The design and functions of the clutch in the VAZ 2114
In a VAZ 2114 car, the clutch is a simple unit in design.
The system is equipped with a special cable, which, compared to a hydraulic unit, does not require constant maintenance. And you can change this element yourself if necessary. The drive includes the following parts:
- cable for changing position in a special shell;
- a pedal that the driver controls from inside the car;
- clutch shift fork handle;
- a clamp securing the tip of the cable sheath;
- brake and clutch pedal retainer.
The mechanism is designed to transmit force from the pedal in the car interior to the fork in the engine compartment. This element removes the friction shaft from the flywheel of the power unit. Thanks to the use of cable transmission, AvtoVAZ engineers have ensured that the driver will not encounter problems with oil leakage or the need to remove air pockets from the clutch control system. In VAZ 2114 cars, the cable is considered the weakest component, so car owners are often faced with the procedure of replacing it. If you correctly install and tighten the cable when adjusting, this will ensure that the driven pulley is pressed well against the flywheel of the machine motor and basket when the clutch is activated.
Clutch device in VAZ 2114
When to calibrate the clutch
To maintain a car in proper condition, it is worth carrying out timely diagnostics of its main elements, which include the clutch. It is worth noting that today there is no specific time frame or vehicle mileage after which it is necessary to adjust the speed shift control mechanisms, since the degree of wear may depend on the driver and the style in which he drives his car. The main signs that indicate the need to perform such a procedure may be the following:
- presence of clutch pedal failure;
- very fast or too slow response to lever pressing.
Clutch cable
The main element that can be responsible for all these functions is the clutch cable. This is a fairly reliable part, but sometimes it happens that the time comes to replace it. Among the most common causes of clutch cable failure are considered to be violation of the rules for using a car, increased loads, and deformation under the influence of an aggressive environment. As for the last option, this is a kind of consequence of a seal failure. Clutch adjustment should be carried out when there is an urgent need, and also if you have observed changes in control characteristics.
According to numerous recommendations from experts, drivers should carry out timely diagnostics, the essence of which is to measure the distance of the pedal from the floor.
As soon as you notice any deviations in the operation of the clutch system, you need to immediately take appropriate measures, since a lot depends on this kit. The main thing is that without a clutch you will not be able to engage any gear, and therefore you will not go anywhere. It happens that the pedal fails, or, on the contrary, works very hard. In both cases, adjustment will be required.
In fact, it is not so difficult to look into the integral part of the VAZ 2110 - the Bible and the Kama Sutra - the instruction manual. Everything is described there quite clearly. But we will try and explain in an accessible, understandable, step-by-step manner how the adjustment is carried out.
Stage 1:
Checking the pedal travel. This is where you need to start. According to the factory settings, its stroke on a VAZ 2110 is considered normal if it is about 13 centimeters. But it becomes larger as the driven disc lining wears out, since in this situation the pedal rises. Measuring its progress will not be difficult. All you need is a ruler.
Measuring the clutch pedal travel
So, open the door on the driver’s side and lean towards the pedal. Even those who do not understand car repair at all know its location - the far left of the three available there. We rest the ruler against the mat, perpendicular to the pedal, and carefully look at what distance it is from the floor. If we see 16 cm or more on the scale, urgent adjustment is needed.
Stage 2:
Direct adjustment. Actually, you don’t really need to disassemble anything, everything comes from the engine compartment, as well as from the interior. You only need two regular 13mm wrenches. Open the hood, find the tip of the clutch cable and the locknut on it. Use one of the keys to loosen this locknut. Using the same key, turn the adjusting nut. By “rolling” it onto the tip, we increase the full stroke of the pedal, and by unscrewing it further away from it, we decrease it.
Eventually
In conclusion, it should be noted that there are some “homemade” ones who specifically move the release bearing away from the basket, explaining their actions by the fact that in this way they will be able to extend its service life. However, they will have to be disappointed - the bearing is unlikely to become more durable, but the petals of the diaphragm spring will gradually be milled by the untwisted bearing race. And, please note, we are not discussing the discomfort from increased pedal travel, which can result in much greater expenses than purchasing clutch elements.
