Hi all! Finally, I was able to devote some time to Nine. This time I decided to clean up the mess under the hood. I decided that for this I should start with the sink. Last year I washed it myself using two compounds (more details here www.drive2.ru/cars/lada/2...4062246863888394058/#post). And now I decided to entrust this matter to the professionals from the car wash. Bottom line
Of course, now it’s much better quality and cheaper (200 rubles, versus 300 rubles for two cans of cleaner). By the way, as a bonus, they treated the engine compartment with a special polymer composition that prevents dirt and dust from sticking to the treated parts. They said that next time the same cleanliness could be achieved by blowing out the engine with compressed air. Well, wait and see.
The next stage is soundproofing the hood (how nice it is to tinker under the hood clean!). The initial state:
Location of the main components of the car
The power unit is located in the engine compartment under the hood; it occupies most of the engine compartment. The power unit is the engine along with the clutch, gearbox (clutch and gearbox are elements of the transmission) and the starter and generator installed on the engine.
The engine includes systems that enable it to operate. These include lubrication, cooling, power and exhaust systems. The operation of the injection engine is controlled by the ECM (electronic engine management system). In addition, the car has an engine starting system (starter, electrical circuits and switching devices) and a power supply system (generator and battery). The last two systems belong to the group of electrical equipment elements.
Engine compartment of a VAZ-2109 car with a carburetor engine
1 – windshield washer reservoir and tailgate glass; 2 – upper support of the rack; 3 – air filter housing; 4 – brake system hydraulic reservoir; 5 – expansion tank of the cooling system; 6 – battery; 7 – gearbox (not visible); 8 – engine.
Engine compartment of a VAZ-21099 car with an injection engine
1 – windshield washer reservoir; 2 – upper support of the rack; 3 – receiver; 4 – brake system hydraulic reservoir; 5 – expansion tank of the cooling system; 6 – battery; 7 – air filter housing; 8 – gearbox; 9 – engine.
What's under the hood? (for Dummies")
So, it all started with my purchase of a car (the choice fell on the VAZ 2107). And as you know, purchasing a car obliges the owner (to begin with) to understand at least a little about its maintenance and, accordingly, repairs. But for me (a novice car enthusiast) everything that was under the hood was a huge secret. Of course, experience is gained over the years, and since I didn’t have the latter (and I knew very little, practically nothing about the “insides” of the car), little by little I began to understand the design features of my Zhiguli. Therefore, so that to my colleagues (novice car enthusiasts) the engine compartment and everything in it does not seem too “dark”, in this article I will tell you what is where and what is responsible for what.
1 - radiator; 2 - battery; 3 - suction pipe; 4 — thermostat; 5 — mounting block of relays and fuses; 6 — air filter; 7 — oil filler plug; 8 — vacuum brake booster; 9 — brake system reservoir; 10 — hydraulic clutch release reservoir; 11 — expansion tank of the cooling system; 12 — washer reservoir; 13 — radiator cap (plug); 14 — ignition coil; 15 — electric fan; 16 — upper radiator hose; 17 — breaker-distributor; 18 — cylinder head cover.
Bottom view
The front of the car.
The levers, braces and anti-roll bar of the front suspension are clearly visible (like the front wheels, they belong to the group of chassis elements).
1 – front wheel suspension arm (chassis); 2 – lever extension (chassis); 3 – engine (sump pan with oil drain plug); 4 – gearbox; 5 – front wheel drive shaft (front wheel drives belong to the transmission); 6 – anti-roll bar (chassis); 7 – exhaust system (exhaust system).
The back of the car's underbody.
The beam is clearly visible, the shock absorbers and springs of the rear suspension are partially visible.
The main muffler of the exhaust system is located next to the wheel. At the rear of the car, behind the rear suspension beam, you can see a niche in the bottom of the trunk, which houses the spare wheel. 1 – shock absorber;
2 – rear suspension beam (chassis); 3 – fuel filter of the power supply system (only a car with an injection engine); 4 – main muffler of the exhaust gas system; 5 – niche in the bottom of the trunk for a spare wheel.
