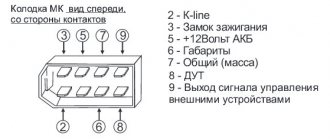
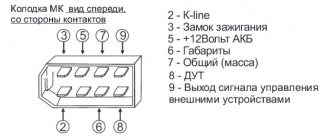
The generator overcharges the battery, where to look for the reasons
Many car owners are faced with a situation where, after starting the engine, the on-board computer or one of the devices begins to show that the battery is being recharged.
The consequences of this situation are very different and depend on how much the voltage in the on-board network exceeds the nominal one.
Slightly increased parameters will only negatively affect the battery (boiling of the electrolyte followed by its evaporation), but if the voltage coming from the generator greatly exceeds the norm, then electrical consumers may fail.
In any case, overcharging is a phenomenon that must be eliminated, otherwise it will not have the best effect on the service life of the battery and electrical appliances.
What does engine speed affect?
Having figured out what voltage the car generator produces, it remains to determine the current, which directly depends on the armature speed. It should be taken into account that any generator has a current limitation and cannot produce more, no matter how much rotor speed increases. Thus, according to current indicators, 3 modes can be distinguished - minimum, rated and maximum current.
The minimum indicator is the current at idle speed of the engine (usually 1500-1800 rpm) and it (minimum current) should be 40-50% of the nominal value. The rated current is an indicator at which the generator components heat up within acceptable limits. In this case, the rated current is close to the maximum. It is this indicator that is indicated in the passport data of the device and on the body of the generator itself. For domestic models of generators, the rated current is achieved at 500 rpm.
When choosing a generator, you should not be guided by what voltage the car’s generator should produce, since it is the same for all models. The main indicator is the rated current of the generator, which should correspond to 200% of the battery capacity with a small tolerance of 10-15%. It is also not recommended to install a larger capacity battery on the car, since it will not sufficiently restore the charge from the alternator already in use.
Battery charging circuit
For a general understanding of the reasons for overcharging, first consider the battery charging circuit diagram. And although it is structurally different on different cars, the general principle of construction is the same.
This circuit includes:
The recharging system works using the example of the VAZ 2106 and other cars from the VAZ classic series as follows: after starting the power plant, by means of a belt drive, the crankshaft begins to rotate the generator rotor, as a result of which this unit begins to generate electricity.
But since automobile generators use alternating current, the generated energy goes to the rectifier unit, where alternating current is converted into direct current.
After the rectifier unit, the electricity goes to the relay-regulator, whose task is to maintain the voltage in a given range.
After the regulator, the electrical energy passes through the circuit through the fuse box, the ignition switch and the charge indicator lamp, then returns to the output of the generator, and from there it is supplied to the battery.
The detailed diagram is shown below.
Features of the circuit
The above is a general diagram of the circuit, without details, but it is enough to understand how everything works. Now about the features of battery recharging.
The generator cannot independently regulate the parameters of the generated electricity, so the output voltage from it varies, and in a significant range, it depends on the crankshaft speed and the load in the on-board circuit. That is, the battery is essentially constantly being recharged while the generator is generating electricity.
In order for the battery to accept a charge, you need to apply a voltage to it slightly higher than the nominal value of the battery itself. The input voltage on the battery differs on different cars, but in general, this figure is in the range of 13.9-14.5 V.
It is at this voltage that the battery can “take” a charge. If the voltage is lower, the battery will be undercharged, and if the voltage is higher, it will be overcharged. Both situations have a negative impact on the battery.
The generator produces a voltage with a high value, and in order to maintain it in the circuit within the required limits, a relay regulator is included in the circuit.
On some models, this element is included in the design of the generator and is combined with a brush assembly (the most common design) or is a separate unit (found, for example, on the VAZ of the classic family).
In fact, the relay-regulator is the only element responsible for ensuring that the voltage in the on-board network corresponds to the norm and that overcharging does not occur, taking into account the load created in the on-board network when electrical consumers are turned on.
