normal wear taking into account operating conditions;
- errors when driving a car, pressing the gas pedal from a standstill;
- poor clutch system movement;
- Incorrect installation or adjustment of the clutch drive.
Note! In such a case, the clutch is compressed with insufficient force.
The elasticity of the pressure plates is lost
VAZ 2109 clutch slips
Clutch disc slipping can occur when the pressure springs are weakened or faulty. This can also occur due to wear or warping of the friction surfaces of the flywheel with the pressure disk.
Note! If the friction linings of the driven disk are oily, then they, along with the faulty pressure plates, are replaced with new ones.
The rubbing surfaces of the flywheel with the pressure disk are processed using grinding. If, when moving the car, there is a smell of burning linings, there is slight acceleration, a decrease in speed, or a slow crossing of hills, then the reason is most likely hidden in the clutch; it may not be fully activated. If the engine turns off, the clutch will work normally, but if this does not happen, then we can conclude that the clutch is slipping.
VAZ 2109 clutch slips
In the best case, it is also recommended to replace friction linings when cracks, burns and scuffs are detected on the surface. Clutch slippage can sometimes occur due to swelling of the rubber elements of the hydraulic drive. Such a defect most often occurs due to the use of low-quality brake fluid, or the composition does not meet the standards. Penetration of mineral oils, kerosene or gasoline into the liquid is not excluded. To fix this problem you need to:
- dismantle the functioning and main hydraulic drive;
- disassemble the system;
- rinse it with purified brake fluid;
- replace swollen parts;
- clean the expansion hole;
- Fill with clean, high-quality liquid.
The elasticity of the pressure plates may disappear due to long-term operation. This can also happen due to insufficient pressure on the disk (driven). It is recommended to check the condition of the plates at a car repair shop, since it is impossible to do without the use of special instruments and devices. As a rule, weakened springs need to be replaced. This also applies to friction lining oil.
Oily or greasy friction linings
This problem can happen for several reasons:
- if the gearbox or engine seal is damaged;
- in case of excess lubricant on the gearbox shaft or on the crankshaft;
- if the seal of the hydraulic drive is broken.
Note! As a result, the friction coefficient of the linings is reduced.
If, during normal movement of the pedal, the clutch still slips, then, most likely, oil has got on the linings. It is necessary to dismantle the clutch and check the driven disc with linings for oiling. Typically, oil penetrates the disc and linings due to its excess in the gearbox, as well as due to contamination of the flywheel drainage gap. To remove oil from the pads, they need to be washed thoroughly with kerosene or gasoline. After this, the parts are wiped dry and cleaned with sandpaper. If the driven disk is very oily, it must be changed; this also applies to the set of friction linings. Next, you need to set the gearbox to a normal oil level and clean the flywheel clearance.
bullet3425 › Blog › #4 Clutch release bearing: principle of operation, symptoms of malfunction
Clutch release bearing: principle of operation, symptoms of malfunction
Today, the most common clutch systems have two discs - a leading one, rigidly coupled to the crankshaft, and a driven one, transmitting torque to the gearbox. To change gears or put the car into idle speed, the clutch discs must be disconnected, which is done using a release bearing that pulls the driven disc away from the drive disc.
This is an important element of the clutch system, and at the same time one of the most vulnerable parts. The clutch release bearing is at rest while the vehicle is moving, and only comes into operation when changing gears. The breakdown of such a small spare part guarantees the impossibility of further operation of the car, so the bearing must be changed immediately when obvious signs of its malfunction appear.
Types of release bearings
Nowadays, two types of release bearings are common: * roller or ball - mechanical units that transmit force to the bearing through a rigid bunch of rods; * hydraulic - here the force is created by hydraulics, due to which the clutch pedal is depressed much easier.
The mechanical clutch release bearing can be called a part from the past, because Moskvich, VAZ and other old cars were equipped with it. New machines, even budget ones, mainly use hydraulic systems. Although a number of domestic cars currently produced are still equipped with mechanics, in order to reduce the cost and simplify them.
The release bearing's job is to connect and disengage the clutch when you press the pedal inside the car. The principle of operation of the part is quite simple: * the driven disk is pressed against the flywheel by a pressure disk, due to which clutch is ensured; * the pressure on the pressure plate is provided by a diaphragm spring, the inner petals of which are acted upon by the clutch release bearing; * the movement of the bearing, which initiates the separation of the discs, is ensured by the clutch fork.
Causes and symptoms of release bearing failure
The reason for the breakdown of this part is uneven loads on it at the moment when the clutch is depressed, and it goes back along with the driven disk. For this reason, holding the clutch pedal for a long time while the gear is engaged is strictly not recommended. In principle, this is a reliable and durable part, and it most often fails among novice motorists.
The most important symptom of bearing wear is the appearance of a slight knocking sound when the clutch pedal is depressed. If the sound appeared in the summer, this is almost a guarantee of future problems, but if it came along with frost, there may be an elementary change in the linear dimensions of the bearing cup due to a drop in temperature outside. The release bearing in most cars has an undeniable advantage - high strength, so even if a knock appears, you can afford to do nothing for a while, but watch to see if it gets stronger.
The clutch slips (“slips”) on VAZ 2108, 2109, 2109 cars
The clutch slips and does not engage completely.
When engaged (clutch pedal released), idling, or with a gear in motion, the clutch must transfer torque from the engine to the transmission (gearbox) without loss.
