A short summary
General structure of manual gearboxes on VAZ
The device of a 5-speed manual transmission Lada Priora, Kalina. General diagram of the gearbox.
New cable transmissions installed on car models with 16-valve engines have become much quieter even when braking the engine. They have reinforced synchronizers (which, however, cannot be called problem-free). They are capable, according to the passport data, of withstanding a torque of 160 Nm. In practice, they work properly even under much higher loads when the car engine is boosted.
You should not think that we are deliberately praising VAZ manual gearboxes; we only noted their well-deserved positive qualities. But, of course, they encounter problems during operation. Let us note the most common malfunctions, their causes and solutions.
Table of the most common malfunctions of VAZ manual gearboxes, as well as their elimination and repair
The most successful manual transmission on Ladas is considered to be the one installed on the Lada Vesta
A new level in the design of VAZ manual gearboxes for front-wheel drive cars has become the VAZ 21807 gearbox, this is a five-speed manual transmission installed on the Lada Vesta. It is considered one of the most successful manual transmissions, as it is reinforced and capable of holding high torque. Problems such as gearbox noise, rapid wear of bearings and gears, oil leaks from seals are not typical for this box, but knocking at idle sometimes occurs, although not on all copies, which is an amazing phenomenon.
It should also be noted that the VAZ 21809 manual transmission is installed on the Lada X-ray. It is as durable as the VAZ 21807, but in the operational practice of owners, oil seal leaks and difficulty in engaging reverse gear are often encountered.
Lada X-ray with manual transmission, which is also quite successful
Shift diagrams for a VAZ manual transmission, gear shifting for a 4- and 5-speed manual transmission
Gear shift diagram for a 4-speed manual transmission used on VAZ 2101, 2102, 2103, 2104, 2105, 2106, 2107, Niva 2121
Small Summary
So, what can we ultimately say about manual transmissions on VAZs and Ladas? Probably the fact that they started out in the 70s with phenomenally high quality, then the 5-speed manual transmissions suffered a little in quality, which, of course, slightly upset the owners. But it’s also impossible not to note how VAZ figured out (well, almost figured out) many of the problems of its manual transmissions. Just look at the box of the Lada Vesta and its Sport version, with a boosted 140 horsepower engine, how wonderfully the box works with a torque of as much as 180 Nm!
All VAZ boxes are incredibly repairable; they can be restored from any condition, and this can be done for relatively little money. Another big question is the quality of spare parts for gearboxes on our market. Now we are talking not only about cheap analogues, but, unfortunately, also about factory spare parts.
Thank you for your attention to this article, we tried to collect a lot of useful information about the operation and repair of VAZ manual transmissions, problems and ways to solve them, as well as other information about VAZ gearboxes. We hope you found it interesting and found something useful and useful for yourself!
Source
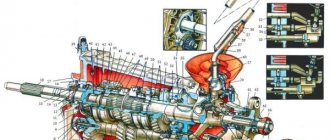
Gearbox design
Cars of the LADA SAMARA-2 family are equipped with a five-speed gearbox combined with a differential and final drive.
The five-speed gearbox is designed on the basis of the four-speed gearbox previously installed on cars of the Sputnik family (Fig. 1).
The main difference between the five-speed gearbox is the additionally introduced fifth gear, the gears of which are installed in an enlarged rear cover. Otherwise, the designs of the boxes are identical, so the features of the general device are considered using the example of a four-speed box; The features of the five-stage are shown separately in Fig. 2.
