The brake system is an important link in a car, as it is primarily responsible for traffic safety and, ultimately, for the life and health of road users. Therefore, its maintenance should be taken very seriously, strictly and promptly follow all the manufacturer’s recommendations. This section includes a fairly wide range of materials. All procedures for replacing pads, cylinders, discs and many other parts of the brake system are described in detail and clearly. Many articles contain not only original information on do-it-yourself repairs, but also include special information blocks with useful tips to make life easier when performing a particular job.
I think there is no need to explain once again that due to poor lubrication of the caliper fingers, certain problems can arise, for example: unevenness.
In this article I will try to talk about such a procedure as replacing the parking brake cables on a Lada Kalina car. For starters, it's worth it.
Yesterday my friend arrived, for whom we recently bought a Kalina sedan. So, his problem was the following: from.
From the first months of using my Kalina, I wrote on this blog about a problem with the brake fluid level sensor. On the panel.
One of the reasons why the brake lights on your Kalina may not work is a failure of the switch or something like that.
Adjusting the handbrake on Kalina involves either tensioning or loosening the cable. In most cases, it is necessary to do the tension, just like that.
Judging by user requests, Kalina owners practically do not experience any breakdowns related to the front brake wheel cylinder. May with.
Before you begin this repair, you first need to measure the thickness of the brake rotor. If it is less than 17.8 mm, then.
Typically, brake cylinders last quite a long time and do not require replacement, but during long-term use a situation may arise where the internal ones.
As you know, rear brake pads do not wear out as much and do not have to be replaced as often as the front ones. But if.
To remove the rear brake drum on Kalina, we will need no more than 20 minutes of time and the tools listed below: Jack.
About a month ago I wrote a topic in which I shared the problem I had with the front brake pads. The essence of this malfunction was as follows.
A couple of days ago the following problem arose: when braking, especially when braking sharply, a strong creaking noise began to appear from the front left wheel.
After a short run of my Kalina, after about 12,000 km, the brake fluid level lamp started flashing, and I got a little worried.
One of the most popular domestic cars is the VAZ 1118 Kalina, which our citizens have come to love for its ease of use, reliability and efficiency. The Kalina brake system has two operating circuits located diagonally. The right front wheel is connected to the rear left, and the front left, respectively, to the rear right. This design ensures safety during vehicle operation and also reduces the likelihood of brake failure.
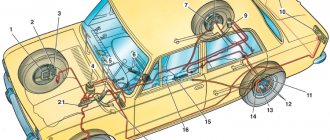
Working brake system: 1 — brake mechanism of the front left wheel; 2, 6, 12, 17 — brake hoses; 3, 7, 11, 18 — brake pipes; 4 — main brake cylinder; 5 — brake mechanism of the front right wheel; 8 — reservoir of the main brake cylinder; 9 — vac>smart amplifier; 10 — brake pedal; 13 — brake mechanism of the rear right wheel; 14 — fluid pressure regulator in the brake mechanisms of the rear wheels; 15 — lever for regulating the fluid pressure in the brake mechanisms of the rear wheels; 16 — brake mechanism of the rear left wheel Note. Some cars are equipped with a braking system with ABS (anti-lock braking system).
The brake system of the Lada Kalina car
The hydraulic brake system of a VAZ 1118 car consists of a pedal lever, a hydraulic master cylinder, a vacuum brake booster 1118, a hydraulic reservoir, a pressure regulator, a regulator drive lever, pipelines, flexible reinforced rubber hoses, tees, and fastening clamps. At the same time, the brakes on this VAZ model can be equipped with an anti-lock braking system, but it was not installed in the first series of Kalina production. Today, almost the entire line of cars comes with an ABS system.
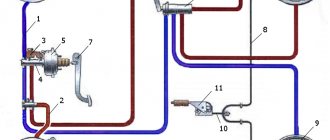
Vacuum booster on a VAZ 2170 2171 2172 Lada Priora: 1 - tip mounting flange; 2 — rod; 3 — diaphragm return spring; 4 — sealing ring of the master cylinder flange; 5 - main cylinder; 6 — amplifier pin; 7 — amplifier housing; 8 - diaphragm; 9 — amplifier housing cover; 10 - piston; 11 — protective cover of the valve body; 12 — pusher; 13 — pusher return spring; 14 — valve spring; 15 - valve; 16 — rod buffer; 17 — valve body; A - vacuum chamber; B - atmospheric chamber; C, D - channels
Features of the front wheel braking system
The front wheels of the VAZ 1118 are equipped with a ventilated disc system with a piston floating caliper. It includes a wheel cylinder and a caliper, which are tightened together with special screws. The cylinder itself is attached to the guide pins with two bolts installed in the guide block (holes). The pads are pressed against the guide grooves by springs. Inside the cylinder there is a piston with a sealing ring having a rectangular cross-section. The elasticity of the ring provides an optimal gap between the disc and the brake pads, which ensures high-quality functioning of the system.