This is achieved due to the fact that the driven disk is tightly pressed by the drive disk of the basket to the engine flywheel and rotates with it and the transmission input shaft (see image below). The release bearing is pressed against the petals of the damper (pressure) spring of the basket, but does not press on them and also rotates with it.
If the clutch slips, this means that for some reason the driven disk is not pressed tightly against the flywheel by the driven disk and slips relative to them.
clutch of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars is included (diagram)
Signs of clutch slipping on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— While driving, when you press the gas pedal, the engine picks up speed - “roars”, but the car does not accelerate or accelerates with some delay. This becomes especially noticeable when going uphill.
— It is difficult to move away. The engine may stall when the clutch pedal is released. It takes more gas to move the car.
— There is a smell of burnt disk linings.
— Fuel consumption increases sharply.
Checking for clutch slipping on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 vehicles
In the early stages of a malfunction, when there are no obvious signs yet, you can diagnose the clutch using a tachometer. While driving, sharply press the gas pedal and watch the tachometer. The revolutions have jumped, and the car accelerates sluggishly, then the revolutions drop somewhat, the car begins to accelerate normally - the clutch will soon require adjustment or repair.
Reasons for clutch slipping on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
Clutch drive not adjusted
After repairing the clutch, replacing its elements, drive, etc., during preliminary adjustment, it is possible that the clutch was “tightened too much”, the pedal stroke was more than 125-135 cm and the clutch will “grab” high. As a result, the clutch “slips”. It is necessary to adjust its drive as quickly as possible, otherwise severe wear of the friction linings of the driven disk occurs and the situation with slipping quickly worsens. The clutch pedal should be approximately level with the brake pedal. For more details, see “Adjusting the clutch drive on VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099”.
Adjusting the clutch drive of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars by rotating the adjusting nut
Oiling of the flywheel, drive and driven disks
Leakage of engine oil from under the rear oil seal of the engine crankshaft, gearbox input shaft oil seal, flywheel bolts, valve cover gasket and contact with the friction surfaces of the clutch leads to slipping of the driven disk relative to the flywheel and slipping of the clutch even with a correctly adjusted drive. Traces of oil leakage can be visually seen on the engine. The only thing that will help is disassembling, eliminating leaks (there may be several reasons) and wiping the clutch discs and flywheel with gasoline (kerosene, white spirit), followed by rubbing the linings with very fine sandpaper. A heavily oiled driven disk should be replaced with a new one.
Reduced force (wear) of the damper (pressure) spring
As a result of constant and prolonged operation, the petals of the pressure spring of the clutch drive disk lose their elasticity, and an annular groove appears at their ends. This happens at approximately 100 thousand km. The clutch begins to slip because the pressure spring creates insufficient pressure on the driven disc and it begins to slip relative to the flywheel. To check the spring, special equipment is required, so in a garage, only replacing the “basket” will help. Replacement is also necessary if the size of the annular wear from the release bearing on the petals is more than 0.8 mm.
Indirectly determine the decrease in the elasticity of the “basket” pressure spring by the increased softness of the pedal when the clutch is disengaged (pressed) and its working stroke increases.
Wear, destruction or burning of the friction linings of the driven disk
Over time, the friction linings of the driven disk wear out (on average, over a mileage of 50-60 thousand km). An incorrectly adjusted drive or the habit of driving constantly with your foot on the clutch pedal accelerates wear. When the friction linings of the driven disc wear out, the clutch begins to slip as the free play of the pedal increases. Visually, the clutch pedal rises higher than the car's brake pedal. With slight wear (the lining is considered completely worn out if the distance between the rivets and the working surfaces is less than 0.2 mm), clutch slipping in this case can be eliminated by adjusting the drive, and with large wear, only replacing the driven disk will help.
Design and operating principle of clutch master cylinders
Typical diagram of a hydraulic clutch release drive
The most simple design of the GCS is with the tank removed and installed on the body. The basis of the device is a cast cylindrical body, on which lugs for mounting bolts and other parts are made. At one end the housing is closed with a threaded plug or a plug with a fitting for connection to the pipeline. If the housing is closed with a blind plug, then the fitting is located on the side surface of the cylinder.
In the middle part of the cylinder there is a fitting for connecting to the tank via a hose or a seat for installing the tank directly on the body. There are two holes made under the fitting or in the seat in the cylinder body: a compensation (inlet) hole of small diameter and a bypass hole of increased diameter. The holes are located in such a way that when the clutch pedal is released, the compensation hole is located in front of the piston (from the drive circuit side), and the bypass hole is located behind the piston.
A piston is installed in the housing cavity, on one side of which there is a pusher connected to the clutch pedal. The end of the body on the pusher side is covered with a corrugated protective rubber cap. When the clutch pedal is depressed, the piston is retracted to its extreme position by a return spring located inside the cylinder. In double-piston gas pumps, two pistons are used, located one behind the other, with an o-ring (cuff) between the pistons. The use of two pistons improves the tightness of the clutch drive circuit and increases the reliability of the entire system.
Such cylinders work as follows. When the clutch pedal is released, the piston is in its extreme position under the influence of the return spring and atmospheric pressure is maintained in the clutch drive circuit (since the working cavity of the cylinder is connected to the reservoir through a compensation hole). When you press the clutch pedal, the piston moves under the influence of the force of your foot and tends to compress the fluid in the drive circuit. As the piston moves, the compensation hole closes and the pressure in the drive circuit increases. At the same time, through the bypass hole, liquid flows behind the back side of the piston. Due to the increase in pressure in the circuit, the piston of the working cylinder moves and moves the clutch release fork, which pushes the release bearing - the clutch disengages and you can change gear.