Four-speed gearbox: 1 – gearbox housing; 2 – filler and control hole plug; 3 – drain plug; 4 – adjusting ring; 5 – left front wheel drive; 6 – driven gear of the 1st gear of the secondary shaft; 7 – synchronizer clutch for 1st and 2nd gears with reverse gear; 8 – driven gear of the second gear of the secondary shaft; 9 – retaining ring; 10 – persistent half ring; 11 – driven gear of the third gear of the secondary shaft; 12 – synchronizer clutch hub for 3rd and 4th gears; 13 – driven gear of the 4th gear of the secondary shaft; 14 – needle bearing of the secondary shaft gears; 15 – thrust washer of the 4th gear gear; 16 – ball bearing of the secondary shaft; 17 – rear cover of the gearbox; 18 – ball bearing of the input shaft; 19 – breather; 20 – synchronizer blocking ring; 21 – sliding clutch for synchronizer of 3rd and 4th gears; 22 – retainer block; 23 – input shaft; 24 – locking ball; 25 – fork of the sliding clutch for the synchronizer of 3rd and 4th gears; 26 – roller bearing of the input shaft; 27 – clutch release fork lever; 28 – clutch release fork bushing; 29 – clutch housing; 30 – clutch release fork; 31 – clutch release bearing; 32 – roller bearing of the secondary shaft; 33 – secondary shaft; 34 – driven gear of the main gear; 35 – tapered roller bearing of the differential; 36 – differential box; 37 – satellite; 38 – locking ring of the side gear; 39 – semi-axial gear; 40 – speedometer drive gear; 41 – drive of the right front wheel; 42 – speedometer drive; 43 – satellite axis; 44 – retaining ring of the satellite axis; 45 – protective cover of the gear shift drive hinge
Gearbox VAZ 2107 design description, device
The VAZ 2107 gearbox is designed to change the magnitude and direction of the torque transmitted from the engine to the drive wheels of the car. VAZ 2107 cars have a gearbox with five forward gears and one reverse gear. The gearbox of the VAZ 2107 consists of a steel front cover (installed in the clutch housing) and a cast aluminum alloy housing and rear cover. The connections between the gearbox housing and the rear cover and the clutch housing are sealed with gaskets. In front of the gearbox there is a clutch housing mounted on seven studs, which is attached to the gearbox with nuts and spring washers. At the rear, the gearbox is mounted on two studs to the power unit support. Front cover
VAZ 2107 gearbox is pressed into the clutch housing.
The input shaft oil seal is installed in the cavity of the gearbox cover. There is a hole in the end wall of the gearbox cover to drain oil flowing from the gearbox housing in case of damage or wear of the oil seal. The gearbox housing
contains: primary and secondary shafts with gears and synchronizers, an intermediate shaft and gear shift drive parts.
There is a filler hole in the left side wall of the gearbox housing, closed with a plug with a conical thread. From below, the gearbox housing is closed with a cover stamped from steel and secured to ten studs with nuts. The lid has a drain hole, closed with a plug with a conical thread and a permanent magnet. The cavity of the gearbox housing communicates with the atmosphere through a hole on top in the front wall of the crankcase and a breather mounted on the clutch housing. There is a hole in the rear wall of the crankcase to allow oil to pass into the cavity of the rear cover. The volume of oil poured into the gearbox on VAZ 2107 cars is 1.6 liters. The gear shift drive
is mechanical.
The gear shift drive consists of a gear shift lever, a gear selection mechanism, three rods with forks, clamps and a locking device. A handle is attached to the top of the lever on a thread. The shift lever shaft is connected to its lower part through elastic damper bushings, which absorb vibration and provide smooth gear shifting. The gear shift lever housing assembly with the gear selection mechanism and the ball joint housing is secured on top of the rear cover studs with three nuts. The spherical part of the gear shift lever is movably installed in the ball joint housing. The lower part of the lever fits into the groove of one of the rods. The gear shift lever, turning in the ball joint, acts on the rod, moving it and the fork fixedly fixed to the rod. The shift fork rod for the 1st and 2nd gears and the shift fork rod for the 3rd and 4th gears are movably installed in the holes in the front and rear walls of the crankcase. The fork rod for selecting V gear and reverse gear is installed in a hole made in the boss of the rear wall of the crankcase. The rods are held in the neutral or on positions by spring-loaded ball retainers, for which there are three slots in each rod. The clamps with springs are located in bushings pressed into the holes of the gearbox housing and closed with a common cover. To prevent the simultaneous engagement of several gears (moving the rods), the drive has a locking device consisting of three locks located in the holes of the rod of the 3rd and 4th gears and the rear wall of the crankcase. The rear cover
of the VAZ 2107 gearbox is installed on six studs and secured with nuts and spring washers.
The speedometer drive is mounted on the left side of the rear transmission cover, the driven gear of which meshes with the drive helical gear mounted on the splines of the rear journal of the secondary shaft. The input shaft
of the gearbox is manufactured integrally with a constant mesh helical gear.
