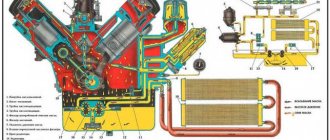
For normal operation, hydraulic compensators require an uninterrupted supply of oil, which is supplied under pressure. The supply occurs through a special channel with a check ball valve, which prevents oil from draining from the channel after the engine is stopped. In addition, there are channels located on the lower plane of the bearing housing, which supply oil to the camshaft journals.
Hydraulic compensator design:
To enlarge the image click on the image!
The disadvantage of hydraulic compensators is their excessive sensitivity to the quality and purity of the oil. The presence of mechanical inclusions and other foreign elements in the oil leads to rapid failure of the hydraulic compensator plunger pair. This malfunction is most often accompanied by increased noise emission and intense wear of the camshaft cams.
Let's summarize. Hydraulic lifters are knocking - reasons
- Hydraulic lifters can knock due to problems with oil, including the fault of a faulty oil system, as well as as a result of a mechanical malfunction of the hydraulic compensator itself.
- If hydraulic compensators knock when cold , but the knock disappears when hot, then, according to experienced mechanics, there is nothing wrong with this; this phenomenon occurs in most car owners.
- If the hydraulic compensators knock when hot , that is, after the engine has warmed up to operating temperature, this is a clear sign of a malfunction that must be eliminated immediately.
Hydraulic compensators for VAZ 2114 8 valves: installation, adjustment, replacement, additional lubrication
After installing the HA, the car engine begins to run much quieter, since the valves stop knocking. In addition, there is no need to periodically adjust the valves during vehicle maintenance.
Hydraulic compensators VAZ 2114
The only condition that should be immediately noted is the need to fill in high-quality oil, since dirty oil can cause clogging of the hydraulic compensator mechanism. A constant supply of oil (under pressure) ensures uninterrupted operation of the hydraulic system.
This supply is carried out through a special channel that has a check ball valve, which, after turning off the engine, prevents oil from draining from the channel. In addition, on the lower plane of the bearing housings there are channels through which oil is supplied to the camshaft journals.
The presence of mechanical inclusions and other impurities in the oil leads to rapid wear of the plunger pair of the hydraulic valve and, as a consequence, severe wear of the camshaft cams.
Operation of the hydraulic compensator
The installed hydraulic compensators on the VAZ 2114 (8 valves) may, over time, begin to produce a characteristic knocking sound, which will indicate the presence of certain problems.
Among the main reasons for the appearance of such a sound, experts identify:
- Problems with the quality and purity of the oil or the use of the wrong brand, which does not have the appropriate viscosity, temperature characteristics, etc.
- Malfunctions of the oil system, namely:
- the presence of plaque and dirt in the oil channels;
- airing the system (the presence of air increases the oil compression rate);
- oil filter clogged;
- malfunction of the oil pump.
- Mechanical failures of the main body:
- presence of exhaustion in the plunger pair;
- problems with the correct operation of the oil supply valve (options: situational sticking or failure);
- defects on the surface of the hydraulic compensator.
It is important to note at what engine temperature a knock appears in the hydraulic tappets. If this happens when it is cold, and when it warms up sufficiently, the knocking disappears, then this situation is quite acceptable. If, on a fully warmed-up engine, the picture does not change and the sound does not disappear, then this indicates existing malfunctions that require elimination.
Hydraulic compensator kit
Problems in the oil system that can cause knocking in hydraulic compensators:
- Clogged oil channels (dirt in the channels, plaque);
- Airy oil system (air present in the system increases the compression ratio of the oil). Air in the oil can occur as a result of high or low oil levels;
- Clogged oil filter;
- The wrong oil has been filled in (does not match: viscosity, fluidity, quality, temperature characteristics);
- There may be interruptions in the operation of the oil pump;
- Overheating of the engine, as a result of which the oil burned, losing its viscous and lubricating properties.
How to check hydraulic compensators - video
The knocking noise of the engine does not go away or appears after warming up
Much more dangerous is the knocking of hydraulic compensators, which appears as it warms up or only intensifies as the power unit reaches operating temperatures. In this case, the hydraulic compensators constantly knock at idle speed of a warm engine; the knock may be present under load, etc. The list of causes for this malfunction is wider than knocking noises on a cold internal combustion engine.