How to choose a battery for Lada Kalina
The issue of choosing a replacement for an old battery must be approached responsibly. There are several important criteria, each of which is worth considering in detail.
Brand
Western countries use much more advanced technologies in the production of batteries. They even check in a completely different way. In our country, the charge is tested with a load fork, with the help of which the load is applied for 10 seconds, and the charge should not fall below 9 V. The European test involves 30 seconds of load with the same minimum threshold of the “drawdown” voltage. As a result, Russian batteries are inferior in quality to their foreign counterparts. It cannot be said that there are no brands on our market that are not inferior in quality to European ones, but there are not many of them. And you shouldn’t focus only on a popular brand; characteristics and compliance with the required parameters are much more important.
Date of manufacture
Proper storage of batteries is important. If the charging rules were violated, or the devices were in aggressive conditions of unacceptable temperatures, then their characteristics will be distorted even before they are purchased and installed under the hood. The best option is that the device was manufactured no more than four months ago. You should be very careful when buying a battery that has been stored for a year or more. Checking with a load fork is mandatory.
Capacity
Capacity selection is a broad topic and there is a lot of controversy surrounding it. But it all comes down to the fact that you need to choose a battery with a capacity no lower than the factory one. More is possible, but not less. In everything you need to know when to stop and understand that a battery with a large capacity simply will not fit in its rightful place due to its increased size.
Starting current
This parameter is indicated directly on the battery. It is not recommended to buy a battery with a starting current lower than the minimum declared for the Lada Kalina. The same amount or more is allowed. At subzero temperatures, the battery can lose up to 40% of its charge, and insufficient starting current may not cope with the difficulty of starting a frozen engine. In this matter, you need to find a middle ground, since options with a high starting current are quite expensive.
Polarity
The battery can be with direct or reverse polarity. This means that the terminals can be in opposite places. It is worth considering this when choosing a device. The cost of models with reverse polarity is somewhat lower, but installing them on Kalina, where direct polarity is provided, will not be easy.
Reasons for overcharging
A malfunction of the relay regulator is the most common cause of battery overcharging.
Due to a breakdown, this unit ceases to perform its functions and “passes” all the voltage generated by the generator into the on-board circuit, and it can reach 25 V. Naturally, not a single electrical appliance in a car is designed for such a voltage, so the elements of the on-board network begin to burn out .
Regulator failure can be partial or complete. In the first case, this element still performs its functions, but “passes” a voltage slightly higher than needed (for example, 15 V).
In this case, the overcharge of the battery can only be detected by readings from measuring instruments or the on-board computer. Electricity consumers practically do not “suffer” from such voltage, but even such an overcharge negatively affects the condition of the battery - with a constant process, the battery “boils out” and fails.
If the relay-regulator is completely malfunctioning, high readings (over 16 V) begin to damage consumers - light bulbs and fuses burn out first, then other devices. A significant excess of voltage can cause a fire in the electrical wiring.
Despite the fact that a partial breakdown of a relay does not pose a significant threat to the vehicle’s on-board network (with the exception of the battery), it should not be ignored, since at any moment it can develop into a complete failure of the element.
Since the relay-regulator is the only element that prevents the battery from overcharging, many car enthusiasts, when they detect increased voltage in the on-board network, immediately replace this unit.
But installing a new regulator does not always help; often the problem remains. Naturally, suspicion in this case falls on the generator. This unit can actually overcharge in the event of a breakdown of the diode bridge or a break in the windings, or a breakdown of the armature to the housing.
READ ON THE TOPIC: Car generator voltage, normal at idle and under load.
But if replacing the regulator relay does not help, you should not immediately change or send the generator for repair.
IMPORTANT: Often the reason for overcharging the battery lies in poor contact of the wiring of the battery charging system circuit (described above).
The reason is very simple: at the point where the contacts are oxidized, resistance arises, which the relay-regulator “perceives” as a load in the on-board network. For example, this can happen in the fuse box.
To compensate for it and prevent a drop in voltage, the regulator begins to “pass” large values, resulting in an increased voltage being supplied to the battery.
