Eliminate camshaft knock (axial runout) with your own hands
Many people already know that the VAZ 2111 injection engines have the following disease: “Axial runout of the camshaft.” This disease does not progress and does not cause damage to other timing components, but it manifests itself in the form of an unpleasant camshaft knock. It just so happened that the developers of the 2111 engine missed this point.
Where carburetor engines used to have a fuel pump and distributor, injection engines have a regular plug into which the camshaft rests. The camshaft axial play set by the manufacturer should not exceed 0.15-0.20mm. Over time, as the camshaft pastel wears out, the axial play increases, and a distinct knock begins to be heard from under the valve cover. Of course, you can continue to drive with this knock and not worry, but not every car enthusiast will be pleased.
Camshaft damage
Camshafts are considered wear-resistant engine parts and typically last the entire life of the vehicle. This is why camshaft damage is a rare occurrence. Especially when it comes to old cars. In more modern engines, the camshaft has a greater risk of damage, but nevertheless, defects in this part are also rare.
True, if a modern car is used in normal mode. If you often drive at high engine speeds (“screwing” the car), then the camshaft in a modern engine will fail much earlier than in an old car. But again, this does not apply to all cars. It all depends on what camshaft the automaker uses and what timing design is in the engine.
A little about the camshaft
Fortunately for many, the camshaft is not one of the components that are positioned as capricious, often and quickly failing. The resource largely depends on the quality of the part and operating conditions.
The camshaft has a life limit. Uninterrupted operation can last from 50 to 150 thousand kilometers. These are fairly average indicators, since each situation is still individual. Active work is already underway to remove this element from the engine design. Moreover, experts say that in the future the camshaft may completely cease to be part of the engine. It will be replaced by electromagnetic actuators.
It is difficult to say how effective and realistic this will be in the near future. Plus, some skeptics doubt the correctness of the transition from a mechanical part to a computer-controlled actuator.
Engine assembly design
Replacing the camshaft on a VAZ 2109 is extremely rarely required due to the fact that it is one of the strongest parts in the design. The camshaft itself is a solid metal product with a set of cams, so it is not afraid of most loads.
However, under certain conditions the shaft may suffer mechanical damage or deformation. Most often these are collisions and accidents, less often - overloads. In such cases, it will simply need to be replaced with a new one along with other damaged parts.
Along with the camshaft, two more parts are often checked: the oil seal and the gear. The oil seal is a rubber-metal cuff that protects the shaft from foreign liquids, moisture and dirt. If it is damaged or deformed, this will lead to incorrect operation of the camshaft.
The gear is connected via a chain transmission to the crankshaft, which ensures the mutual operation of the 2 mechanisms. It may also become damaged, causing the engine to malfunction.
Sometimes the bed in which the part is placed becomes a problem. If liquid, dirt, dust, or oil gets there, this can affect the performance of the camshaft.
How to determine valve knocking in a VAZ 2114 engine
The power plant of the VAZ 2114 is an internal combustion engine consisting of two main parts - the cylinder block and the cylinder head, which are a protective housing for the main working units. The camshaft, valves, piston group, cylinders and crankshaft rotate the flywheel, which in turn drives the vehicle's transmission. And all this, when the engine is running, rotates and moves in a forward-return rhythm with enormous frequency, under conditions of vibration and high temperature. The stress on every metal part of this automobile unit is incredibly high, so it is not surprising that parts wear out and sometimes make themselves known through abnormal operation or loud sounds.
Why is the engine knocking?
Among car enthusiasts who are quite far from professional knowledge of the design and physical essence of the operation of automobile units, but due to long-term driving practice, who consider themselves to be great experts on automobile “guts,” there is an opinion that if a knock appears in the engine, then it is the valves that are knocking. In reality, everything is not so simple. One very experienced automobile mechanic told a case that can serve as a clear illustration of incompetence and disrespect for the opinion of a professional.