First, you need to make sure that it is the hydraulic compensators that are knocking when hot, since there are many reasons for knocking in the engine. To do this, you need to know how to identify a knocking hydraulic compensator. It is also important to be able to determine which hydraulic compensator is knocking, which will help more accurately localize the fault.
Note that the knocking of compensators has a characteristic sound. The pitch is high, the knock is loud, reminiscent of a metal ball striking another metal part, and is localized under the valve cover. Can be easily heard with a stethoscope. If the main valve knocks constantly, then it may soon become completely jammed or other breakdowns will occur. In such a situation, the engine needs repair; it is possible to replace the hydraulic compensators. In some cases, the seat of the hydraulic compensator is also broken. After the motor heats up, thermal expansion of the parts occurs, and the hydraulic fluid begins to “dangle” at the installation site and knock. A more accurate determination of a knocking main engine is possible after partially disassembling the motor and removing the cover.
As already mentioned, on a cold engine, contamination of the channels can cause knocking, after which the extraneous sound disappears as it warms up. In the case of a hot internal combustion engine, exactly the opposite happens, when, parallel to the increase in temperature, the deposits in the channel soften and shift, completely blocking the supply of lubricant to the main fluid chamber. In this case, it is also recommended to flush the hydraulic compensators and lubrication system, change the engine oil, or clean the engine after disassembling it.
The oil filter should be checked, which may be the cause of insufficient pressure in the lubrication system and, as a result, knocking of the engine when hot. If there is insufficient pressure in the hydraulic compensators, an air lock is created. The oil level in the engine also deserves special attention, which should not be lower or higher than normal (oil overflow into the engine). It should be noted that when cold, at low speeds and problems with the oil level, the HA may not knock. After the engine warms up, the amount of air in the oil increases and a knocking sound from the hydraulic compensators appears, as the oil and air become a compressible mixture. It is also advisable to check the operation of the oil pump and measure the pressure in the lubrication system if problems with the hydraulic fluid appear on a hot engine.
How to solve the problem of knocking hydraulic compensators?
- You can try changing the oil if it has been changed for a long time or looks bad (dark brown color, bad smell, etc.). As a rule, after replacement, the knocking of hydraulic compensators disappears. If the knocking does not disappear, you will have to take out the main battery and see what’s wrong.
- If adding oil did not lead to anything, and washing the engine did not give any result, you can try another way to solve the problem of knocking hydraulic valves. The principle is to remove the main hydraulic valves, perform a visual inspection of them, in case of insignificant wear and normal condition, you can disassemble and wash the hydraulic compensators. When removing, I recommend remembering or writing down where which hydraulic compensator was installed. After washing, everything is assembled and the operation of the engine is checked; if washing the hydraulic compensators does not lead to anything, the only way out is to replace the hydraulic compensators .
Hydraulic compensators for VAZ 2114: how to get rid of knocking
Experts recommend two ways to solve the problem:
- Changing the oil and oil filter is carried out when the oil has already used up some of its service life and has a bad odor and color (dark brown).
- Removing hydraulic tappets - used if adding oil does not solve the problem. The removed HAs need to be inspected and, if the wear is insignificant, then disassembled and washed separately.
During the process of removing hydraulic compensators, you should remember/write down where and which hydraulic compensator was installed previously. This way, during the reverse operation (reinstallation) there will be no problems.
Hydraulic compensator device
To flush hydraulic compensators, the following steps should be performed sequentially:
- Open. When performing an autopsy, you should knock the core out of the housing. To do this, forcefully strike the glass with the open part of the glass (through the fabric) on a hard surface. After opening, two separate elements are obtained - the core and the body itself. The core consists of: a piston, a cylinder and a spring. The piston is easily removed from the cylinder.
You should not knock on hard but thin materials (for example, plywood), as this complicates the task by “absorbing” shock impulses.
- There is a hydraulic valve inside the piston, which must be cleaned. They open it by picking out its cover with a (thin) screwdriver.
- All these parts must be thoroughly washed (especially the valve hole and the well at the bottom of the housing).
- Now you need to assemble the piston: the ball is placed on the spring, everything is covered with a lid, which is pushed into the mount with a thin screwdriver. A piston spring is installed on top and covered with a cylinder.