When the pedal is released, the piston in the main circulation center returns to its original position, the pressure in the circuit drops and the clutch is engaged. When the piston returns, the working fluid that has accumulated behind it is squeezed out through the bypass hole, which leads to a slowdown in the movement of the piston - this ensures smooth engagement of the clutch and the return of the entire system to its original state.
If there is a leak of working fluid in the circuit (which is inevitable due to insufficient connection density, damage to seals, etc.), then the required amount of fluid comes from the tank through the compensation hole. This hole also ensures that the volume of working fluid in the system remains constant when its temperature changes.
The design and operation of a cylinder with an integrated reservoir for working fluid is somewhat different from that described above. The basis of this GCS is a cast body installed vertically or at an angle. In the upper part of the housing there is a reservoir for the working fluid, under the reservoir there is a cylinder with a spring-loaded piston, and a pusher connected to the clutch pedal passes through the reservoir. On the wall of the tank there may be a plug for adding working fluid or a fitting for connecting to a remote tank.
The piston has a recess in the upper part, and a small diameter hole is drilled along the piston. The pusher is installed above the hole; in the retracted state, there is a gap between them, through which the working fluid enters the cylinder.
It is not difficult to operate such a GVC. When the clutch pedal is released, atmospheric pressure is observed in the hydraulic circuit and the clutch is engaged. When you press the pedal, the pusher moves down, closes the hole in the piston, sealing the system, and pushes the piston down - the pressure in the circuit increases, and the working cylinder actuates the clutch release fork. When the pedal is released, the described processes are performed in reverse order. Leaks of working fluid and changes in its volume due to heating are compensated through a hole in the piston.
Why the clutch slips: reasons, do-it-yourself adjustment
Hi all! Clutch failure does not bode well for the car and its owner. The sooner signs of problems can be detected, the better. A fairly common question on this topic is why the clutch slips or slips. Different terminology is used, but the essence remains the same.
It is important to understand that modern cars use dry and wet, also known as oil, clutches. In the first case, we are talking about simple friction, while in the second, the procedure is carried out in a special oil, which additionally cools the clutch discs and other elements. Most often we encounter the dry type. Wet is used on cars with dual clutch and robotic gearboxes. It is difficult to adjust and repair a wet clutch with your own hands. This requires the help of specialists.
The most common sign of unit malfunction is slipping. Moreover, for some it happens constantly, while for others it sometimes stalls, sometimes not. This can happen both hot and cold, that is, before and after the unit warms up.
Self-diagnosis of the clutch on a VAZ 2114
You can understand that the clutch assemblies have worn out and need preventive inspection, and possibly repair, by the following four signs:
- If you have a manual transmission, and the clutch “grabs” when the pedal is still in the upper position. And the earlier the setting occurs, the worse the condition of the node turns out to be.
- The speed characteristics of the car have decreased. The clutch discs slip and this causes loss of power. The torque is not completely transmitted from the internal combustion engine to the gearbox and wheels. The first sign of a problem is a drop in dynamics when trying to tow a trailer.
- The car starts moving abruptly and jerkily. The reason lies in the destruction of the ferodo surface. Warping of the disc occurs due to its overheating, which is caused by increased force on the clutch part.
- It is difficult to switch some gears at the gearbox. When switching from one speed to another, an unpleasant grinding noise appears. If repairs are not started in a timely manner, soon all speeds will stop switching. This occurs because the driven and driving discs do not move completely apart when the pedal is depressed, and the clutch “drives.”
Some proven methods will help make sure that all of the above signs really indicate a problem with the clutch. To do this, it is advisable to choose a flat and, if possible, deserted section of the road. In 4th gear, accelerate the car to 65 km per hour and take your foot off the gas pedal. The car will slowly slow down. When the speed reaches 40 km per hour, or becomes “choking”, increase the gas. At the same time, carefully monitor the speedometer and tachometer readings. When the clutch is working normally, the arrows of both instruments will begin to move evenly to the right. If the engine gains power, but the speed does not increase, it is obvious that the clutch discs are worn out. And even if the discs are worn out, a characteristic whistle may appear on the motor side. If several signs of a failed clutch appear, you need to go to a car repair shop for diagnostics, which is performed using special equipment.
The photo shows a “dead” clutch
How the problem manifests itself
Most often, the cause of clutch slipping is normal mechanical wear of the assembly elements. This allows you to diagnose an impending problem even before serious consequences appear. This is done by simply observing changes in the behavior of the machine.
If you notice one of the following signs on your Niva, passenger car or scooter, be sure to diagnose the clutch or contact a service center.
- Extraneous sounds occur during system operation. They appear in the form of knocking noises when the pedal is depressed or released;
- If the noise disappears when the clutch pedal is depressed, the problem is most likely in the release bearing;
- There are signs of vibration on the pedal;
- In this case, the pedal may sink too much or be pressed too hard;
- A characteristic burning smell emanates from the clutch. The clutch usually burns if the driver operates it incorrectly.
The manufacturer provides each vehicle with instructions that indicate all recommendations for routine maintenance and replacement of clutch assembly elements. Most often, the driven disk needs to be replaced.
Before you try to adjust the system yourself, be sure to familiarize yourself with the principle of operation of the clutch. In our previous article we discussed this issue.
