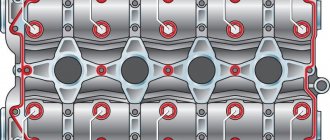
The order and tightening torques of the cylinder head bolts on a VAZ.
This order is necessary in order to correctly dock the cylinder head and cylinder block. To avoid distortions and excess metal tension.
Diagram and procedure for tightening the cylinder head on a VAZ 2101 - 07 (classic)
The cylinder head bolts are tightened in two steps.
First run: bolts 1 – 10 are tightened to a torque of 3.5 – 4.1 kgf*m.
Second pass: the same bolts, but tightened with a torque of 10.5 - 11.5 kgf*m
Bolt 11 is tightened last, with a torque of 3.5 - 4.0 kgf*m.
The procedure for tightening the block head of VAZ 2108 - 09, Samara.
The tightening order is similar to the classic one, also starting from the center.
But it is carried out in 4 steps.
1. Bolts are tightened to a torque of 2.0 kgf*m
2. Tighten to a torque of 7.5 – 8.5 kgf*m
3. The bolts are turned 90 degrees.
4. Once again turn 90 degrees.
The procedure for tightening the block head of 16-valve VAZ engines.
Same as everyone else, from the center.
1st reception – 2.0 kgf*m
Step 2 – tighten the bolts 90 degrees
Step 3 – tighten the bolts again by 90 degrees.
Attention! On 16-valve engines, reuse of cylinder head bolts is allowed, BUT if their length without head does not exceed 95 mm. If the bolt length is more than 95 mm, it must be replaced.
The length is measured with a washer.
To work you need to use a torque wrench
Its cost is from 600 rubles, more professional ones from 1300 or more.
From time to time, the cylinder head gasket may fail due to wear and tear of its material or burnout. The main signs that it is time to replace the gasket with a new one are the appearance of local leaks of oil and coolant at the point of contact between the cylinder head and the engine.
It should be remembered that when replacing a gasket, not only the tightening torque of the VAZ 2114 cylinder head is important, but also the entire sequence of operations - after all, the replacement itself is a very important and serious procedure, errors during which can lead to engine malfunction.
Required Tools and Process
In order to do it correctly, you will need:
- set of socket heads;
- extension;
- ratchet/wrench;
- torque wrench.
The replacement process itself should be performed according to the following scheme:
- Disconnect the wires leading to the emergency oil level and coolant temperature sensors.
- Drain the coolant.
- Remove the thermostat.
- Remove the air filter housing.
- Disconnect the exhaust pipe inlet from the manifold.
- Remove the casing, as well as the camshaft belt itself.
- Disconnect the drive rods of both dampers from the carburetor.
- Disconnect the wires going to the cylinder head.
- Disconnect the hoses suitable for the cylinder head by loosening their clamps.
- Remove the cylinder head.
- Remove the worn gasket.
- Clean the contact surface of the cylinder head from any remaining gasket material.
Installing the gasket and mounting the cylinder head in place is carried out in exactly the same sequence, but in reverse order. At the same time, it is worth paying close attention to such a factor as the tightening torque of the cylinder head of the VAZ 2114 8 valves - we will talk about it below.
Installation and dismantling procedure
The part called the cylinder head is attached to the cylinder block with 10 screws. They are unscrewed with a 10mm socket wrench. The procedure for dismantling the cylinder head is shown in the first photo.
Reversal sequence (1-10)
The standard screw length is 9 3 mm. If the screw has been pulled out to at least 95 mm, it is replaced with a new one (AvtoVAZ requirement).
During installation, a different scheme is used (photo 2). Each screw is lubricated with machine oil, otherwise the efforts will be reduced to nothing.
The order of tightening the head is indicated in this photo
Tightening torque for cylinder head cover bolts
For VAZ-2112, the cylinder head tightening torque is standardized:
- First pass – the force is 20 N*m;
- Each screw is turned 90 degrees to the right;
- Wait 20 minutes, then turn the screws another 90 degrees.
At first the effort is very small. But at “step 3” it will be difficult to cope with the work. Use the lever.
Why are guide bushings needed?
Before installing the cylinder head, perform the following steps: clean the threaded holes, as well as all holes for the bushings (photo 1). Each bushing is installed in place, and only then a gasket is placed on top.
Everything is ready to install the cylinder head
Metal parts adjacent to the gasket must be degreased. We looked at the cylinder head tightening diagram, but the cylinder head itself must be installed correctly:
- We place the cylinder head on the cylinder block;
- By moving the part in different directions, we ensure that the bushings fit into the recesses.
After “step 2” the screws can be tightened.
Sealant
No sealing compounds are used when installing the gasket! Solidol, CIATIM and other lubricants are not even needed. The main thing is that the metal must be degreased. And the cylinder head gasket must be new.
How to tighten cylinder head bolts correctly?
Before you begin installing the cylinder head, you should first pay attention to the condition of its bolts. They must have a good thread and the length meet the required standards.
The normal overall length of the cylinder head bolt is 135.5 mm. If the bolts removed during gasket replacement meet this parameter, they can be reused. If the bolts have lengthened during engine operation, then they can no longer be used and new ones should be purchased.
Having dealt with the bolts in this way and installing them in place, you should proceed to tightening. It must be done only with a torque wrench. Tightening bolts “by eye” can lead to very serious consequences, including damage to the engine itself.