Adjustment of valves
“A car arrived at the workshop, the owner asked to adjust the valves. When we started the car for diagnostics, a characteristic knocking sound of the connecting rod in the crankshaft was revealed. This is a clear and unambiguous signal for immediate overhaul; there was no question of any valve adjustment; with such an engine it was impossible to even move away. The owner said that all friends and acquaintances and simply knowledgeable people unanimously affirm that this is the knocking of the valves. I was offended by the car mechanics and got into the car, but I couldn’t get far; a connecting rod broke and pierced the cylinder block. The engine had to be changed."
Instructive story. And she reminds you to read your car's owner's manual and listen to the opinions of professionals. In fact, knocking in the VAZ 2114 engine can be caused by several reasons:
- The crankshaft main bearings are knocking. This is usually a metallic thud. Most often it appears at idle when giving gas.
- The connecting rod bearings are knocking. The sound is sharper than when knocking on the main wheels, and also appears at idle. You can determine the location of the sound source by turning off the spark plugs.
- The pistons knock muffledly and quietly. Often simply replacing the pistons or rings will get rid of this sound.
- Valve knocking, inlet or outlet. The frequency of this sound is less than that from the crankshaft and the sound is slightly different, more sonorous. The causes of valve knocking are varied:
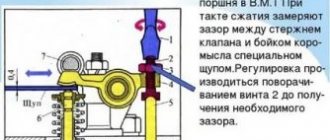
— the gaps in the valve mechanisms have increased;
— the valve spring is broken;
— a large gap has formed between the valve and the guide sleeve;
- The cams on the camshaft are worn out.
What to do if valves are knocking
Extraneous noise in the engine appears most often on cars that the owners do not take care of, and if they do, it is from time to time, and the breaks in these cases are usually very long. An illustration of this can be an analysis of the reasons why valves knock.
The most common reason is increased clearance between the arms and the camshaft cams. And this reason can be eliminated simply by adjusting the valves. And, again, an elementary thing that every driver should know - the valves must be adjusted every fifteen thousand kilometers. This is a mandatory rule.
Careless drivers have had cases when they remembered the valves after 70 thousand miles, and then the car mechanic could not do anything with them, they could not be adjusted.
Car owners often worry about valve knocking on a cold engine. That is, when the engine is cold, there is a clear knocking sound, but as the engine warms up, these sounds disappear. Experienced automobile mechanics explain this by saying that on a car with a fairly high mileage, parts wear out, and this especially happens with parts of the power plant. Small gaps appear between them, which generally do not affect the operation of the systems for the worse, but manifest themselves in a cold state. It is because of these resulting gaps that such annoying sounds appear for drivers. When heated, the metal expands, the gaps disappear, and along with this the unpleasant sound disappears.
However, this does not mean that one should be indifferent to extraneous noise in the engine when it is cold, especially if the owner monitors the timeliness of all adjustments. After all, on a cold engine, at idle speed, the main or connecting rod bearings of the crankshaft can make noise, and this is already very serious. You should definitely contact a specialist for diagnosis.
Every driver heard the valves knocking when hot. Especially with a sharp increase in speed. The most common reason for this is low-quality gasoline. But there may be other reasons, for example, a knock sensor has failed. Or the oil pressure has dropped.
In addition to increasing the clearance, the causes of noise produced by valves can be:
- wear of the camshaft cams - in this case it is necessary to replace the entire camshaft;
- valve spring failure - if this is detected, a new spring must be installed;
- the guide bushing may need to be adjusted or replaced;
- Valve knocking can be caused by completely different reasons, for example, a poorly tensioned timing belt or poor flow of oil through the camshaft to the fingers due to clogged channels in the valve.
It is very difficult for an inexperienced person to determine by ear that the valves on a VAZ 2114 are knocking. Nevertheless, experts recommend some folk remedies, recalling that the camshaft rotates twice as slow as the crankshaft and, accordingly, the sound of the valves should not be frequent. For better sound perception, they suggest placing an empty metal mug to your ear and placing it on the hood. In this case, the sound becomes clear and easy to hear.