Types of clutch
According to the clutch design, there are three types:
- friction;
- hydraulic;
- electromagnetic.
In the first option, torque is transmitted using friction force. In the second case, using a fluid flow, and in the third, due to the action of a magnetic field. The most common is the friction clutch, which in turn can be of three types:
- single-disc;
- two-disc;
- multi-disc.
In addition to this, one more important division should be highlighted:
- dry;
- wet.
In the case of a dry clutch, dry friction between the discs occurs, while in the second, a special fluid is used.
Note! Today, most cars are equipped with a dry single-plate clutch.
Dry single disc clutch parameters
This device consists of:
- flywheel;
- clutch housing;
- pressure and driven disk;
- springs;
- couplings;
- trip bearing;
- clutch forks.
Possible consequences
A slipping clutch is a fairly common occurrence. This is especially true for domestic cars, motorcycles and cars with high mileage.
Practice and experience clearly show that slipping is usually associated with wear and damage to elements. This can happen on any car or other vehicle. Judging by the requests of fans of self-repair, most often the problem of a slipping clutch is solved on the following vehicles:
- VAZ 2107;
- VAZ 2114;
- IZ Planet;
- UAZ Bukhanka;
- Jupiter;
- KAMAZ;
- Minsk;
- VAZ 2110;
- Renault Logan;
- Kia Rio;
- Lada Priora;
- GAZelle, etc.
Despite the obvious cause of such problems, many car owners stubbornly continue to ignore all recommendations for maintenance and timely repair of the unit.
If you feel characteristic signs of problems, you should take prompt action.
When buying a used car or getting behind the wheel for the first time, some people think that they are simply driving the vehicle incorrectly, are not yet fluent in manual shifting techniques and are making some mistakes. In reality, it may turn out that the clutch is failing.
It is important to pay attention to the characteristic signs. Namely:
- the car loses dynamics;
- cravings drop;
- the car is difficult to climb;
- speed is gained slowly;
- the pedal vibrates;
- there is a smell of burning in the cabin;
- the pedal is too tight;
- the pedal fails;
- gear shifts with a crunch;
- Extraneous uncharacteristic sounds appear when switching.
If you do not pay attention to this in time, the engine flywheel is highly likely to be damaged, not only the coupling unit, but also the gearbox will suffer. The problem mainly affects the gearbox input shaft.
Replacement
Not all car owners decide to replace the release bearing (TR) themselves. But if you are ready for this kind of work, then go for it.
The main difficulty in replacing the gearbox is the need to dismantle the gearbox. Without this event, it will not be possible to replace the component.
Therefore, think twice before making a final decision. There is always the opportunity to contact a car service.
To work you will need the following set of tools and materials:
- Set of wrenches;
- Jack;
- Several durable bricks;
- New release bearing;
- Screwdriver Set;
- Container for draining transmission fluid;
- Clutch holder;
- Garage with a pit or lifting mechanism.
It is better to divide the entire replacement procedure into two main stages.
- Removing the gearbox.
- Bearing replacement.
Many people make the mistake of relaxing too much when they finally change the bearing. In practice, reassembly often causes more problems than dismantling work. Please take this into account.
Dismantling the gearbox
- Place the car over a hole or overpass.
- Lift the hood, remove the negative terminal from the battery and throw it aside.
- Disconnect the ground wire from the clutch housing.
- Use a screwdriver to remove the engine splash guard. To do this, you need to unscrew several screws that hold the mudguard to the elements of the side wings. For the VAZ 2109, a key size of 8 is used. Having removed all the screws there, remove the parts of the engine mudguard and put them away for now.
- Disconnect the transmission drive rod. To do this, use a 13mm wrench to loosen the clamp bolts. Next, use a screwdriver to separate the ends of the clamp and disconnect the element from the gearbox.
- Be sure to disable the reverse optics sensor.
- Place blocks or bricks under the rear wheels of the car to prevent the car from moving.
- Remove the front wheels by first loosening the bolts and lifting the front part of the body. After removing the wheels, place pre-prepared bricks under the body.
- Using a 17 wrench, unscrew the nuts securing the ball joint to the steering knuckle on both sides.
- The extension is moved to the side, and the fastening screws of the left extension to the vehicle's suspension arm are unscrewed.
- Using a 10 mm wrench, remove the fasteners of the lower clutch housing cover.
- Remove the transmission mounts. This is done as follows. Place supports or bricks under the engine and a jack under the box. Unscrew the mounting screws of the support to the body with a 17mm wrench. After removing the bolt, remove the support bracket by unscrewing several corresponding nuts.
- We proceed directly to dismantling the gearbox. Using a 19 wrench, unscrew the fasteners of the clutch housing to the cylinder block. Use a jack to lower the gearbox slightly and move it away from the engine. Lower until the input shaft begins to come out of the box.
- Enlist the support of a partner, since it is quite difficult to remove the gearbox alone.
- Make sure that the gearbox input shaft does not rest on the clutch spring petals. If you allow this situation to happen, you will simply damage them.
- Carefully place the gearbox on the supports, being careful not to hit it. Otherwise, repairs will cost much more than buying a new bearing.
Removing a gearbox is a complex procedure that requires a lot of time, patience and skills. Therefore, without these, it is better not to undertake work with your own hands.
Replacing VP
To change the release bearing, follow the instructions.