Brake system
The service brake system is hydraulic, dual-circuit (with diagonal separation of the circuits), with a pressure regulator in the hydraulic drive of the brake mechanisms of the rear wheels, a vacuum brake booster and a sensor for insufficient fluid level in the reservoir. In normal mode, when the system is working properly, the brake mechanisms of both circuits operate: right front - left rear and left front - right rear. If one of the circuits fails (depressurizes), the other circuit provides braking to the vehicle, although with less efficiency.
The brake pedal is a suspended type, equipped with a return spring. Above the pedal there is a brake signal switch, the contacts of which close when the pedal is pressed. To reduce the effort on the brake pedal, a vacuum booster is used, which uses the vacuum in the receiver of a running engine. The vacuum booster is located between the pedal pusher and the main brake cylinder and is attached to the front panel.
The brake master cylinder is attached to the vacuum booster housing with two studs. A plastic tank with an insufficient fluid level sensor is inserted into the holes located in the upper part of the cylinder through rubber sealing bushings.
The front wheel brake is a ventilated disc with a single-piston floating caliper. The floating front brake caliper includes a caliper and a wheel cylinder held together by two screws. The cylinder is secured with two bolts to the guide pins installed in the holes of the shoe guide. The brake pads are pressed by springs to the grooves in the pad guide. The cylinder contains a piston with a rectangular rubber sealing ring. Due to the elasticity of this ring, a constant optimal gap between the brake pads and the disc is maintained. The rear wheel brake mechanism is drum-type, with a two-piston wheel cylinder and automatic adjustment of the gap between the shoes and the drum.
The automatic clearance adjustment device is located in the wheel cylinder. The main element of the device is a steel split thrust ring mounted on the piston with an axial clearance of 1.25-1.65 mm. The thrust rings (two per cylinder) are inserted into the cylinder with tension, providing a shear force along the cylinder surface of at least 350 N, which exceeds the force of the brake shoe tension springs. When the brake linings wear, the thrust rings shift under the action of the pistons by the amount of wear. If the cylinder mirror is damaged due to mechanical impurities in the brake fluid, or due to corrosion (presence of water in the brake fluid), the rings may “sour” in the cylinder and one or even both pistons will lose mobility. In this case, the cylinders must be replaced.
Rear wheel brake mechanism: 1 - lower tension spring; 2 — front block; 3 - guide spring; 4 — spacer bar; 5 - working cylinder; 6 — upper tension spring; 7 — lever for manual drive of the pads; 8 — rear block; 9 — tip of the parking brake cable
The pressure regulator in the hydraulic drive of the rear wheel brakes is mounted through a bracket in the left rear part of the body. As the load on the rear axle of the vehicle increases, the elastic regulator lever connected to the beam is loaded, transmitting force to the regulator piston. When you press the brake pedal, fluid pressure tends to push the piston outward, which is prevented by the force from the elastic lever. When the system comes into balance, a valve located in the regulator shuts off the flow of fluid to the wheel cylinders of the rear wheel brakes, preventing further growth of braking force on the rear axle and preventing the rear wheels from locking ahead of the front wheels. As the load on the rear axle increases, when the traction of the rear wheels with the road improves, the regulator provides greater fluid pressure in the wheel cylinders, and vice versa - as the load decreases, the pressure drops. The parking brake system is driven mechanically, by cable, to the rear wheels. It consists of a lever, an adjusting rod, an equalizer, two cables, pad drive levers and spacer bars.
continuation>>
Announcements of articles from friendly sites
Main problems with the brake system of the VAZ 1118 Kalina
Everyone understands the importance of this system in a car, and therefore timely maintenance can significantly improve safety and also prevent accidents. At the same time, during intensive use, as well as the specificity and quality of the components in the mechanism, some of its elements may fail ahead of schedule.
That is why you should constantly monitor its condition, and also pay attention to possible malfunctions.