When operating a car, the driver must remember that extraneous noise in the engine can be avoided by constantly monitoring the condition of all systems, promptly replacing spare parts that have been used under warranty, and making all necessary adjustments.
nadomkrat.ru
Camshaft function
The camshaft in a four-stroke engine controls the opening and closing of the valves in the cylinder head and thus controls the gas exchange in the engine. To do this, there are cams on the camshaft (usually their number corresponds to the number of valves in the engine), which convert the rotational movement of the camshaft into valve stroke movement. If the camshaft cam pushes the valve down (via a pushrod or rocker arm), an inlet or outlet in the engine's cylinder head opens.
The valve then closes. It is pushed back by the valve spring.
The camshaft is driven by the crankshaft. The camshaft rotates at half the crankshaft speed. The crankshaft and camshaft are usually connected via a timing belt or timing chain (in older cars the connection was via a gear reducer).
Linear motors (flat power units) can have a maximum of two camshafts. V- and W-engines can rotate up to four camshafts in the cylinder heads.
Remove the camshaft cover.
To begin with, using a powerful old-fashioned key of 17, we set the camshaft gear to the mark. This is necessary so that the “pin” that is on the camshaft does not interfere with removing the cover.
Then, using a 10mm wrench, unscrew the cover (2 nuts and one bolt with a rubber ring).
Only 2 are visible in the photo, the third from the back:
Carefully remove the cover.
Here you can see how this pin passes through the slot in the cover:
This is the same pin:
OHC and DOHC – what does it mean?
Volkswagen Beetle camshaft: The cam (left) transmits movement through a long plunger to the valve rocker arm
Modern engines only use overhead camshafts (OHC = overhead camshaft). Often modern engines have two camshafts. One serves for the intake valves, the second is responsible for the exhaust valves (DOHC = double overhead camshaft).
In older engines, engines were typically designed with a single camshaft. Also in them, the valves in the cylinder head were controlled by plungers. This motor design results in a lot of mechanical friction, making these types of power units less efficient and less powerful.
Below in the graphic animation you can see how two camshafts work in a modern four-cylinder engine (DOHC principle).
Removing the camshaft
Camshaft VAZ 2110 8 valves
This way you can determine the value of the noise, check its location, and draw up an accurate action plan for replacing equipment. It is necessary to repair those parts that are damaged. Since the camshaft play must be eliminated, this part must first be removed from the car engine. To carry out this work, you must follow the rules that will help in case of breakdown:
- The rear timing belt cover is removed.
- The cylinder head cover suffers the same fate.
- Since the work is very specific, the oil pressure sensor may be damaged. It needs to be disconnected or at least the wires disconnected.
- Using a socket wrench with the number “8” it is necessary to unscrew the 20 bolts that secure the camshaft bearing housing.
Note: work on unscrewing bolts must be carried out using a specific system. Each part must be unscrewed gradually. Do not completely unscrew one bolt and then the other.
- The camshaft bearing housing is removed.
- Specific plugs are installed on the technological holes. There are two of them here. They must be removed from their locations.
- The exhaust camshaft is dismantled.
- The camshaft for the intake valves is disconnected.
- The seals must be removed from each shaft.
- After removing the oil seals, you must carefully examine each journal and cam of the mechanism. It should not have cracks, scratches or other visible damage.
Assembly and installation is a specific matter
Camshaft VAZ 2110 16 valves
It is slightly unusual to install this mechanism in the previous position. While most car parts and mechanisms can be installed in the reverse order of disassembly, camshafts require a special approach to assembly:
- The first step is to completely lubricate all parts of the camshaft with machine oil.
- The camshafts, after the lubrication process, are carefully placed in the cylinder head.
Note: An important step is to place each shaft in its proper position. Each part has its own marking. They need to be placed in their places. To do this, just read the numbers on the shafts:
- 1006014 – exhaust camshaft.
- 1006015 – intake camshaft.