- After dismantling the gearbox, you can examine the condition of the release bearing. Spin it by hand. If at the same time there are extraneous noises and crunching sounds, then it is obvious that the VP has lost its former performance and needs to be replaced.
- Using a screwdriver, remove the ends of the spring clip and remove the clutch release.
- Move the spring petals of the pressure ring and remove the release bearing from the clutch. To do this you will need to remove the holder.
- At this point, bearing dismantling can be considered complete, so install a new bearing instead of the old element.
- Before installation, make sure that the element is in good condition, rotates freely along its axis, there are no jams, there are no crunches or extraneous noises.
- Swap the old and new bearings. Insert the element into the coupling so that its protruding part is directed towards the coupling.
- Secure the bearing with the clutch holder. You need to hold the bearing in place.
- Take some regular motor oil and apply it to the shaft.
- Install the squeezer onto the shaft and secure the part with a spring.
- During the reassembly process, strictly adhere to all recommendations and maintain surgical precision.
After such manipulations, many people forget about an important point - clutch adjustment. If the system is not adjusted, the service life will be significantly reduced, and therefore very complex repair work will soon have to be performed again.
Obviously, replacing such a small element as a release bearing requires a lot of time, effort and skill. A beginner should under no circumstances start such work.
Many people love the VAZ 2109 for its excellent maintainability. But this does not mean that it is necessary to bring its components and assemblies to such a state. And if this does happen, and even with the clutch, then most likely it will need to be replaced. This will be our topic today.
The procedure itself is simple, but it will require you to remove the gearbox. Therefore, this procedure can be time-consuming.
The good thing is that there is no need to dismantle the drives (the gearbox is removed along with them) and drain the oil. But you definitely need to find an assistant, because the gearbox is a heavy unit.
If you have never changed the clutch or removed the gearbox yourself before, then it is better to entrust this task to the experts from a car service center. Everything will take them 20-30 minutes, and it will cost you 1000-1500 rubles.
If you do not have experience, then replacing a VAZ 2109 clutch can take a lot of time and effort. If, despite the warning, you decide to carry out this operation yourself, then below we will present you with a number of recommendations. Namely:
- replacement procedure;
- the easiest way to remove the gearbox;
- other tips.
Independent and quick diagnostics
If this is just the beginning of the emergence and development of a problem associated with clutch slipping, inexperienced drivers may not notice it.
There is a fairly simple diagnostic method that is almost error-free. You can do it yourself after replacing the clutch, when adjustments have been made, or simply when you suspect that the system is not working correctly.
- place the machine on a level surface;
- start the engine;
- turn on the handbrake;
- go into first gear;
- start trying to move away;
- gradually press on the gas;
- release the clutch at the same time;
- watch the result.
If the engine stalls during such manipulations, this is good. That is, the clutch does not slip. But when the engine does not stall, the car begins to move, the unit actually slips.
Appropriate measures should be taken immediately to correct the problem.
When to replace the clutch disc
Unfortunately, not a single manufacturer indicates exact replacement figures or, and this is not surprising, since the serviceability and service life of this unit will largely depend on the driver. It should be noted that the service life and the risk of current malfunctions directly depend on the quality of clutch operation. According to statistics, the driven or driven clutch disc often breaks. The following defects may be observed:
- any mechanical deformations;
- damage to damper springs;
- malfunction of the hub splines;
- wear of friction linings.
All these troubles indicate an urgent change of the clutch disc.
Note! Since the manufacturer does not set deadlines for changing parts, you need to remember experience and national automotive advice. Almost all technicians advise diagnosing the element once every 80 thousand km. Of course, if during this period there are no signs of a unit malfunction.
Symptoms of a problem
This:
- clutch slip;
- shutdown is not performed;
- vibration is felt when turned on;
- the pedal does not return to the reverse position.
Note! Before deciding to replace the clutch disc, it is necessary to accurately diagnose its condition.
The corresponding check can be done either at a service center or on your own in a garage using detailed instructions. If the second replacement method is implied, the actions will need to be performed carefully and efficiently.
Causes of slipping and ways to eliminate them
Not in all cases you will necessarily have to buy a completely new clutch. Once, out of inexperience, I changed a unit, which turned out to be almost completely serviceable. In reality, it was just necessary to change one inexpensive component. But sometimes you have to learn from your mistakes.
From everything I have learned, I realized that determining the cause of clutch slipping plays a key role here. Your further actions directly depend on this.
- The clutches are worn out. Your actions depend on the degree of wear. When the distance between the working elements used is less than 0.2 mm, you can simply adjust the free play of the pedal. In case of severe wear, the driven disk and linings are replaced;
- Oil appeared on the linings. Oil on the friction linings may appear due to certain problems in the flywheel drainage or an excessive amount of lubricant in the box. The oil should be removed and the surface dried. Kerosene works well. After cleaning, go through with fine sandpaper;
- Damage to the integrity of the rubber components of the hydraulic drive. When they swell, the clutch very often begins to slip. Here you will have to remove both cylinders (worker and main), wash them with alcohol, replace the rubber elements and clean the expansion holes. Don't forget to bleed the clutch and the brakes themselves;
- Loss of elasticity of pressure springs. This problem occurs on old cars that have been in use for over 10 years. Elasticity decreases gradually, which causes the required level of pressure on the driven disk to drop. As a result, the clutch slips. The check is carried out by removing the clutch disc. If elasticity has decreased, they will have to be replaced.
Clutch does not work: possible reasons
The main problem is wear of the clutch disc, since this is the most loaded element.