The spur ring of the 4th gear synchronizer is pressed onto the rear belt of the shaft and then welded. On the crown of the 4th gear there is a spring-loaded synchronizer blocking ring secured with a locking ring. The teeth of the inner ring of the synchronization ring engage with the teeth of the 4th gear synchronizer. The front part of the shaft has splines on which the clutch driven disc is located. The shaft rotates in two ball bearings; the front one is located at the end of the crankshaft, and the rear one is located in the front wall of the gearbox housing. An adjusting ring in the groove of the rear bearing outer race prevents axial movement of the shaft. The secondary shaft, located on the same axis as the primary shaft, rotates in three bearings. The front roller bearing is located in the bore of the end of the input shaft, the intermediate ball bearing is located in the rear wall of the crankcase. The rear roller bearing is installed in the socket of the rear cover of the gearbox and is sealed from the outside with an oil seal. A flange of an elastic coupling (propeller shaft) is attached to the rear splined end of the secondary shaft. Transmission gears with synchronizers are movably mounted on the secondary shaft. They are made in the form of a single block, consisting of a helical transmission gear and a synchronizer ring gear, with blocking rings attached to them. The gears of the gears are in constant mesh with the corresponding gears of the intermediate shaft and the gear block of the 5th gear and reverse gear. The intermediate shaft
of the gearbox is made in the form of a block of four gears and rotates in bearings installed in the front and rear walls of the VAZ 2107 gearbox housing. The intermediate shaft drive gear is in constant mesh with the input shaft gear.
The block of gears of the 5th gear and reverse gear is bolted to the rear end of the intermediate shaft. The other end of the block rests on the bearing in the wall of the rear cover of the gearbox housing. A reverse gear is installed on the splines of the secondary shaft
between the rear wall of the crankcase and the 5th gear.
The reverse gears are connected through an intermediate gear mounted on the axle, with the possibility of axial movement. The axle is secured with a nut on the rear wall of the crankcase. The annular groove of the gear includes a gear shift fork, when moved, the intermediate gear meshes with the reverse gears. The synchronization clutch hubs are fixedly mounted on the secondary shaft. The protrusions on the inner surface of the hubs of the synchronization clutches of the 1st - 2nd and 3rd - 4th gears fit into three grooves on the shaft, and the hub of the 5th gear clutch is put on the splined part of the shaft. A gear synchronization clutch is placed on the outer gear rim of the hub with its inner gear rim, forming an engagement with the clutch. The gearshift forks
fit into the ring grooves on the outside of the synchronization clutches. When the rod moves, the fork displaces the coupling. The clutch, acting on the synchronizer blocking ring, moves it. Under the influence of friction forces arising between the clutch and the synchronization locking ring, the rotation speed of the gear and hub is equalized. The teeth on the gear synchronization clutch mesh with the teeth on the gear timing ring. The moment is transmitted from the gear through the clutch and hub to the secondary shaft.
Gearbox VAZ 2107: what is it
What is a gearbox in a car design? The abbreviation “KPP” stands for “gearbox”. This is the name of the unit, which is designed to change the frequency of torque.
It is curious that the first gearboxes were invented not for cars, but for machine tools to change the speed of rotation of the equipment.
The purpose of the gearbox is to perform the function of converting the amount of torque that comes from the engine and transferring this energy to the transmission. This is the only way to change speeds in increasing increments.
Gearbox configurations
Below are the most successful gearbox configurations depending on the engine. For a more detailed selection, you can use a calculator on the Internet.
- The most suitable gearbox configuration for a civilian naturally aspirated engine: 18 row gearbox + main pair 3.9.
- The most suitable gearbox for a sports naturally aspirated engine: 7th row gearbox + main pair 4.3.
- The most suitable gearbox configuration for a turbo civilian engine: row 104 + main pair 3.5.
The differential is two-satellite, the tension is adjusted by different thicknesses of the adjusting ring.
Sports cars often use a differential lock.
A differential lock is a mechanism that locks the differential so that both wheels rotate evenly. Initially, locking was used on SUVs to ensure that the front and rear axles rotated evenly.
In our case, screw locks are especially popular, because they are easily installed in the gearbox, increase cross-country ability on wet roads, and provide an advantage during acceleration due to uniform constant rotation of the wheels.
Main technical characteristics of the VAZ 2107 box
The “seven” gearbox works in conjunction with the clutch. The VAZ 2107 is equipped with a single-plate dry clutch, which has only one (central) pressure spring. This is quite enough for convenient control of vehicle speeds.
The gearbox is only mechanical, three-code, five-speed. The VAZ 2107 has synchronizers for each forward gear.