Therefore, in searching for the cause of battery overcharging, you should first check the relay-regulator, then the charging system circuit (all connections, as well as the fuse), and only after that remove and diagnose the generator.
Low voltage when starting the engine: how to find the cause
Let's start with the fact that the battery is not always the culprit of all troubles, although quite often reduced voltage occurs as a result of problems with the battery. In any case, before you start diagnosing a car regarding electrical parts, you must have a special auto tester (multimeter).
It is important that the device accurately measures certain parameters. As a rule, the functionality of the device should allow you to measure voltage, resistance, and current. At the same time, when troubleshooting voltage-related problems, you also need to take into account the crankshaft speed.
Checking the car battery
So, when diagnosing, you need to start by checking the battery, as well as the car generator. The condition of the battery is assessed by connecting the tester to the battery terminals. Normally, the voltage on the battery, taking into account the absence of load (all consumers are turned off), should be at least 12.6 V. A decrease in this indicator means that there is a partial undercharge or problems have arisen with the battery itself (sulfation of the plates, boiling off of the electrolyte, etc.).
You can also measure the voltage with a voltmeter, turning on the side lights and high beam headlights for the load. Typically, the discharge current under such a load (taking into account the installed halogen incandescent lamps) is about 5–6 A, and the voltage is about 11.5 V. If this is the case, then the battery is working and the problem needs to be looked for further.
Quick starter diagnostics
If we talk about the voltage directly at the moment of starting (when the starter turns), the voltage at the battery terminals should not fall below 9.5 V. In cases where this happens on a working and charged battery, it can be argued that a starter malfunction has occurred. In other words, the starter requires too much electrical energy when operating, which should not normally be the case.
Let us add that to measure the current you need an ammeter, which is connected to the gap. At the same time, it is highly not recommended to break the circuit in a car; also, not all ammeters are able to work correctly and record high readings that occur when the internal combustion engine is started.
For this reason, it is better to have a special motor tester for such tasks. The main advantage of the device is that the measurement accuracy is quite high, and there is no need to connect the tester to the break, since the device has separate sensors. These sensors are overhead and work even through wire insulation. These elements are capable of effectively recording changes in magnetic field strength when a current of one or another magnitude passes through the wires in the circuit.
Diagnostics of the relay regulator
Checking the relay regulator when recharging the battery is not a complicated procedure and you can do it yourself using a multimeter.
The test comes down to measuring the voltage at the battery terminals under different operating modes of the power plant. That is, we simply connect the multimeter probes to the terminals and measure the voltage first at XX, then at medium speeds, and then at high speeds.
At idle, the normal voltage is 13.2-14.0 V, at medium speeds - 13.6-14.2 V, at high speeds - up to 14.5 V.
If the values exceed the specified values, you should check and clean the contacts of the charging system circuit and repeat the procedure again.
If cleaning does not help, we check the relay separately (removed from the car), but for this you will need a power source with regulated voltage (you can use a battery charger), as well as a regular 12 V lamp.
The essence of the test is this: we connect the negative wire from the charger to the housing, and connect the positive wire to the regulator terminal. The lamp is connected to graphite brushes (polarity is not important).
When checking, we first set the voltage at the source to 12.7 V, at which the lamp should light up. We gradually increase the value to 14.5 V. When the specified value is reached, a working regulator should operate and the lamp will go out.
If it continues to light when exceeding 14.5 V, then the unit is faulty and requires replacement.
Normal voltage of a fully charged car battery and methods for measuring it
No load: what the tester shows at 100% charge
12.6-12.7 Volts at +20…+25°C. This is the voltage that should be present on the car battery 6 hours after being fully charged from a household outlet or parked with the engine not running. When taking measurements, it is important to disconnect one of the terminals and take into account the temperature of the battery. Let's say, at -10...-15°C, a “voltage” of 12.7 V already corresponds to a 75% charge.