However, clutch malfunctions can be associated not only with the disc and arise for a variety of reasons.
Clutch drive
In the clutch drive device with a cable, it is the cable that often stretches and breaks. The clutch hydraulic drive may become airy or leaking, and the slave cylinder may also fail.
On robotic boxes with electric drive, the actuator electric motor becomes unusable, and malfunctions in the operation of the control unit also occur.
Clutch mechanism
As for the clutch itself, the release bearing and pressure plate often fail, and the pressure plate diaphragm spring becomes deformed or breaks.
We also recommend reading the article on how to change the clutch fork without removing the gearbox. From this article you will learn about available methods for installing the clutch fork without removing the gearbox.
The driven disc also suffers, since the friction linings are worn out or damaged, oil gets on them, the disc hub gets stuck on the splines of the gearbox shaft, and the damper springs wear out and break.
Why the car clutch slips: main reasons and repairs
The clutch in a car is the most important unit, since this mechanism transmits torque from the engine to the transmission, in fact, connecting these units together. The clutch also allows you to separate the engine and gearbox at the moment of gear shifting.
Taking into account the fact that this unit is subject to heavy loads, often during operation the driver is faced with the fact that the clutch slips. The malfunction usually occurs due to wear of the friction linings of the clutch disc, as well as wear or breakage of other elements.
As a rule, clutch slipping manifests itself in such a way that the car does not accelerate, traction deteriorates and a loss of power is observed, vibrations appear, etc. Next, we will look at how to determine that the clutch is slipping, the causes of slipping and repair methods.
SneiKSlik › Blog › How to understand that it’s time to change the clutch
In mechanics, a clutch is a mechanism whose operating principle is based on the action of sliding friction. Often the term "clutch" is used to refer to one of the components of a vehicle's transmission that is used to connect the engine flywheel to the transmission. Depressing the clutch pedal temporarily disconnects the power transmission from the engine.
The clutch mechanism is necessary so that you can start smoothly from a standstill, without jerking. The speed of the car begins to increase only at a certain minimum number of engine revolutions. The clutch is also used when it is necessary to match the vehicle speed and the engine crankshaft speed, that is, it ensures smooth transmission of torque from the engine to the gearbox and, if necessary, at some point completely disconnects the manual transmission gears from the engine transmission mechanism.
There are several different types of clutch. Often these are one, two or more friction discs, pressed tightly against one another or against the flywheel using springs.
When the driver presses the pedal, the clutch discs are disconnected, and an air gap appears between them; the clutch is disengaged at this moment, and torque is not transferred from the engine to the gearbox. If the pedal is released, the clamping springs return the discs to their initial position, and they again come into close contact; the torque from one drive disc is transmitted through the action of friction to the driven disc.
Clutch slipping: what to look for
So, as mentioned above, the clutch allows you to transmit and interrupt the supply of torque from the engine flywheel to the gearbox input shaft. However, the resource of this mechanism is limited.
The first signs of clutch wear and slipping are a loss of vehicle dynamics. For example, the driver engages a gear when starting from a standstill, releases the clutch and presses on the gas.
If you accelerate too much, you can feel the characteristic unpleasant smell of a burnt clutch in the cabin (similar to when a driver burns the clutch while the wheels are slipping in mud, snow or ice). The only difference is that the clutch is scorched, but the wheels do not slip.
In the future, a worn clutch leads to the fact that in addition to loss of traction, difficulties arise with shifting gears. At the same time, during clutch operation (both when engaging and disengaging), extraneous sounds may appear (crunching, knocking, grinding, squeaking, etc.).
One way or another, the appearance of such signs (both individually and in combination) indicates problems with this node. The smell of a burning clutch, especially if the driver does not quickly release the pedal, indicates that the clutch discs are “slipping” instead of reliably engaging and transmitting torque to the gearbox.
In such a situation, at a minimum, replacement of the clutch driven disc will be required. At the same time, it is important to promptly diagnose the clutch, as there is a risk of damaging the engine flywheel or gearbox input shaft.
Clutch: disc, basket and release
So, in general terms, the design of a traditional mechanical clutch (single-plate) assumes the presence of the following elements:
- clutch pedal inside the car;
- drive mechanism, which may be hydraulic, pneumatic or mechanical;
- clutch fork;
- release bearing;
- driven disk;
- clutch basket;
The moment the driver presses the pedal, the force is transmitted to the clutch fork. Then, through the release bearing, the force is transmitted to the petals of the basket. Next, the basket presses the driven clutch disc away from the flywheel, thereby opening the gearbox and internal combustion engine, that is, the power flow is interrupted. Let us add that in robotic gearboxes it is not the driver who is responsible for pressing the clutch, but the actuators, since there is no clutch pedal.
Let's move on
If we look at the clutch basket in more detail, it is important to understand that it is this element that makes it possible to connect and disconnect the disc and the flywheel. In other words, the basket engages/disengages the clutch
In this case, damage, wear, deformation and other defects of the basket lead to the fact that the entire mechanism begins to work incorrectly.
Article on the topic: Engine speed cut-off: what is it for?
The clutch basket itself is a single piece that includes the pressure plate, diaphragm spring and housing. The basket is also in close contact with a number of parts. The basket casing is bolted to the flywheel. The return spring, which is mounted in the basket, interacts with the release bearing.
The pressure plate allows you to connect the driven disc and the flywheel. When the clutch is disengaged, the pressure plate presses on the driven plate, which is in contact with the flywheel.