VAZ 2110 clutch diagnostics: signs of malfunction, parameters
In the case when we find difficulties with shifting gears, the culprit of the problem is the gearbox itself. As a rule, the first thing to check is the clutch. On old VAZ models, the clutch release drive was hydraulic and there were practically no problems with it. A manual drive on modern budget cars brings unpleasant surprises much more often. However, difficult gear shifting may be associated not only with the drive:
- release bearing wear;
- wear of the friction linings of the driven disk;
- oiling of clutch friction linings;
- mechanical damage to the working surface of the crankshaft flywheel;
- deformation or breakage of the release bearing drive fork;
- incorrect installation of the driven disk;
- destruction of the membrane plates of the clutch basket.
All this can easily cause difficult gear shifting, slipping, or lead to the clutch starting to “drive.” However, practice shows that it is the cable drive that often leads to problems with gear engagement. This is the easiest way to check, since there is no need to remove the gearbox and all drive elements in plain sight.
How to check the clutch of a VAZ 2110 correctly
At the same time, you need to understand that problems are not always associated with breakdowns. Elementary natural wear of the friction linings will cause the clutch to slip and the gears to not engage clearly. This becomes especially noticeable when starting from a stop or when engaging reverse gear, and also while moving, difficulties will arise when shifting. It is not at all necessary to immediately think about replacing the clutch or driven disk. With a high mileage after repair, 100-120 thousand - yes. The average clutch life of a VAZ 2110, according to owners' reviews, is 50-70 thousand ; of course, its mileage depends on driving style. But the clutch cable can die after 10-12 thousand mileage, depending on the quality.
The free play of the clutch pedal A on a VAZ 2110 should not exceed 5 mm
Therefore, independent diagnostics will not hurt every 7-12 thousand km . AvtoVAZ has established standard indicators by which one can judge the condition of the entire unit and, in particular, the drive. The main indicators that you need to take a closer look at are, of course, the behavior of the car when starting from a stop, the smoothness and precision of gear shifting. The factory recommends observing the following values for free play and clutch pedal play:
- The maximum pedal stroke should not exceed 160 mm .
- Normal working full stroke is 120 mm .
- The free play of the clutch pedal, play, should not exceed 5 mm .
Clutch drive VAZ 2110
These parameters are measured simply using a ruler or tape measure, and if they do not correspond to the ratings, we proceed to adjustment.
Measuring the free and working travel of the pedal
System modernization
If you decide to increase engine power, the factory clutch installed on the car must be upgraded, otherwise it will not correspond to the acquired accelerated capabilities of the engine. This is because the increase in power (and especially torque) often increases by 30% or more from the factory calculation, while significantly exceeding the established permissible load on the clutch (with an existing reserve of 20% to 50% above the existing torque) . In this case, the disc constantly slips and does not properly transfer all the power to the wheels from the internal combustion engine (ICE). In this case, significant modification of the unit is simply necessary.
Diagram of the VAZ 2110 basket arrangement
An automatic transmission is not installed on the VAZ 2110 in principle, but there are different types of tuning and modifications to the clutch and manual transmission. In general, the clutch itself includes a pressure and driven disc, but other important details are not directly related to the tuning process. There are two design options - single- and multi-disk, which is decisive for the quantitative characteristics of the driven parts. Such structures, with relatively small sizes, provide a fairly strong torque. The reason for this phenomenon is that the friction itself involves many more than two surfaces for imparting torque (four or even more).
The driven disks themselves in the design of our mechanism are also divided into two types - depending on the characteristics of fastening the splined parts, they are available with a rigid or damper type of fastener. Discs with rigidly fastened splined parts are often used in the manufacture of racing models for technically prepared cars, where the priority is to increase rigidity, relative lightness and increase efficiency. Clutches of this kind are not recommended for installation on production vehicles.
Clutch repair and replacement - the best price in St. Petersburg, excellent quality
Prices for repairing clutches, gearboxes, replacing sensors, seals and other things
carries out clutch repairs in St. Petersburg on domestic and imported cars. Our experienced, qualified craftsmen will repair this unit of any degree of complexity, be it a complete replacement of the clutch assembly or repair of its individual element (for example, replacing a rocker).
At the same time, we guarantee all car owners the impeccable quality of all work performed and the spare parts and consumables used in them, as well as short deadlines and competitive prices for all our services!