The device weighs quite a lot - 26.9 kg without oil.
Video: operating principle of a VAZ manual transmission
What kind of gearbox can be put on the “seven”
The VAZ 2107 will willingly work with both a four-speed and a five-speed gearbox, so only the driver decides which model to choose.
If we talk about domestic “VAZ” gearboxes, then initially the “seven” was equipped with a four-speed unit, so you can always buy and install this particular unit. The main advantage of such a box is its increased performance - the driver drives 200 - 300 thousand kilometers without ever investing in repairing the device. In addition, the four-speed gearbox is more suitable for low-power 1.3-liter engines or for drivers who often transport heavy loads by car, since the gearbox is initially designed for high traction.
Five-speed gearboxes allow you to reach higher speeds. Younger drivers like this, since at the start and when overtaking you can squeeze maximum power out of the car. However, over time, such boxes began to be made from low-quality materials, so switching is not always clear.
Foreign gearboxes can also be installed on the VAZ 2107. Boxes from Fiat are most suitable, since it was this car that became the prototype of domestic models. Some car enthusiasts install boxes from older versions of BMW, but the installation procedure can take a lot of time, since the car’s original design does not provide for non-standard units.
VAZ 2107 gearbox malfunctions
The VAZ 2107 is rightfully considered a “workhorse”. But this model cannot last forever. Sooner or later, the car begins to act up. If any faults appear in the box, the owner needs to immediately take the necessary measures, since these defects directly affect the ability to operate the car.
Why don't the gears turn on or turn on randomly?
This is every driver's nightmare when the car does not obey his orders or performs actions in a random order. To prevent this from happening in reality, you should find out the source of these problems at the very first problems with turning on gears:
Why does it knock out a gear when it is turned on?
There are often cases when the driver cannot engage one or another gear. Accordingly, the motor experiences increased loads, which negatively affects driving. You need to figure out what exactly the problem is and take action:
You can hear noise and crunching from the box
It is very unpleasant when loud sounds and heartbreaking crunches are heard while driving. It looks like the car is about to break in two. However, the reason for this is a malfunction in the gearbox:
Why is oil leaking from the box?
Full operation of the gearbox on a VAZ 2107 is impossible without good lubrication. About 1.6 liters of oil is poured into the box, which is usually completely changed only during a major overhaul. The oil itself cannot leak out anywhere, since the body is sealed as much as possible.
However, if a puddle accumulates under the car while parked, and the internal parts under the hood are heavily oiled, it is necessary to urgently look for the cause of the leak:
Gear ratios (row)
These are the gears of each gear, which also have their own size.
They characterize the speed of the car in one gear or another. The standard VAZ uses the following numbers:
| Gearbox ratios: | |
| I | 3,636 |
| II | 1,95 |
| III | 1,357 |
| IV | 0,941 |
| V | 0,784 |
| reverse | 3,53 |
Above are the specifications with standard parameters.
The standard series on 2114 is far from ideal. The first gear is too short, the second is too long. Due to this, there is a sharp drop in dynamics when switching from first to second. Not only is there a failure, but when switching sharply, the second speed synchronizer slowly dies.
Therefore, there are sports series where the gap between 1st and 2nd is removed, and not only: sports series are selected according to the type of engine. It could just be a good city engine, or a sports engine, or tailored for 402-meter racing. There are also “turbo” gears designed for a turbo engine.
Repair of VAZ 2107 gearbox
Repairing the box yourself is a task that only an experienced car owner, who is accustomed to servicing and repairing the car on his own, can handle.
Removing the box
The box can be repaired only after it is removed from the car, so you will have to drive the “seven” onto an overpass or inspection hole and get to work.
For work, it is better to prepare in advance:
The procedure for removing the gearbox is carried out according to the following regulations:
Video: instructions for dismantling work
How to disassemble a gearbox
The removed box must be installed on a level and clean place. To disassemble the device for parts, you will need the following tools:
The procedure for disassembling the box is one of the most difficult procedures when working on a VAZ 2107. The design of the gearbox has many small parts; inattention to any of them can lead to disastrous results. Therefore, it is recommended to disassemble the box yourself and replace worn-out elements only if you have extensive practical experience in this area.
Video: instructions for disassembling the mechanical box
We change bearings
All three shafts in the gearbox rotate thanks to the bearings. However, experienced drivers know that it is the bearings that cause the main heap of problems, since during operation sooner or later they begin to leak, knock or wear out their service life.