If the clutch is disengaged, there is no pressure plate pressure on the driven disc, that is, the disc rotates separately from the flywheel. By the way, the pressure plate is connected to the basket casing using special leaf springs (tangential springs). When the clutch is disengaged, the springs act as return springs.
Also in the basket design you should highlight a diaphragm spring. This spring creates the necessary force to effectively connect the disc and flywheel. It turns out that the transmission of torque from the internal combustion engine to the gearbox will depend on the clamping force.
The diaphragm spring looks like petals and is attached to the edge of the casing. In the inner part of the casing, the spring is attached to the casing with bolts or support rings (depending on the design features). The clutch release bearing presses against the ends of the paddles on the outside of the clutch basket. This pressing allows you to ensure that the spring inside the basket does not press on the pressure disk itself.
Article on the topic: Flushing hydraulic compensators without removing the engine
Also within the framework of this article, it should be noted that clutch baskets can be of different types. Among the main types, one can distinguish the exhaust and push type. However, the principle of their operation is somewhat different.
As a rule, of all types of release baskets, it is the basket with the push principle that is used most often in the clutch device. The main feature is that when the clutch is engaged, the petals of the basket move closer to the flywheel. The design is simple, proven and reliable.
If the machine has a basket with a traction operating principle, then the petals move from the flywheel. The second type of baskets is smaller in size and is often installed in order to save space in the engine compartment.
There are also baskets, the design of which differs from the standard one. Typically, such baskets are needed for powerful forced internal combustion engines and have a reinforced diaphragm, which makes it possible to significantly increase the clamping force (up to 1.5 times or more compared to the standard).
For this, the basket and individual elements are made of durable alloys, and the geometry of the spring itself becomes more complex. Typically this type of basket is found on supercars, sports cars and non-production vehicles.
If the clutch slips: how to check and what the driver should do
To check whether the clutch is slipping or not (especially if the symptoms are only primary or the problem is floating), it is not necessary to immediately go to a service station. You can check the clutch for slipping on your own:
- First you need to start the engine, then you need to tighten the handbrake (parking brake) well;
- Now you should turn on first speed and start moving away slowly (the handbrake does not lower);
- when starting, you need to lightly press the gas pedal and smoothly release the clutch, performing actions in parallel;
- after the clutch “grabs”, the engine should normally stall (this indicates that the clutch is not slipping, the load on the internal combustion engine increases, but the engine does not “pull” and stalls).
- If this does not happen, that is, the engine continues to run, then signs of clutch slipping are obvious.
Let's say the driver discovers that the clutch is slipping. Again, not in all cases you need to immediately contact specialists or change the clutch kit, that is, carry out complex and expensive repairs. Not always, but often you can solve the problem of clutch slipping with your own hands in an ordinary garage. The main thing is to know why the clutch is slipping.
- Most often, slipping occurs as a result of the friction linings wearing out (wearing off). Everything will depend on the degree of wear and tear.
If the distance between the working surfaces is at around 0.2 millimeters, you can adjust the free play of the clutch pedal. If the wear turns out to be large, then the driven disk with linings needs to be changed.
- Another reason why the clutch slips is oil on the friction linings. If oil gets on the linings, the linings must be cleaned and dried.
To clean, simply wipe with kerosene, after which the linings are also wiped with a dry, clean rag and lightly sanded with fine-grain sandpaper.
- The next cause of clutch slipping on the list may be hydraulic drive elements and parts made of rubber. In fact, such parts swell, as a result of which the hydraulic drive is unable to operate normally and the clutch slips.
The final stage is replacing the brake fluid, after which the brake system is pumped and the clutch is additionally pumped.
- Experts also highlight the loss of elasticity of compression springs. If the car is used and the age of the vehicle exceeds the ten-year mark, the overall wear of the clutch may be insignificant, even in this case the elasticity of the pressure springs deteriorates.
As a result, the pressure of these springs turns out to be weaker than necessary, the springs do not put full pressure on the driven disc, and the clutch slips. To check the springs, you need to remove the clutch disc. As a rule, if it comes to removing the clutch, and the mileage of the car is more than 70 thousand km, it is separately recommended to immediately change the mechanism completely, that is, install a new set.
Moreover, this is done regardless of the state of the already installed clutch. The reason is that the average clutch life is about 80-100 thousand km, that is, leaving the old clutch or changing individual parts (only the release bearing, driven disc or basket) is simply impractical.
The fact is that after 10-20 thousand km. it will be necessary to remove the clutch again due to the inevitable wear of those elements that were not replaced earlier. Considering that the clutch replacement procedure itself is labor-intensive, it is better to immediately replace the entire mechanism as a set.
How to deal with a tight clutch pedal
Most drivers do not want to put up with this state of affairs and try in every possible way to improve the performance of the clutch.
Among the most common recipes for dealing with a tight pedal are the following:
- Replacement of the basket and all clutch assembly elements with a known quality product. The best option would not even be a new Valeo, but the assembly recommended by the manufacturer. Often, for many car enthusiasts, the situation became a revelation when, after replacing cool branded baskets with conventional Russian options, the clutch pedal turned from extremely tight to an option with a comfortable level of effort;
- It is considered cheaper and more accessible to pack all rubbing surfaces with lubricant. To gain access to blind lubrication points, there is a diagram indicating drilling locations, where transmission oil is subsequently pumped with a syringe or oiler;
- Replacing the cable with a stronger model, regularly filling brake fluid or engine oil with a syringe under the casing. If spindle or similar oil still gives a good effect, pouring brake fluid or WD-40 is pointless and useless. They only contribute to the destruction of the outer sheath of the cable.