Clutch replacement in St. Petersburg - a few words about this element of the car
The main purpose of the clutch is to regulate torque, in terms of its transmission from the engine flywheel to the transmission.
In simple terms, this element allows you to smoothly disconnect and dock the engine flywheel with the transmission at the right moments. This device comes in two main types:
- Single-disc - this clutch is installed on the vast majority of passenger cars;
- Multi-disc - it is more often found in trucks and special equipment.
In addition, the clutch can be:
- Dry or “wet” (when the main mechanisms are immersed in a kind of oil bath);
- With electric, mechanical, hydraulic and combined drive;
- With a pressure disk pressure design in the form of a circular spring arrangement or with a central diaphragm.
Clutch repair prices
| Name of works | Domestic cars: | Foreign cars: | SUVs, minibuses |
| Remove/install gearbox | from 3,000 rub. | from 4,500 rub. | from 5,300 rub. |
| Clutch cable adjustment | 300 rub. | 300 rub. | 300 rub. |
| REPLACEMENT: | |||
| — Gearbox cushions | from 500 rub. | ||
| — Speedometer cable drive | from 300 rub. | from 500 rub. | from 1,200 rub. |
| — Gear selector rod seal | from 500 rub. | from 500 rub. | from 800 rub. |
| — Drive oil seal | from 1,300 rub. | from 1,500 rub. | from 1,500 rub. |
| — Input shaft oil seal (on the removed gearbox) | from 350 rub. | from 350 rub. | from 350 rub. |
| — Speedometer cable | from 800 rub. | from 800 rub. | from 1,600 rub. |
| — Clutch cable | from 700 rub. | from 800 rub. | from 1,100 rub. |
| — Speed sensor | from 300 rub. | from 500 rub. | from 600 rub. |
| — Reverse gear sensor | from 300 rub. | from 500 rub. | from 600 rub. |
| — Clutch kit (basket, disc, release bearing) | from 3,300 rub. | from 4,800 rub. | from 5,600 rub. |
| — Clutch bracket | from 350 rub. | from 350 rub. | from 450 rub. |
| — Bearing fastening/guide elements (on the removed gearbox) | from 150 rub. | from 300 rub. | from 300 rub. |
| — Clutch master cylinder | from 500 rub. | from 600 rub. | from 800 rub. |
| — Clutch slave cylinder | from 550 rub. | from 700 rub. | from 900 rub. |
| — Clutch forks (on the removed gearbox) | from 150 rub. | ||
| — Clutch fork supports (on the removed gearbox) | from 150 rub. | from 300 rub. | from 300 rub. |
| — Flywheel | from 3,300 rub. | from 4,800 rub. | from 5,600 rub. |
Replacing the clutch - cost and signs of trouble with this unit
Symptoms that should alert the driver and which may indicate that clutch replacement is just around the corner:
- Difficulty switching between reverse and forward gears.
- Slipping (incomplete engagement) of the clutch, including lack of acceleration appropriate for a given gear and a noticeable loss of power on inclines.
- Jerking when the clutch is engaged, as well as extraneous noises and knocking.
- The clutch pedal squeaks and jerks when you press it.
- A pronounced smell of burnt plastic when operating the machine.
As for the price of replacing the clutch, it, of course, depends on the severity of the breakdown and on the number of parts of the assembly that require replacement (up to a complete replacement of the clutch assembly).
Clutch repair - the price depends on the complexity of the task and the broken element of the unit
Of course, this is not the cheapest service - clutch replacement, and the price for it, by definition, cannot be symbolic, because this procedure is very labor-intensive and responsible, since a faulty clutch can provoke a serious accident when the car is moving.
However, a complete replacement of the clutch assembly is not always required; sometimes the situation allows us to limit ourselves to updating one of its individual elements, such as:
- Replacing the clutch basket, which is rigidly connected to the engine flywheel and with release springs in the center, may require preliminary balancing of the new part on a specialized stand.
- Replacing the clutch disc (driven) is strictly indicated when its damper springs are weakened or completely broken or there is end runout and will almost certainly eliminate the strong noise when the clutch is engaged and the “driving” effect of the device when it is disengaged.
- Replacing the clutch cable can save the car owner from slipping and driving the device during operation; often replacing the clutch cable is accompanied by replacing the entire driven disk or its linings.