- Now the glass is turned over and filled with oil.
- Using a thin rod, we press on the valve ball, pushing the piston into the glass. This operation should be repeated several times, until air stops escaping from under the valve.
You need to make sure that the piston is not pressed. To do this, press on the cylinder with your finger.
- Pour a little oil into the hydraulic pusher body, and then insert the core assembled earlier into it (push with your hands with sufficient force).
Installation of hydraulic compensators
After washing and installing the hydraulic valve in place, check the results: if washing does not help eliminate the knocking, then the only solution to the problem is to replace the hydraulic compensators.
Please note that after replacement, some noise may occur when the motor is first started. This will last until the hydraulic compensators are completely pumped.
Didn't find the information you are looking for? on our forum.
Prevention is cheaper than repair!
In order to extend the life of hydraulic lifters, it is necessary to regularly change the engine oil and oil filter. Do not buy fakes or cheaper analogues just because they cost less; during operation, such savings, as they say, can “come out sideways.” Even a fake filled once can permanently “ruin” your car’s engine or at least reduce its service life.
Select the vehicle modification to search for hydraulic compensators
Engine: volume – 1.4 l., power – 90 hp, type – petrol, model – VAZ-11194. Drive: front. Year of manufacture: 2008-present time
Engine: volume – 1.4 liters, power – 88 hp, type – petrol, model – VAZ-11194. Drive: front. Year of manufacture: 2008-present time
Engine: volume – 1.6 liters, power – 82 hp, type – petrol, model – VAZ-21114. Drive: front. Year of manufacture: 2004-present time
Engine: volume – 1.6 liters, power – 84 hp, type – petrol, model – VAZ1110. Drive: front. Year of manufacture: 2010-present time
Engine: volume – 1.6 liters, power – 90 hp, type – petrol. Drive: front. Year of manufacture: 2004-present time
In the next step, for an expanded selection, you can enter the vehicle's Vin code to go to illustrated catalogs, where you can find the layout of parts down to the bolt and duplicates that are not in the catalog of analogues.
How to change hydraulic compensators?
If after changing the oil the problem does not go away (after 5 minutes of working with the new product, the knocking should go away) and significant damage is found, it is necessary to install new spare parts. In some cases, washing with a special liquid without removal or manually (dismantling is required) helps.
For the procedure you need:
- Screwdriver Set;
- spanners;
- the details themselves;
- camshaft seals;
- cylinder head cover gasket;
- sealant;
- magnet (useful for removing parts).
The replacement algorithm is given in this article below.
How much do hydraulic compensators cost? This question cannot be answered unequivocally, because the final price tag depends on many factors. One of the most significant is the make and type of car. For domestically produced cars (for example, VAZ 2112), replacement may be limited to two thousand rubles. Working with belt-type foreign cars costs about 30% more. Working with the “chain” option costs seven thousand rubles (with SUVs the prices are of the same order).
The price tag for new parts depends on many conditions. On the Internet you can easily find online stores and forums to search for a suitable unit. You can consult before purchasing in the chat on the aggregator Uremont.com (professionals of partner car services answer questions).
How to change hydraulic compensators?
They are successively de-energized, disassembled using a magnet, new spare parts are lubricated and installed back.
The sequence of actions using the example of replacing Priora hydraulic compensators is given below:
- disconnect the terminals from the battery;
- remove the engine casing;
- disconnect the explosive wires from the spark plugs and coil;
- de-energize the injectors;
- disconnect the ventilation pipe;
- dismantle the oil dipstick and fastening;
- in the area of connection between the cylinder block and the exhaust manifold, unscrew the nuts and bolts;
- loosen the bolts of the gas distributor belt casings (upper and lower);
- remove the camshaft belt by loosening the tension roller;
- unscrew and remove the camshaft gears (it is important not to lose the keys in the process);
- remove the gas distributor cover from the rear;
- remove the cylinder head cover;
- remove the bearing housing;
- remove the camshafts, having previously marked the position;
- by pressing your finger, check the operation of the compensators (if there is no resistance, replacement is required);
- remove faulty elements with a magnet;
- new spare parts, lubricated with oil, are installed.
If it is not clear how to replace hydraulic lifters on your own (you don’t have the time or skills), contact a technical center.