Video: how to visually determine wear of bearings on shafts
The VAZ 2107 gearbox contains bearings of different sizes, but none of them provide for a repair and restoration procedure. Therefore, during repairs it will be necessary to knock the shafts out of the bearings and install new hinge devices.
Video: instructions for replacing the bearings of the primary and secondary shafts
The role of oil seals in the operation of the gearbox, how to replace it
A seal is a dense rubber gasket, the main task of which is to seal the joints between different parts in the box. Accordingly, if the oil seal is severely worn, the sealing of the device is broken, and oil leaks may occur.
To prevent loss of lubricant and restore the tightness of the device, it will be necessary to change the oil seal. To do this, you will need simple tools that the driver always has at hand:
Input shaft oil seal
This product is made of CSP and NBR composite, which ensures the longest possible service life. In working condition, the oil seal is completely immersed in transmission oil, due to which its elasticity is maintained for a long time.
The input shaft seal of the VAZ 2107 gearbox is located in the clutch housing. Therefore, to replace it, you will need to dismantle the casing. And to do this, you need to drive the car onto an overpass or inspection hole.
Replacement of the input shaft gasket is carried out as follows:
Photo gallery: replacement procedure
Secondary shaft oil seal
The product is also made from high quality composite materials. In terms of technical characteristics, the secondary shaft oil seal is not much different from the primary shaft oil seal.
However, it weighs a little more - 0.028 kg and has larger dimensions - 55x55x10 mm.
The location of the oil seal explains some of the difficulties in removing and replacing it:
Photo gallery: work procedure
How to replace gears and synchronizers
As mentioned above, independent work with gearboxes, and even more so with shafts and their elements, is fraught with many errors. Therefore, it is better to entrust the replacement of gears and synchronizers to specialists at auto repair shops.
Experienced VAZ 2107 owners can watch a special video that explains all the nuances of changing these parts.
Video: a unique video on removing gear from fifth gear
Gearbox oil for VAZ 2107
A special transmission oil is poured into the VAZ gearbox. It is necessary to lubricate gears, as it extends their service life.
The choice of gear oil depends on many parameters: the driver’s finances, manufacturer’s recommendations and the preferences of the owner of a particular brand. You can undoubtedly fill the gearbox of the “seven” with gear oil from the following companies:
The volume of liquid poured is usually 1.5 - 1.6 liters. Filling is done through a special hole in the left side of the box body.
How to check the oil level in the gearbox
If you suspect an oil leak, you need to check the level in the box. To do this, you will have to put the VAZ 2107 on the inspection hole and start working:
How to change the oil in a VAZ 2107 gearbox
To change the oil in your car, you will need to prepare in advance:
It is recommended to replace it immediately after driving the car, as hot oil will drain out of the box faster. The replacement procedure is relevant every 50 - 60 thousand kilometers.
Operating procedure
To prevent the work from causing trouble, it is best to immediately cover the space around the box with rags. Next, follow the following diagram:
Photo gallery: do-it-yourself oil change in a box
How the gearbox works on a VAZ 2107
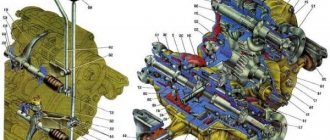
The five-speed gearbox (gearbox) is one of the main units of the VAZ 2107 car. Its design and assembly diagram are distinguished by a high level of complexity, which is why maintenance and repairs are usually trusted to professionals.
However, for the general development and understanding of the physics of the processes occurring in your car, it does not hurt to study the structure of the box. Let's start with the purpose of the gearbox: the five-speed gearbox of the VAZ 2107, according to its functional purpose, is designed to perform the function of converting the amount of torque received from the engine, with its subsequent transmission to the transmission. The gearbox used in the VAZ 2107 has only six speeds - five forward and one rear. The gear shift pattern is similar to the standard four-speed, to which a fifth speed has been added - to the left all the way and forward. Switching between them is carried out by moving the gearshift knob. The layout of the main structural elements is as follows:
The VAZ 2107 box consists of body 3, closed on three sides with special covers. A shift knob 5 is installed in the upper part.
The main components and mechanisms of the gearbox are mounted in housing 3. Below is a diagram of the location of gearbox parts.