- Replacing the clutch cylinder will also save you from slipping and dragging of this device during its operation.
- Replacing the rocker (or, in scientific terms, the gearbox drive rod) will allow you to do it with little effort without labor-intensive disassembly of the entire clutch assembly, and a sign of its malfunction is usually the loss of control over one or more gears in the box.
- Replacing the clutch fork (more precisely, the clutch release fork) will correct the situation with slipping when changing gears.
Clutch replacement in St. Petersburg - contact the professionals
Of course, motorists are always tempted to try their own hand at repairing their “iron horse,” but the clutch is not the unit with which you can start your car mechanic experiments, because the safety of your driving this car is at stake! Therefore, it is better to entrust such important tasks as replacing a clutch disc or cylinder, its fork, cable and slides to our qualified craftsmen, who will accurately determine the cause of the malfunction and quickly eliminate it.
And finally, we want to give a simple recommendation, following which you will significantly extend the working life of your clutch, and you will not have to change it every year: try not to keep your foot on its pedal all the time, even if it seems to you that your foot does not touch its surface. After all, even the lightest pressure on the pedal wears out the driven disc. But even the most careful handling of car systems will not extend their service life indefinitely, and sooner or later you will need to replace the entire clutch or its individual elements (link, cable, cylinder, disc, basket, and so on).
Our service centers repair and replace clutches for cars of all brands and models, including VAZ 2107, VAZ 2109, VAZ 2110, Ford Focus 2, Peugeot, Chevrolet, Toyota, Nissan, Kia, Opel, VW Golf and many others!
Stages of clutch replacement work
On a VAZ-2112, replacing the clutch begins with removing the gearbox. It is much more convenient to do this on an overpass or inspection hole.
- With the left wheel removed, unscrew the nuts from the ball joint and steering rod. In the future, the box must be moved so that it does not create interference; the left drive must be removed without hindrance.
- Having loosened the rocker nut, it is removed from the gearbox shaft.
- The next step is to remove the starter by first disconnecting it from power.
- Place a support or jack under the gearbox housing, and then unscrew the mountings of the cushions that hold the box.
- You need to unhook the cable of the speed measuring device, remove the reverse wiring from the sensor and the ground.
- Unscrew the nut with three bolts that attract the gearbox housing to the engine.
- Carefully move the box to the side, while pulling out the right drive.
We must remember that having pulled out one drive, in its place to support the differential, for example, a suitable tube is installed. And the oil must be drained from the gearbox crankcase. You can replace it using the opportunity. Experienced car enthusiasts carry out clutch repairs without removing the gearbox. To do this, the two upper bolts are replaced with bolts of much longer length. Then you don't have to remove the gearbox. The length of the bolts will allow you to move it to the side, see 15. In this case, there is no need to unscrew the transverse rod. The back of the box can be placed on it. Such conditions are enough to make it quite possible to change all the parts of the clutch assembly.
When is clutch adjustment necessary on a VAZ-2110
As the friction linings on the clutch driven disc wear out, the free and working stroke of the pedal increases.
This may result in the clutch not fully disengaging when the pedal is fully depressed. As a result, the clutch will “drive”, and difficulties may occur when engaging first and reverse gears, or when changing gears on the go. This situation creates additional stress on the gears, shafts and synchronizers of the gearbox, which leads to premature wear of the gearbox.
The factory stipulates permissible backlash, free travel and working travel of the clutch pedal, which must be adhered to during vehicle operation..
- The nominal full travel of the clutch pedal is 120 mm .
- The maximum allowable is 160 mm .
The full travel of the clutch pedal (all the way) should be in the range from 120 to 130 mm.
However, it is better not to reach 160 mm , since this threatens increased wear of the clutches and gearbox elements, and in addition, difficulties with shifting and engaging gears may arise at any time. To measure the clutch pedal travel, we need a regular ruler. We rest it on the floor under the pedal and measure the distance to the rubber pad.