Immediately after turning off the charger crocodiles, the potential difference is slightly higher. There is no specific figure. For example, for AGM it can be around 13.8-14.8 V, for EFB and calcium - 13.8-14.4 V.
Under load: what does the load fork show at 100% charge and should you trust it at all?
All batteries that hold more than 10V during the first 5 seconds are considered to be in good condition. Yes, the status is blurred, but the plug will not tell you the exact degree of discharge or charge without a detailed analysis of the parameters. That is why you should not rely on the readings of a device with additional resistance, even when checking a new battery before purchasing it in a store.
The problem is that each battery has its own A*h rating, but there is no single voltage corresponding to a 100% charge under load. There are no tables either, but there is another headache. There are no uniform requirements for the manufacture of load forks. As a result, you can buy a device that consumes, say, 200 A or 100 A. And then confusion arises.
It remains to rely on real data taken from experiments. It is known that a regular 55 Ah battery is considered fully charged if the load plug produces 10.5 V, and:
- The voltage after removing the load is restored to 12.66-12.7 V.
- Ambient temperature is about +15°C.
- Load – 100 A.
Getting to the repair site
Finally, about what to do if an overcharge is detected while on the road and you need to get to the place of repair.
If the voltage does not exceed 15 V, then you can safely continue driving, but try not to give high speed to the engine and reduce the number of switched on electrical consumers as much as possible (keep only the necessary ones).
If the overcharge is strong (more than 15 V), you can first loosen the tension of the generator drive belt, which will reduce its performance (although the belt will quickly wear out).
If loosening the belt does not give any results, you can turn off the generator (disconnect the wires from it). In this case, the on-board network will be powered only from the battery.
If the battery is well charged with a minimum number of consumers on its charge, you can drive 70-90 km, but after that the battery will need to be well charged.
Source
What to do if the potential difference is below 12.6 V
- Charge. 12.3-12.4 V. Up to this voltage, you can discharge the car battery without much harm to it. Above 60% charge level, sulfation occurs slowly. To restore the battery, it is recommended to “drive” the current to 10% of its capacity for 6-7 hours. If the product is often recharged and maintains normal battery life, ask why the battery discharges quickly when idle.
- Perform desulfation. In untreated cases, it is enough to connect a desulfating device to the battery terminals for several days and the capacity will be restored. The special device is expensive, so many people imitate its functionality using a regular charger and a lamp from a car headlight.
Communities › Auto electrics › Blog › Vehicle on-board voltage (discussion)
Greetings to all community members! This topic has been brewing in my head for a long time, and since there is very little information on the Internet, I decided to discuss it, so to speak, with “colleagues.” Every more or less experienced car owner, and even more so an electrician, even a beginner, knows that the voltage in the on-board network of a passenger car should be 13.8-14.2 V, low voltage means undercharging or too high consumption (short circuit), and high overcharge. This is a theory. Now practice: repeatedly when reading errors through the diagnostic connector, I observed voltages of 14.5, 14.9 and even 15.2 V on a variety of cars, the last 15.2 V I saw on Montero Sport. In general, I could not answer my question: is this voltage normal or is it a generator malfunction?
I couldn’t find a clear answer on the Internet; for Lada cars everything is more or less clear, but what about foreign cars? In general, I want to hear the opinion of nuclear electricians - professionals, who thinks what?
Comments 60
Tell me, the turn signal relay starts blinking more often when the engine is running, but as usual when the engine is off. When the engine is off, the mains voltage is 12.8 and when the engine is running it is 14.5. The emergency lights are blinking at the same frequency.