Is it possible to install hydraulic compensators on an 8 valve engine?
- To the beginning of the forum
- Forum Rules
- Old design
- FAQ
- Search
- Users
_________________ you can have whatever beliefs you want as long as they do not disagree with ours.
I will leave the bliss of paradise for the poor; the poor in spirit must have a king and a god.
ILNYR
How did you plan to supply oil to them?
So how will shafts designed for a pusher with clearance work on guides without clearance? I think it's going to happen..
_________________ you can have whatever beliefs you want as long as they do not disagree with ours.
I will leave the bliss of paradise for the poor; the poor in spirit must have a king and a god.
The phase will become wider, the rise will be greater. By the way, the idea is that the ride will be more fun, especially at the top. The main thing is that the spreader does not get damaged from backlash-free work, for which it is not intended at all. But I also think that it will live.
I don’t remember exactly the gaps between the well and the guide, but what is measured in hundred square meters is accurate. The gap there is minimal, and this will be your biggest problem IMHO. There are also requirements for the cleanliness of the surface treatment... In short, the idea is interesting, but very difficult to implement.
So I’m asking what the gap is, in theory the tolerance under the hydraulics should be smaller, like it will be lubricated there with pressure, so that the oil doesn’t squeeze out a lot. And at 8V there should be more so that the oil at least gets there. There are still questions about winter, how will all this crap behave in cold oil? And why, in a letter to a VAZ car, someone was told that it was necessary to re-design the head for compensators, but he asked it there like why you can’t remake it for hydraulics like on a classic, they probably understood him about the rocker.
PS I’m just that kind of person, I don’t want to be like everyone else. There are a million people driving front-wheel drive, so let them drive, but I want mine to be the best!
There is an oil channel next to it, you just need to drill it correctly to get into this channel
Source
Valves knock during acceleration - how to deal with this?
- Valves knock during acceleration - how to deal with this?
- Causes of valve knocking
- What to do if valves knock during acceleration?
- How to fix valve knocking during acceleration?
It’s great when the car is new, the engine runs quietly and you can’t hear it when accelerating with the pedal to the floor. But time moves inexorably forward and a moment comes when you notice that the former silence has simply disappeared, and under the open hood you see a bubbling monster, which previously emitted a pleasant singing, now offends your ears with something completely absurd.
- Causes of valve knocking
- What to do if valves knock during acceleration?
- How to fix valve knocking during acceleration?
Noisy operation of a car engine is often associated with problems in the gas distribution mechanism: increased gaps and knocking always appear, like an uninvited pair of inseparable guests. The very first thing that might come to mind is to adjust the clearances in the valve drive. Often this helps, but sometimes it may seem that the knocking has only gotten worse, because one or even several valves continue to knock. And at first glance it is not clear why this is so? The clearances have been adjusted and the camshaft looks quite good. And the thought immediately comes to mind that the problem is not on the surface, but is hidden somewhere inside, but where? It’s about to be sorted out, but my hands still don’t get around to it, and the knocking gets louder and louder!
Causes of valve knocking
The main reason influencing the appearance of knocking is the increasing gap between the camshaft cams and the levers. If the gap between these parts increases, the cam will knock on the rocker, resulting in extraneous sounds, like a metallic clatter. The larger the gap becomes, the more wear and damage will increase, which will ultimately lead to complete failure of the entire internal combustion engine. The gap between these parts is set by manufacturers depending on the make of the car, but is the same size for certain models.
A reduced gap is also bad, because in this case the valve becomes clamped, and after a certain time it will stop closing completely. If you continue to drive with the valves not tightly closed or clamped, then you cannot avoid engine overheating, as well as a decrease in compression.
The possibility of complete failure of one or even several cylinders cannot be ruled out.
To prevent such a scenario from becoming a reality, it is necessary to adjust the valves in a timely manner. Approximately every 10-15 thousand kilometers. In addition to improperly adjusted valves, knocking in the engine can also be caused by detonation of the power unit. Engine detonation is similar in nature to a micro-explosion, during which a fiery wave hits the cylinder walls and other elements of the piston group.