Car engine structure
The cars are equipped with four-cylinder, four-stroke carburetor engines of various cylinder capacities, with an in-line arrangement of cylinders and a camshaft located on the cylinder head. The engine is specifically designed for transverse mounting in a front-wheel drive vehicle. Therefore, its layout and main dimensions were chosen such that it, together with the gearbox, could be placed transversely between the mudguards of the front wheels. Three unified engines with a working volume of 1100, 1300 and 1500 cm 3 are formed by a combination of three blocks of different heights and diameters of the cylinders, two cylinder heads with intake ports of different diameters, as well as two pistons differing in diameter (76 and 82), and two crankshafts shafts with crank radii corresponding to piston strokes of 60.6 and 71 mm.
When assembled with the gearbox and clutch, the engine forms a single rigid unit - the power unit. It is installed on the car on three elastic supports. They perceive both the mass of the power unit and the loads that arise when the car starts, accelerates and brakes. Elastic supports absorb vibrations from a running engine and do not transmit them to the body, thereby reducing noise inside the car. On the other hand, elastic supports protect the power unit from sudden impacts when the car moves over uneven roads.
The car uses a three-point mounting scheme for the power unit, consisting of front, rear and left supports. The front and left supports have the same structure and consist of an outer steel ring and an inner aluminum bushing, between which there is rubber vulcanized to them.
Where is the fuel pump located on the VAZ-21099 injector
Removing and installing a gasoline pump (PG) is not a difficult job and does not require extensive plumbing experience or high qualifications. But if you don’t have to look for a fuel pump on carburetor cars for a long time (it is located on the engine, under the hood), then a beginner may not find it on the injector on the first try. Where is the fuel pump located on the VAZ-21099 sedan injector? Let's figure it out step by step:
- we move the front seats in the car forward as much as possible to free up space in the rear;
- open the rear left door of the car, find a small hinge on the rear sofa, which is located at the junction of the “seats” approximately in the middle of the cabin;
- pull the loop up, thereby raising the back of the lower seat;
- under the carpet we see the gas tank flap;
- unscrew the two fastening screws, remove the hatch and find the fuel pump underneath.
Where is the mass of the VAZ-21099 injector (main)
If the starter turns weakly, or the engine does not start at all (clicks occur when starting), various electrical problems arise, it is likely that the car does not have normal weight. Fixing such a problem is generally not difficult, but to do this you still need to know where the mass of the VAZ-21099 injector is located.
The main mass (thick) wire goes from the negative terminal of the battery to the engine, the thinner wire is connected to the car body, all energy consumers in the car depend on this connection. If the contact is poor, the battery stops charging normally; in order for the starter to turn well, you should check the reliability of these contacts and clean the metal from oxidation. If, due to a heavy load (for example, when installing additional equipment), the ground wire heats up and there is clearly not enough of it, you can “lay” additional ground almost anywhere where good contact between the engine and the body is ensured. The main thing is that this wire has a sufficient cross-section.
Where is the starter relay located?
Just like the engine cooling fan, the starter is controlled by a relay, and its malfunction can cause problems:
- when you turn the ignition key, nothing happens, the engine does not show any signs of life;
- When I try to start the engine, clicks are heard, but the starter does not crank.
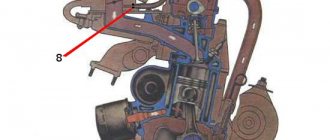
Finding out where the starter relay is located on a VAZ-21099i car is very simple; to do this, you just need to open the hood of the car and look behind the air pipe of the injection engine; the part you are looking for is shown below in the picture.
Electrical diagram of VAZ 2109: required reading
“Nines” are one of the most popular domestic front-wheel drive cars in Russia. They are inexpensive and relatively easy to repair. Often they are serviced by the owners themselves, vehicles are tuning items, they turn into a hobby for their owners. Owners install new equipment on their cars. The electrical circuit diagrams below will be very useful during repairs.
The VAZ 2109 electrical diagram will always help car owners check which instruments and devices are out of order. To find out, you need to check them with a “tester”. Having identified any problems, you can repair the machine yourself.
Where is the temperature sensor located?