These include:
- Primary shaft 4 with drive gears and synchronizers installed on it;
- Secondary shaft 10 with gears;
- Intermediate shaft 1, assembled.
Since the diagram of this mechanism is quite complex, we will dwell on it in more detail.
- Primary shaft
- Secondary shaft
- Intermediate shaft
Primary shaft
It is integral with the gear and rotates on bearing 3, installed in the gearbox housing and sealed with an oil seal.
Secondary shaft
It is a continuation of the primary in space. It contains gears of the first (23), second (24) and third (25) gears, which move freely and in certain positions engage with the corresponding gears of the intermediate shaft 1. All gears have different diameters, which ensures a change in the amount of transmitted torque .
The secondary shaft rotates on bearings 9, 11 and 12. The first of them is roller, installed in the primary shaft, the rest are pressed into the crankcase and the rear cover, respectively.
Intermediate shaft
Designed to transmit a certain amount of torque from primary to secondary. Rotates on bearings 2, 22 and 19. The gears are integral with the shaft. In the same block, gears of the fifth speed 18 and rear 20 are installed. The latter is installed on a separate shaft 21, connected to the secondary one on splines.
To fill the VAZ 2107 gearbox with oil, there is a special hole 11 on the left side of the housing, which is closed with a plug. The bottom of the case is closed with a steel lid, which is secured with ten nuts. All connections between the lids and the box body are sealed with special gaskets that prevent oil leakage. The bearings of the primary, secondary and intermediate shafts are sealed with seals that prevent oil from leaking out of the transmission pan.
The filling volume of oil for the VAZ 2107 gearbox is approximately 1.6 liters. Some car enthusiasts prefer to fill oil through the top, at the place where the handle is inserted into the gearbox. This method is much simpler than the standard one, since the handle is located in the interior and access to it is not difficult, which cannot be said about the filler hole.
Gear shifting is controlled by a set of forks that are driven by a handle. The structure and main details of the gear shift mechanism are clearly illustrated by the following diagram.
Here numbers 1, 2 and 16 indicate the gear shift forks: third and fourth, first and second, rear and fifth, respectively. Numbers 5, 7 and 9 indicate the rods of the corresponding forks, which are driven by handle 8, located in the interior of the VAZ 2107 car.
The operating diagram of the switching mechanism is as follows: when handle 8 changes its position, its hinge engages with a recess on one of the rods, the other end of which is rigidly coupled to the fork with a bolt 3. The fork, in turn, fits into a groove on the corresponding front gear (16 , 23, 24, 25) or intermediate (20) reverse. Thus, handle 8 ensures the movement of the fork and a certain gear of the secondary shaft is engaged with the corresponding intermediate gear. In this case, the torque transmission chain is closed, the secondary shaft begins to rotate at a speed corresponding to the gear ratio of the gears currently engaged. When the reverse gear is engaged, unlike the others, the handle is “recessed” down when moving.
As you can see, the design of the VAZ 2107 gearbox is quite complex, so it is not recommended to repair it without having the appropriate skills. It is better to entrust this matter to specialists.
Backstage at the checkpoint - what is it for?
In the language of service station specialists, the rocker is called “gearbox control drive rod.” The shift lever itself is mistakenly taken for the backstage when the backstage is a multi-component element:
As part of the gearbox, the link plays the role of a connecting link between the lever and the driveshaft. Being a mechanical device, it can wear out, so the driver will immediately begin to notice problems in driving the vehicle. Current breakdowns are usually associated with the exhaustion of the life of the link, and less often with a drop in the oil level in the gearbox.
Self-adjustment of the scenes
If you have the first problems with shifting gears, you can first try adjusting the rocker. It is quite possible that some connections have become loose and a little intervention can fix this problem:
Usually these actions are quite enough to return the car to its original controllability.
Backstage
On modern cars, including the new Grants, Kalinas, and Priors, gearboxes with cable drive gears are installed, making gear shifting easy and precise. In Samara: 2114 -2113-2115 the gear drive is carried out not by a cable, but by a rocker.
Backstage
The slide is a development from the 80s, so the gears may not engage the first time, may not engage well, etc.
On sports tuned cars they often install a “short-throw” rocker.
The essence of the short-throw shifter is that the path of the gearshift lever from neutral to gear becomes shorter than it was before. Simply put: the gears are easier to engage, the lever travel is shorter, which gives a significant advantage when shifting.