As a result of such impacts, valve knocking can occur. Remember also that sometimes a metallic clatter is not necessarily associated with damage to the valves. The main signs characterizing the occurrence of detonation are: increased vibration, black smoke from the exhaust pipe or another unusual color of smoke, decreased power and overheating of the power unit. If valve knocking occurs in a warm engine, the reason is mainly hidden in high speeds and low oil pressure, which occurs due to increased clearances and damage to parts. Next, we will talk about how to understand the cause of valve knocking in your particular case:
1. Check not only the engine intake valve, but also the exhaust valve. First of all, ensure normal oil pressure and check all its basic characteristics.
2. If valve knocking occurs “when cold,” then this is the first sign that the pusher has worn out. If the tappets are dirty or leaking, they can cause insufficient oil flow to the valves. That is why during overheating a characteristic metallic knock can be heard.
If the oil pressure is normal, check the clearances; it is quite possible that valve adjustment will be required. The gaps are adjusted using special feeler gauges. They are installed in the gap between the rod and the rocker arm or the pusher and the cam, it all depends on the location of the camshaft. If everything you do is unsuccessful, then you should seek help from qualified specialists, otherwise you will ruin your power unit.
Prevention of breakdowns
As it became clear, checking, repairing and installing hydraulic compensators are simple procedures, and adjustment of the unit is not required at all. Despite this, absolutely no motorist wants to allow car breakdowns, so it would be advisable to talk about preventing malfunctions and compensators.
The main thing in prevention is to remove cheap and low-quality lubricants from the “diet” of the car engine. How can you identify a good oil manufacturer, you ask? The answer is very simple - according to reviews from motorists. According to research from our resource, the best oils are from the following companies:
- Liqui Moly is a German organization famous for its huge number of lubricants for cars. Let us immediately note that there is no need to buy additives for hydraulic compensators from Liqui Moly (such products from any manufacturer only clog the engine cavities), but motor oil is a must;
- Motul is a British manufacturer of the same lubricants for cars. Perhaps the most important competitor in its field of activity for Liqui Moly, what is best for you - decide for yourself. We can definitely say that both manufacturers are worthy of attention and respect;
- Castrol (Castrol) - as well as Motul, a manufacturer from Foggy Albion. In terms of status and reviews, this company is, of course, inferior to those discussed above. However, compared to other representatives of the market, it is Castrol that has the best reviews about its products, so our resource can only recommend its oils for purchase.
In addition to selecting lubricant, it is advisable to remove hydraulic compensators at least once every 80-100,000 kilometers for cleaning and quality check. Otherwise, these timing elements do not require maintenance and, if used correctly, will cover the full service life of any car’s engine.
In general, there is nothing more to say on today's topic. We hope that the material presented above was useful to you and provided answers to the questions you were interested in. Good luck on the roads and in car maintenance!
If you have any questions, leave them in the comments below the article. We or our visitors will be happy to answer them
How to correctly diagnose valve knocking in an engine
Inexperienced motorists have difficulty identifying the source of the noise by ear.
That is, there are a lot of components and mechanisms in the car, and only an experienced driver can determine which of them is the cause of the unusual sound. However, the knocking of valves still has its own characteristic features - namely, a ringing sound, as if metal is knocking on metal. The source in this case is located near the timing mechanism. Moreover, changing engine speed does not affect the sound in any way. But even if it is possible to determine that the knocking comes specifically from the valves, then only very experienced car owners can accurately identify the cause of the malfunction. However, there is a certain diagnostic algorithm with which you can more accurately determine the cause of the problems that have arisen. You need to do the following:
- Open the hood and unscrew the engine oil filler cap.
- Listen carefully to the running engine. An increase in the volume of the sound without the cap is a clear indication that the valves are the source of the problem.
- A stethoscope, which should be placed closer to the suspected faulty part, will help determine the source of the noise even more accurately.
How to check hydraulic compensators?
Check parts for wear and contamination.
If you detect the characteristic knock described above, contact a car service center for diagnostic work. On your own, if you have certain skills, you can check the degree of wear of the ball valve, hydraulic pushers, and a pair of plungers. If the service life has expired, you need to install new parts.
Don't forget to inspect the pusher "inside". If it is contaminated with grease, the hydraulics can be washed and coated with a layer of new high-quality oil. The operation of the springs is checked by pressing a finger through a soft rag on each small element. If all is well, the parts are returned to their place.