Replacing the oil seal
Replacing the VAZ 2109 camshaft oil seal is carried out after access to the gear is gained. Having removed the gear, you will see that a little further on the shaft there is a cuff, this is the oil seal. The oil seal can be pulled out by prying it with a slotted screwdriver.
Lubricate the new camshaft oil seal on the VAZ to make it easier to install it in its seat. We put the cuff on the installed camshaft and hammer it into place using a mandrel.
Take a test drive and look at the instruments. If the oil sensor shows that the fluid level is normal, then all the work has been done correctly.
The described tips can help guide owners of “nines” and their modifications (for example, VAZ 21093) in cases where knocking occurs from the engine. Some points are also described in the car manual. If you have no experience at all in disassembling car components, it is better to visit a car repair shop.
We make a washer.
For the material for the washer, I took a piece of galvanized sheet about 0.5mm thick and secured it to a piece of MDF panel with four self-tapping screws (so it wouldn’t fidget).
I drew 2 circles with a marker (inner diameter 25mm, outer 35mm) and hollowed out the inner diameter with a chisel.
I cut out the outer diameter with metal scissors, and I ended up with a curve like this, with the washer blank all covered in burrs:
I processed the inner diameter of the washer with a round file, and sharpened the sharp corners on the outer one:
Install the washer.
We put the washer on the camshaft (it should fit freely, if not, then adjust the dimensions).
I entered freely:
Put the cover back and tighten it.
Attention! Be sure to check if the camshaft is jammed.
To do this, take a key set to 17 and try to rotate the camshaft.
It should turn with the same force as before installing the washer.
If the camshaft becomes very difficult to turn, or is completely jammed, then remove the cover again, take out the washer and grind it to thickness:
Shutdown.
After the washer is adjusted, the cap is tightened and the camshaft rotates freely - start the engine and enjoy the silence of its operation!
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
( 1 rating, average 5 out of 5 )
Camshaft pitting - The appearance of depressions on the surface
The phenomenon of pitting occurs primarily in high-speed motorcycle engines. But sometimes this phenomenon is also observed in passenger car engines. Pitting translated from English means “pit”. Thus, camshaft pitting means that indentations begin to appear on its surface.
Damaged camshaft surfaces in these areas cause less than optimal lubrication, leading to premature wear of the camshaft and its components. In addition, flaking metal is a serious problem in the engine oil circuit, as these metal particles cause clogging of the engine and can cause engine damage.
Causes of sounds when hot
Knocking in the engine when “hot” can occur for all of the above reasons.
In any case, it is important to determine the nature of the extraneous noise, the approximate place where it is coming from, and then take action. Almost always, in road conditions it will not be possible to eliminate the malfunction; the car will need to be delivered to the repair site to accurately determine the cause
Almost always, in road conditions, it will not be possible to eliminate the malfunction; the car will need to be delivered to the repair site to accurately determine the cause.
But preliminary diagnostics will tell you which way the car will have to be delivered.
If there is a knocking sound at the top, you can drive the car under your own power, but check the oil level before doing so.
A sharp sound from the bottom of the engine will indicate a problem with the crank mechanism, which is why the car must be delivered by a tow truck.
Valve timing systems
Phase adjustment: The camshaft is adjusted by a special system. This allows you to adjust the opening and closing times of the valves.
Modern gasoline engines often have a camshaft adjustment system ( Variable Valve Timing , VVT) . This system allows us to achieve compliance with modern environmental standards adopted by the European Union and a number of other countries. Thanks to this system, the camshaft timing is adapted to the current driving situation. For example, when the car is stopped and the engine is idling, the camshaft control system adjusts the engine's valve timing system to operate more efficiently to reduce fuel consumption and, accordingly, reduce the level of harmful substances released through the vehicle's exhaust system.
On powerful engines, the valve timing system is usually common on both the intake and exhaust sides. The camshaft adjustment mainly consists of a hydraulic adjustment system and a control valve. Thanks to this valve timing system. For example, different engine operating modes require different valve timing values. So, when the engine is idling, the phases should be short. At high speeds the phases should be wider.