If the temperature sensor does not show on the instrument panel, there is a high risk of overheating the engine, since the instrument panel does not inform the driver about the heating of the internal combustion engine coolant. Of course, the instrument panel or electrical wiring may be faulty, but most often the temperature sensor (DTOZH) on the engine itself refuses to work.
Where is the temperature sensor located on an injection car 099? Of course, you need to look for it in the engine compartment:
- open the hood;
- we find the wiring that is located between the rear of the engine valve cover and the air filter housing;
- where the DTOZH is located can be seen in more detail in the following photos.
Where is the speed sensor located?
The speed sensor (DS) on front-wheel drive VAZ cars reads pulses depending on wheel speed and transmits the data to the electronic control unit (ECU). When braking the engine, the fuel supply is turned off with the help of the diesel engine and the computer, thus achieving more economical operation of the internal combustion engine. If the sensor is faulty, an error code is recorded, gasoline consumption increases slightly, and idle speed decreases, especially during heavy braking. It is difficult to immediately detect where the speed sensor is located, since it is hidden under the air filter housing (AFC).
Where is the fuel filter located?
The fuel filter (TF) on the VAZ-21099i is designed to clean gasoline from debris, dirt and various impurities; it is a monolithic structure with a rigid metal body and a filter element inside. The frequency of its replacement is every 20-30 thousand km of the distance traveled, also if the car begins to move jerkily, and diagnostics showed that the fuel pump is clogged.
It’s easy to find out where the fuel filter is located; to do this, you need to install the car on an inspection hole or a car lift. The TF is located on the bottom of the body, next to the rear beam and the gas tank, and is secured with a special clamp, which is tightened with a bolt and nut.
Before you start changing the filter, you need to relieve the fuel pressure, otherwise when you unscrew the fuel fittings, gasoline will splash under high pressure. You can relieve pressure in the line using a special nipple located at the rear of the fuel rail. Before starting such an operation, it is necessary to prepare a plastic container into which gasoline should be poured, then unscrew the safety cap.
To release the pressure, you can use a standard flat-head screwdriver; when you press the nipple valve, gasoline will come out of the system.
After removing fuel from the line, we proceed to replacing the fuel pump.
Related articles:
- The VAZ-2109 starts and stalls: causes of malfunction, solution to the problem The VAZ-2109 model with a carburetor engine is an unpretentious Russian car, characterized by a low price, economical fuel consumption, high maintainability, very good […]
- Front spar of the VAZ-2109 - replacement, repair, cost of work The VAZ-2109 is a car that does not have a strong body; iron corrodes quite quickly, and almost all body parts rust. Replacement of the front side member is required […]
- Self-repair of the underbody of a VAZ-2110 car The car body is subject to corrosion over the years, and it begins to rust especially quickly if you do not take care of it and do not apply an anti-corrosion coating. How soon do they begin to cover […]
VAZ 2109 injector diagram: how it works
In 1997, they began producing 2109-20 cars, which are equipped with an engine with a distributed injection system (injector). This improves their efficiency, environmental and traction performance. Distributed injection is so called because fuel is injected directly into each cylinder by a separate injector.
Such a system makes it possible to somewhat reduce the toxicity of exhaust gases, as well as improve the driving performance of the 2109 car. Today, there are injection systems without feedback and with feedback. Both presented systems can include domestic and imported components. Each system has its own design, repair and diagnostic features.
I would just like to note the main principles of the design, normal operation, engine repair (if necessary) and subsequent diagnostics of the fuel injection system (the VAZ 2109 injector diagram is presented below).
The automotive fuel injection system, which has feedback, is used mainly on export VAZ 2109. The exhaust system of these cars is equipped with a catalytic converter for exhaust gases and an oxygen sensor. It provides feedback. Using an oxygen sensor, the oxygen concentration in already exhaust gases is monitored.
Next, the electronic control unit (ECU) of the vehicle, according to its signals, maintains the appropriate ratio of fuel and air, that is, one at which the special converter works extremely efficiently. The injection system, in which there is no feedback, is not equipped with a converter and an oxygen sensor.
Their function (regulating the concentration of CO in already completely exhausted gases) is performed by a CO potentiometer. They also do not use a gasoline vapor recovery system.