Clutch. Design Features
| Clutch | Single disc, dry, diaphragm | |||
| Clutch release drive | Cable, backlash-free | |||
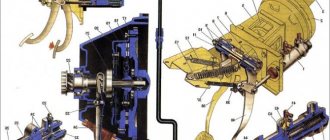
Clutch drive
| 1 – cable sheath; | 10 – the upper tip of the cable; |
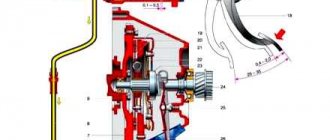
Clutch assembly
| 1 – cable lead; | 8 – gearbox input shaft; |
The clutch is single-disk, with a central pressure spring 11
(Figure Clutch assembly).
housing 3
is attached to the flywheel 6 with six bolts
4
, and is connected to the pressure plate
5
by three pairs of elastic plates.
Driven disk 7
assembled with a damper, it is located on the splines of the input shaft
8
of the gearbox.
On cars with a VAZ-2112 engine, a clutch with different characteristics of the pressure spring of the leading part of the clutch and the damper springs of the driven disc is used. To distinguish the leading parts of the clutch, clutch 2112 has a mark in the form of a hole in one of the slots in the pressure spring petals. The two drive disc damper springs 2112 have white paint stripes on them.
The clutch drive is cable-type, backlash-free (there are no gaps in the drive).
Clutch pedal 14
(Figure Clutch drive) is installed in bracket
16
on the axle.
The upper part of the pedal is connected to the end of the cable 10
.
The upper tip of the shell 12
is secured to the clutch pedal bracket using a thrust plate
11
.
The lower tip 2
is fixed in the bracket
3
on the power unit.
The cable guide 8
is connected to the clutch release fork
9
. The clutch release bearing is a closed type and does not require lubrication during operation.
ADDITION
What is a clutch and how does it work. Types and description of clutches
| After the internal combustion engine was built and improved, the question arose about transmitting torque to the driving wheels of the car. Thus, the need arose to create vehicle transmission mechanisms, the main ones being the clutch and gearbox. Fluid Drive coupling |
The clutch mechanism is located immediately behind the engine. The need for a friction clutch in a car with an internal combustion engine and a gearbox is dictated by the impossibility of starting such an engine under full load and, in addition, the presence of a clutch makes it possible, after starting the engine, disconnected from the transmission mechanism, to move off smoothly and quite softly when it is gradually turned on. The friction clutch also serves to decouple the engine and transmission mechanism when changing speed. It is common practice for all clutches to have one or more retaining springs. To change speed, pressing the pedal disengages the clutch, and after the gearbox gears are engaged, it is engaged again when the pedal is released.
Since the days of the first automobiles, the clutch mechanism has gone through several stages of development, with the so-called “dry” type of single-plate clutch dominating in modern passenger cars. But it was not always so. On cars of the beginning of the century, two types of cone clutch mechanisms were very widespread: with a direct and reverse cone. As a rule, a straight cone was installed in the engine flywheel, the rim of which was bored at an angle of 15° to form an outer cone, and the inner cone was pressed against that outer cone by one or more cylindrical springs. In a reverse cone, the outer portion consisted of a cast iron or steel ring bolted to the flywheel rim, into which an inner cone fit into the engine flywheel end. The reverse cone was well suited for use in engines with monobloc cylinder castings, as it was more compact, and its springs were located between the flywheel and the clutch cone. The working surfaces of the cones were covered with leather. The larger the cone size, the stiffer the spring was, and therefore the more labor-intensive engagement of the clutch, which takes more energy from the driver. To replace the leather pads, the clutch had to be disassembled, and the spring often jumped out and could injure the mechanic or driver. In order to avoid wear of the gaskets, they were greased daily. Three people took part in this procedure: one pressed the pedal, another rotated the crank, and the third, having removed the hatch cover in the floor of the body, made his way to the clutch mechanism and applied grease to the lining.
Multi-plate clutch operating in oil
Cone clutch mechanisms have been replaced by clutches with mechanical discs. This type of clutch played an important role in the development of the automobile transmission, although it was used for a fairly short period of time. This would be the first type of multi-plate clutch with metal discs operating in oil. It was this kind of mechanism that replaced the bevel clutch on luxury and expensive cars, since it was no longer possible to transmit more power through the bevel clutch. Most multi-plate clutches had conical discs made of bronze and steel, mounted alternately. They had V-shaped grooves whose sides formed an angle of 35°. In such clutch mechanisms, only the sides of the grooves came into contact, and the remaining parts of the discs served to dissipate heat. In the inner walls of the grooves, closer to their tops, there were holes through which oil could flow freely. This clutch was characterized by some wedging action, similar to what occurs in bevel clutches, so less spring pressure was required than with a clutch of flat discs of the same number and size to transmit the same power. However, to obtain sufficient clearance, the disks had to be spaced apart at a greater distance.