Batteries made using calcium technology require increased charging voltage. This is the bulk of batteries currently produced. In these batteries, roughly speaking, antimony is replaced with calcium. This was done to give modern batteries low-maintenance properties and completely maintenance-free - calcium batteries are almost not subject to boiling when charged. However, this requires a higher charging voltage. They are also not afraid of overcharging, during which antimony batteries boil away and really don’t like deep discharge! In short, something like this. Therefore, the voltage of the on-board network of modern cars is 14.5-15.1V. This is normal, although the light bulbs in the headlights cover up faster))) More details here: www.drive2.ru/l/5914573/
I read everything and was enlightened! Thank you
Modern cars are crammed with electricity and electronics. Consumption (especially in winter) is very high, so there are only crumbs left to recharge the battery. With consumers turned on and the engine idling, i.e. at low speeds, even the relay regulator will not maintain the required network voltage and it will drop even below 13.8. And if the battery is fully charged and the consumers are not turned on, then a short-term increase in the voltage in the on-board network to 15 V is quite possible. Of course, if the network is constantly 15 V, then this is a cause for concern.
measure the voltage at the battery and at the generator output, compare with the readings of the ECU...
If we talk about standards, there is no need to discuss this. They should be. We have GOST R 52230-2004 “Automotive and tractor equipment”. There are standards for battery manufacturers. The norm is 13.8 - 14.2 V. With some deviations according to various sources. Below is undercharging and sulfation, as I understand it. Above is recharge. As they said here - “boiling” of the battery.
But GOST concerns only domestic equipment, and the question is specifically about foreign cars
Right. But equipment that complies with our GOST is sold “over the hill.” Like their equipment, it is certified and complies with standards.
If we talk about standards, there is no need to discuss this. They should be. We have GOST R 52230-2004 “Automotive and tractor equipment”. There are standards for battery manufacturers. The norm is 13.8 - 14.2 V. With some deviations according to various sources. Below is undercharging and sulfation, as I understand it. Above is recharge. As they said here - “boiling” of the battery.
At 14.2 maximum one ampere will be used for charging, what kind of recharge is there especially in city traffic
Let's sum it up
In modern cars, wiring problems are quite common. This is a problem that can actually cause significant trouble. You need to be aware that you should not go on a long journey in a car with electrical problems. Also, you should not continue to operate the machine when such problems have been discovered. And if in one car we are talking about a simple feature of the generator, then in another case it will be important to take into account all the technical aspects of the electrical wiring, each consumer and other factors. Only specialists can deal with these problems.
The cost of repairing the electrical network at a good service station will depend on the causes of the breakdown. Sometimes it is enough for specialists to replace a failed relay to correct the situation. Otherwise, it is necessary to repair the generator, change or remove certain electrical consumers from the system. Therefore, the final costs depend on the problems identified during diagnosis. It is important to remember that any problems should be corrected quickly enough, otherwise problems with the vital organs of your car may occur. Have you ever encountered such problems?
#1 alexrua
- Active users
- 157 messages
- Gender: Man
- Krasnodar city
- Car:VW POLO 2011
#2 silit
- Gender: Man
- Penza city
- Interests: repairing everything that starts, talks and shows
- Car:citroen
#3 alexrua
- Gender: Man
- Krasnodar city
- Car:VW POLO 2011
#4 silit
- Gender: Man
- Penza city
- Interests: repairing everything that starts, talks and shows
- Car:citroen
#5 alexrua
- Gender: Man
- Krasnodar city
- Car:VW POLO 2011
#6 alexrua
- Gender: Man
- Krasnodar city
- Car:VW POLO 2011
#7 IgorSaratov
- Gender: Man
- City: Saratov region. r.p. Dukhovnitskoye
- Interests: cars and everything connected with them
good day everyone, there is such a problem with the viburnum R 0563 Increased voltage of the on-board network although the tester clearly shows 14 V when charging the ECU M74 1.6 8kl engine tried to turn off the generator the same story diagnostics still shows 17 V diagnostics scan doc
Saratov region r.p. Dukhovnitskoye 8-927-155-72-79
#8 alexrua
- Gender: Man
- Krasnodar city
- Car:VW POLO 2011
#9 bald8
- Gender: Man
- Saratov city
- Interests: Fishing, computers
- Car:KALINA, lacetti 1.4
Granta, Kalina Priora
On front-wheel drive LADA cars (Priora, Kalina Granta), the ground wire from the negative terminal of the battery is attached to the thermostat housing. This is a bad decision because... The thermostat is isolated by a gasket and all current flows through two studs. During operation, the contact oxidizes and the voltage in the on-board network drops, difficulties appear in starting the engine, etc. The problem can be solved with a simple modification.