- Air in the brake system. To solve the problem, you need to “bleed” the system, which can be done both in a garage and at a service station.
- Brake fluid leak. Worn pipelines and rubber hoses
- Increased pedal travel. The vacuum booster is faulty; the hose needs to be replaced or its attachment to the fittings checked.
- Low braking efficiency. It is possible that the brake linings become oily, the pistons in the cylinders become jammed, the linings wear out, or the regulator is adjusted incorrectly.
- The car pulls to the side during braking. Different tire pressures, wheel camber/toe angles are incorrect, disks or drums are dirty or oily.
- Brake vibration or squeaking. Weakening of the tension spring, wear of the linings, oiling of the friction linings.
Features of the brake system of the Lada Kalina Sport
Lada Kalina Sport is an improved version of the domestic car, which has higher speed characteristics. As for the brakes, they have been qualitatively improved - the rear drum units have been replaced with disc ones.
In general, the Kalina Sport brake system is more reliable, since it is designed for high loads and speeds higher than usual. In addition, an ABS anti-lock braking system is installed here, which provides additional protection against skidding.
Bay
It is necessary to add liquid during the draining procedure. In this case, both actions should not be performed simultaneously, but in a certain sequence. In other words, you cannot fill in a new fluid composition until at least half of the old one has been drained.
When carrying out work, several points should be taken into account:
- Do not allow air to get inside the brake system. This leads to a deterioration in the performance of the brake pedal - the resistance changes.
- There should also be no bubbles in the bottle or hose. If such a situation arises, then new fluid cannot be added until the entire brake system has been pumped and air has been removed from it.
Upon completion of the replacement, the necessary elements are reinstalled and checked by turning on the engine. If there are no problems, then the amount of liquid in the tank is additionally checked, and if necessary, top up to the required volume.
Brake fluid in a Lada Kalina car is an important component that ensures safe driving of the entire vehicle.
Therefore, it is worth monitoring the condition of the fluid, as well as its level, in order to avoid serious problems, and replace it in a timely manner. It should also be noted that in some situations, old brake fluid or its leak can become the root cause of a serious accident, since in this case the car’s brakes simply will not work.
Features of front and rear wheel brakes
The bolts are placed in the passages of the guide blocks, pressed by the guide spring grooves. A piston with a sealing ring of rectangular cross-section is placed inside the cylinder. This ring provides the most rational distance between the disc and the brake pads. This organization of Kalina's braking system contributes to its efficient functioning.
In addition to the head system, the developers equipped the Lada with a mechanical parking brake, which is driven by the brake mechanisms of the rear wheels.
- adjusting rod;
- lever arm;
- two cables;
- equalizer;
- spacer bars;
- pad drive levers.
Principle of operation
The operating principle of the Lada brake system is as follows. After pressing the brake pedal, the piston begins to move in the cylinder. Fluid from the main exhaust valve enters the Kalina brake system through hydromechanical hoses. The fluid is then directed towards the main wheel mechanism through pipelines, creating the necessary conditions for the movement of the pads to the front wheel disks and to the rear drums. Contact occurs and braking occurs.
- Presence of air in the system. You can solve the problem not only with service, but also yourself. To do this, you need to bleed the brakes.
- Brake fluid leaking. This situation indicates a malfunction of pipelines and rubber hoses.
- Increasing pedal stroke. The problem that has arisen indicates a problem with the vacuum booster. It is recommended to replace the hose and check its attachment points.
- Reduced braking efficiency. In this case, the reason may be oily brake linings, jammed cylinder pistons, compromised gasket integrity, or defective adjustment by the regulator.
- Squeaking or vibration when braking. Perhaps the tension spring is weakened, the linings are out of order, or the rubbing linings are oily.
Working principle of brake caliper
The brake caliper performs its main task - it provides the necessary braking force required to slow down or stop the car.
Pressing the brake pedal causes pressure to build up in the brake line. It is transmitted to the caliper pistons, which at this time strictly parallel fixes the pads relative to the disc. When braking, the calipers compress the pads on both sides of the disc, causing it to slow down. But there is another effect. It involves heating, as friction energy is transformed into heat. This significantly heats up both the disc and the pads and calipers. The temperature of the brake fluid also increases.
This effect places certain demands on manufacturers. So the front brake caliper must have the following characteristics:
- high heat transfer rates;
- strength;
- high resistance to heat (so that increased temperature does not deform the caliper components).