The coefficient of friction of disks operating in oil is significantly less than that of disks covered with asbestos fabric and dry metal. Therefore, to generate the same spring pressure in a multi-disc clutch operating in oil, significantly more discs were required than in a multi-disc clutch operating in dry discs. The result was a greater moment of inertia of the driven part, which made switching gears difficult. However, the greatest disadvantage of clutches with metal discs operating in oil was the effect of weather on the viscosity of the oil. Typically a mixture of 50% motor oil and 50% kerosene was used, but at ambient temperatures below 0 C this mixture became so viscous that the clutch began to slip. The quality of the mixture depended on both the quantity of oil and its quality, and when it was necessary to add oil, it was difficult to obtain a mixture of the desired composition.
To avoid the inconvenience of slipping when switching on, a multi-plate clutch with “dry” discs was developed. It consisted of two sets of metal disks, one leading and the other driven. One of these sets, predominantly driven, was sheathed on both sides with asbestos fabric. This type of clutch did not use engagement levers and spring pressure directly brought the discs into contact. At one time it was customary to install a larger number of discs and keep the pressure per unit area very low, as it was thought that this would increase the service life of the friction lining. But with such a large number of discs, the clutch tended to slip, and after that, switching gears in the gearbox turned out to be difficult, since the driven discs were quite heavy. Therefore, the multi-plate clutches used on cars had a relatively small number of discs.
Gradually, the number of discs was reduced to one or two, and they began to be equipped with linings made of a special friction material that does not require lubrication. However, all of the listed types of clutches did not make such a revolution in the design of the car transmission as did the hydraulic clutch or fluid coupling.
All designs of mechanical clutches turned out to be primitive, since they were engaged jerkily, which had an unpleasant effect on passengers and the car’s mechanisms, and the absence of jerking depended entirely on the skill of the driver. Also, mechanical clutches sometimes slipped or did not engage at all.
In contrast to steam and electric power units, a gasoline engine cannot develop the high torque needed to move a car at low speeds. When starting off, a steam engine immediately develops sufficient torque to move, for example, a long train and begin moving. Also, an electric motor, for example, a starter, develops the greatest torque when it rotates at the lowest number of revolutions, while a gasoline engine has little power at low speeds, therefore, in order for the car to move, it is necessary to reach 1000-2000 rpm. These shortcomings of the internal combustion engine can be negated by its elastic liquid connection with the driving wheels of the car, which is what a fluid coupling or torque converter allows you to do. It was invented in Germany in 1907 by Fettinger and was used on ships to reduce the speed of a steam turbine. And the widespread use of torque converters in cars began shortly after such a clutch, called Fluid Drive, appeared on Oldsmobiles in 1940.
How does a hydraulic clutch work? It consists of two cups with partitions. The cups are carefully adjusted to each other. One of them is mounted on the engine crankshaft instead of a flywheel, the other is mounted on the input shaft of a planetary manual transmission. The bowls are filled with oil. When the engine is running at low speed, only the drive bowl connected to the engine rotates. The cohesion of the oil particles is low, and in the other - driven bowl - the oil remains motionless. When the driver increases engine speed, the fluid in the drive bowl begins to drag along the fluid in the driven bowl. Dense oil rings form between the partitions of the bowls, which press on the partitions of the driven bowl and force it to rotate together with the leading one. This ensures a smooth start of the car. However, all torque converters are late, and the car starts moving with a short period of time. Therefore, fluid couplings and automatic transmissions are not used in sports or racing cars, where even hundredths of a second matter. Up to and for skilled drivers, driving a conventional manual clutch transmission is a pleasure. Although a fluid coupling makes driving a car easier, its design is quite complex, as is its production, so previously fluid couplings were only used on expensive cars with sufficient power reserves. As engines improved, fluid couplings became widespread in medium and small cars, and the widespread use of automatic clutches and gearboxes is probably a thing of the future. (Alexander Novikov)