You should move the negative wire coming from the battery from the thermostat to the engine:
Or install an additional wire from the thermostat to the engine (photo diamond1309):
It would not be a bad idea to additionally extend the ground from the negative terminal of the battery to the body and generator:
Replacing the voltage regulator and checking it on viburnum
Welcome! Voltage regulator - it is installed on the generator and is directly connected to it, thanks to it, the entire current that the generator gives out changes and flows more evenly, for example, the more you turn the engine of a car (increase the speed, that is), the generator will work stronger and much more give out current, all this happens because the generator is connected to the engine (namely, it is connected to the crankshaft), but the voltage in the on-board network will also change from this (The more current the generator gives, the stronger this current increases in the entire on-board network car), therefore, when the speed increases, the light will constantly burn stronger, and when it decreases, it will dim because the current strength will decrease, so no matter what happened, a voltage regulator was invented, thanks to which the current strength in the on-board network always remains the same, but it changes when you turn on additional devices that need more current, that is, for example, you turn on the high beam headlights of a car and the current supply increases through the regulator so that there is enough power for these headlights, in addition, the current supply flowing through The regulator is constant and does not jump higher or lower, so the headlights work in the same mode and do not shine either stronger or weaker.
Note! In order to change or check the voltage regulator, you will need: Two different types of screwdrivers, as well as two wrenches that will be “12” in size, and you will also need a DC voltmeter thanks to which you can clearly determine what voltage you have in your on-board network and whether it is jumping, and among electrical appliances, a megohm meter is also useful, thanks to which you can check the regulator’s capacitor for serviceability, thanks to which the current strength remains constant when supplied to the on-board network!
Summary:
Where is the voltage regulator located? It is located on the generator itself, as was already said a little earlier, a plus wire and a wire block are also suitable for it, so that the regulator does not become dirty; for this purpose it is also closed with a plastic cover, in more detail the pin that comes out of the regulator you can look at photo which is located below, in this photo you can just see the same plastic cover that closes the regulator, and in the other photo (Small) you can see that the cover has already been removed and only one pin sticks out, which comes from the regulator (This pin is on both indicated by a red arrow in the pictures).
When should you change the voltage regulator? It needs to be changed when it begins to pass alternating current into the on-board network (Alternating current is the current that rises or falls under the condition that the circuit leaves its direction unchanged), in other words, if the current strength fluctuates (And this should not happen), then the regulator must be replaced, if the current fluctuates, for example, the headlights may burn either worse or more intensely (Depending on the engine speed, at high speeds the headlights will burn stronger), and the regulator must also be replaced if it begins to produce either less current than necessary (In this case, you will have an undercharge of the battery), or more (With a stronger current, you may burn out the main part of the wiring in the car that will not withstand the heavy load, or if you have fuses, then at best they will have time to open the circuit and nothing bad will happen to the wiring).
Vesta
Required
: wire (article AX632).
The on-board computer used to show a voltage of 14.0-14.1 V, now it’s 14.1-14.3 V. I don’t notice any shuddering when the fan is activated.
Another example of installing additional mass on Vesta:
It’s similar on other LADA models.
Let us remind you that the voltage in the car's electrical system should be 14.2-14.4 Volts.
Source
How to replace the voltage regulator and check its serviceability on a VAZ 1117-VAZ 1119?
Checking the voltage regulator for serviceability:
1) At the beginning of the operation, you will need to find where the generator itself is located and after you find it, move your hand to the side with the rubber cover indicated by the red arrow, this cover covers the “B+” terminal; in simpler words, this is the positive terminal and it comes from the generator to this terminal (By the way, it is also indicated by a blue arrow) you will need to connect the positive wire of the voltmeter and after connecting it, throw another wire (Minus wire) coming from the same voltmeter to ground (The places where you need to connect the wire , indicated by a green arrow), after the operation has been completed, a DC voltmeter will show you the voltage in the vehicle’s on-board network.