Important! All of the above methods, to one degree or another, can effectively deal with a tight clutch pedal. The first recipe will be the best and most effective. In addition to cable drives, hydraulic systems also suffer from similar problems.
But, unlike the cable, due to the high force on the clutch release fork, the cylinder cuffs are destroyed first, and brake fluid leaks
In addition to cable drives, hydraulic systems also suffer from similar problems. But, unlike the cable, due to the high force on the clutch release fork, the cylinder cuffs are destroyed first, and brake fluid leaks.
The video shows what a stiff clutch pedal is and how to fix the problem:
- How to adjust clutch pedal free play
- Replacing the coolant pump
- Operating principle of the contact ignition system
- Device for a contactless car ignition system
When pressing the clutch pedal we definitely have to apply some kind of force, but there are situations when it is pressed too hard.
In such a situation, we are dealing with the problem of a tight clutch pedal. There may be several reasons for such a breakdown. The most common of them are sticking of the lever or cable, wear of the fork bearing. So, in order to restore the correct functioning of the pedal, you first of all have to deal with the so-called symptom of the breakdown (or what led to the breakdown). So, if the clutch pedal becomes stiff as a result of wear on the fork bearing, then when you press the pedal, you will hear some rumbling, which indicates that the release bearing has already served its purpose and needs to be replaced with a new one.
The mechanisms developed in our time are designed to cover long distances (more than 1,300 thousand km), if the driver regularly diagnoses them and the necessary replacement of worn parts.
But if the system is treated carelessly, then it will serve you no more than 50 thousand km. In large trucks, problems can also arise with new, not yet ground-in elements.
You also need to check if everything is in order with the release bearing; it may be damaged and this may cause problems with pressing the pedal. It is also worth checking the diaphragm spring, which is located on the pressure plate, for damage. If you are well versed in your car, then you can perform this type of check yourself, but for a better result, you should still contact the service station workers.
There may also be a problem of incomplete shutdown of the mechanism. In such a situation, the driver of the car should feel a certain grinding noise when engaging the gear. This is due to the fact that the disc is not able to come off the pressure plate normally. To fix this breakdown, it is also better to turn to professionals.
A situation where the device is not completely turned off is possible due to a number of reasons, such as:
- the cable has been adjusted incorrectly;
- the driven disk becomes jammed;
- the system unit is not assembled properly;
- disk warping occurs;
- deterioration of the shutdown mechanism.
A stiff clutch pedal is considered a fairly common breakdown of the system as a whole. In such a situation, it is pressed very hard. To differentiate the source of the breakdown, you should contact a specialist, especially if the breakdown occurred after the installation of a new kit.
How to check disk thickness
So:
- Using a measuring gauge, you can accurately determine the thickness of the disc. There is no need to remove the clutch to complete the process. You can't do without a lift with a gauge and instructions for use. This gauge is connected to the active clutch cylinder.
- It is not recommended to abuse traditional methods, since their use can increase wear. You need to start the engine with 4th-5th gear active, press the gas with the clutch. If the engine does not stall, this indicates wear on the driven disk.
Replacing the disk yourself
It should be noted right away that on front-wheel drive cars, replacing a disc is a little more difficult than on classic models. In addition, different brands and models of cars have their own nuances for removing and installing the clutch. First you need to read the instructions and recommendations for changing the clutch yourself. It would be a good idea to consult with experts.
Note! In the process of replacing a damaged part, there is no need to skimp; it is better to immediately replace all elements that cause suspicion. As for rubber products, they need to be changed unconditionally. According to experts, the release bearing also needs to be replaced.
When replacing the clutch on a VAZ 2109, there is no need to completely dismantle the gearbox, drain the oil, remove it completely, etc.
How to change a clutch in a garage
So:
- First you need to hang the front of the car on tripods.
- Next, the front wheels are removed.
- It is detached from the gearbox and removed from the bracket.
- You also need to disconnect the speedometer cable from the gearbox.
- After this, the mounting bolts that secure the ball joints and steering knuckles are unscrewed.
- Next, you need to loosen the rear left trailing arm fixation.
- Carefully remove the mounting bolts of the extension bracket on the left, after which the lever rotates 90 degrees.
- A “mass” can be attached to the gearbox, which is also dismantled.
- The lower flywheel protective cover is unscrewed.
- The engine mount on the left side is turned away.
- The engine mount located at the rear is removed from the body, this also applies to the gearbox drive clamp.
- The drive is removed from the gearbox.
- The gearbox mount is unscrewed from the engine.
- The gearbox is removed from the engine and will hang on the drives.
- The clutch is unscrewed, in some cases it is the clutch basket.
- The release bearing is replaced.
- Using a convenient mandrel designed for centering such disks, we replace the driven disk.
- Assembly is carried out in the reverse order of disassembly.
In practice, everything will not happen as quickly as in theory, especially for beginners. Today, thanks to videos and photos, you can replace almost any part with your own hands, and you don’t have to contact a car service center. Detailed instructions will help you easily dismantle and properly secure the clutch disc. It is important not only to strictly follow the recommendations, but also to the quality of the purchased spare part. Among the wide variety, you must first of all understand that the price must correspond to the quality.