Kalina increased voltage of the vehicle's on-board network
Brothers, shout. What should be the charging voltage (mains voltage) when the engine is running? I have 14.7 volts. And in my opinion, when I put it in the garage... it smelled of burning.
Where does this info come from? Maximum 14.4V, if the generator produces 15.1V, you will be tortured to add distilled water. (This is in the best case, in the worst case you will simply throw out the battery ahead of schedule)
Actually info from a book on repair and operation.
Thank you..friends for the advice.
With the headlights on, heater 14.5 at 2500 rpm. Is it good or not?
Well, thank you. Then I’ll sleep peacefully... but not while driving. )))))))
Only at such a voltage, do not be lazy to check the electrolyte level, it will definitely boil in the summer.
but I have a different kind of problem. When you get caught in the rain or in a puddle, the voltage sometimes drops to 10.5 volts! The alternator belt does not creak, when the air conditioner was installed, the belt was changed to another one. In dry weather the voltage is always about 14 volts. I have no idea what to do.
When you get caught in the rain or in a puddle, the voltage drops to 10.5 volts! At this voltage, the control indicator on the instrument panel should light up. In general, tighten the belt first.
but I have a different kind of problem. When you get caught in the rain or in a puddle, the voltage sometimes drops to 10.5 volts! The alternator belt does not creak, when the air conditioner was installed, the belt was changed to another one. In dry weather the voltage is always about 14 volts. I have no idea what to do.
Don’t kick too hard, I didn’t find anything specific by searching.
The problem is that the low beam lamps are on, the family ones seem to have lived for 8 months or 25,000 km, I installed OSRAM Silverstar 12v 55w, both burned out one after the other with an interval of one day, they worked for only 2 months and about 3-3.5 t.km.
Voltage drop when starting the Kalina engine
- Registration
- Entrance
- To the beginning of the forum
- Forum Rules
- Old design
- FAQ
- Search
- Users
What is there to sin about? Generator? Battery? Terminal?
Do ordinary lamps (dimensions, for example) sag when starting up? If yes, then look at the terminals, the fastening of the power wires (both + and to ground) - how the terminals are crimped, whether there is corrosion under the bolts, etc. The battery may be dead or dying.
When I start, the minibus swears and the music is cut off for 2-3 seconds, but the BSK does not respond. I'm sorry about the battery, I never charged it when I bought it. The starter turns normally, the engine starts with half a turn or a full turn, so you can’t even reach the battery.
I have the same. IMHO this is normal. In music, apparently, when there is a “drawdown,” some kind of protection is triggered.
The voltage under load should not be less than 9 volts.
How much can the voltage drop when starting the engine? Actually, where does the question come from: when the starter is turned on, the BSK (On-Board Control System) repeats the initialization cycle, all the lamps light up. But not always. It doesn't seem like it should be like that. What is there to sin about? Generator? Battery? Terminal? While driving, the voltage is between 12.8 - 13.6 volts, depending on the connected consumers. I always drive with my headlights on. Car: 2115, year 2005n (January), mileage almost 10 t.km.
Same stuff. Voltage 12.6-13.6V. The minibus swears when starting up. It drops to 11V. The battery is new, charged, 62A/h. All contacts have been cleaned. The starter is new. Replaced the voltage regulator and belt. Now on a cold car it’s 13.4-13.6, and after a little warming up it’s the same again. There is no flickering of headlights. I blame the generator for not delivering its 80A.
How much can the voltage drop when starting the engine? Actually, where does the question come from: when the starter is turned on, the BSK (On-Board Control System) repeats the initialization cycle, all the lamps light up. But not always. It doesn't seem like it should be like that. What is there to sin about? Generator? Battery? Terminal? While driving, the voltage is between 12.8 - 13.6 volts, depending on the connected consumers. I always drive with my headlights on. Car: 2115, year 2005n (January), mileage almost 10 t.km.