And so, how to stretch the head onto a VAZ 2114 correctly? Firstly, you should remember that you should start tightening the bolts from the center to the edges.
This diagram looks like this:
Secondly, tightening should be done in four stages (each of which is performed in exactly the same sequence as indicated in the diagram above).
At the first stage, we tighten each of the bolts with a torque wrench with a force equal to 2 kgf/cm2.
At the second stage, we tighten all the bolts with a force of 8 kgf/cm2.
At the third stage, we tighten the bolts, turning each of them at an angle of 90 degrees.
At the fourth stage, we again turn each of the bolts (still following the diagram given at the beginning) at an angle of 90 degrees.
Once all four steps are completed, tightening the cylinder head bolts can be considered complete.
The tightening of cylinder head bolts should be taken as seriously as possible. All its stages must be performed strictly in the same order and with equal effort at each of them. Failure to comply with this rule can lead to rapid wear of the gasket and the appearance of oil and coolant leaks.
What is needed to replace the cylinder head gasket of a VAZ 2110 (8 valves)
Required tools:
- ratchet with 10mm socket heads; “at 13”, “at 17”, “at 19”;
- wrench with Torx bit;
- screwdriver;
- torque wrench;
- wrench for removing spark plugs.
Suitable accessories:
- the TRIALLI gasket set has the article number GZ1017022, its price is 500 rubles;
- The VICTOR REINZ cylinder head gasket has article number 613666000, its price is 280 rubles;
- The original VAZ cylinder head gasket (VATI) has article number 21083100302020, its price is 140 rubles.
The price of gaskets is relevant for the summer of 2017 for Moscow and the region.
Set the piston of cylinder 1 to the TDC position on the compression stroke. We fix the camshaft toothed pulley from turning with a clamp. We unscrew the candles.
How to properly tighten the cylinder head bolts?
A) Using a 10mm wrench, unscrew the two nuts securing the throttle drive cable bracket to the receiver and remove it. B) Remove the crankcase ventilation hoses and the supply hose from the valve cover fittings. C) Using a 10mm wrench, unscrew the two nuts securing the valve cover and remove it.
Using a 10mm wrench, unscrew the bolts of the front timing cover: two on the side and one in the center. Remove the timing cover.
We check the coincidence of the mark on the camshaft timing pulley with the installation antenna on the rear cover of the timing drive. Using a 17 key, unscrew the pulley.
Using a 10mm wrench, unscrew the nut securing the protective casing and bend the casing.
We see that the timing belt also requires replacement.
Disconnect the oil level pressure sensor connector.
Using a 10mm wrench, unscrew two nuts and one bolt securing the plug. Evenly, using a 13mm wrench, unscrew the six nuts securing the rear camshaft bearing housing. Remove the rear camshaft bearing housings from the studs.
Then, also evenly and using a 13mm wrench, unscrew the four nuts securing the front camshaft bearing housing and remove it.
Unscrew the four nuts securing the muffler to the exhaust manifold.
Cylinder head and valve mechanism (eng.) (disassembly, repair, replacement of cylinder head gasket)
Using an E14 Torx head, unscrew the 10 bolts on the cylinder block and remove the block.
The order and tightening torques of the cylinder head bolts on a VAZ.
This order is necessary in order to correctly connect the cylinder head and the cylinder block. To avoid distortions and excess metal tension.
Diagram and procedure for tightening the cylinder head on a VAZ 2101 - 07 (classic)
The cylinder head bolts are tightened in two steps.
First run: bolts 1 – 10 are tightened to a torque of 3.5 – 4.1 kgf*m.
Second pass: the same bolts, but tightened with a torque of 10.5 - 11.5 kgf*m
Bolt 11 is tightened last, with a torque of 3.5 - 4.0 kgf*m.
The procedure for tightening the block head of VAZ 2108 - 09, Samara.
The tightening order is similar to the classic one, also starting from the center.
But it is carried out in 4 steps.
1. Bolts are tightened to a torque of 2.0 kgf*m
2. Tighten to a torque of 7.5 – 8.5 kgf*m
3. The bolts are turned 90 degrees.
4. Once again turn 90 degrees.
The procedure for tightening the block head of 16-valve VAZ engines.
Same as everyone else, from the center.
1st reception – 2.0 kgf*m
Step 2 – tighten the bolts 90 degrees
Step 3 – tighten the bolts again by 90 degrees.
Attention! On 16-valve engines, reuse of cylinder head bolts is allowed, BUT if their length without head does not exceed 95 mm. If the bolt length is more than 95 mm, it must be replaced. The length is measured with a washer
The length is measured with a washer.
To work you need to use a torque wrench
Its cost is from 600 rubles, more professional ones from 1300 or more.
Some owners of domestic cars do not know that the cylinder head gasket needs to be changed every time the cylinder head is removed. You should never install an old part, since this spare part is disposable.
Replacing the cylinder head gasket on an 8-valve VAZ engine is almost the same as the same work for a 16-valve engine, so this article will also be useful to owners of cars with more modern engines.
Replacing the cylinder head gasket of a VAZ 2111
Useful video
You can glean additional useful information from the video below: Well, at the end, we should once again remind you that before you start tightening, you need to check the length of all bolts (it should be 135.5 mm). If the length differs from the specified one, especially upward, then even the most careful tightening of such bolts will make no sense.
A number of repairs to the car’s power unit involve removing the cylinder head. Dismantling the cylinder head does not cause any particular difficulties, but fitting the unit into place when assembling the engine requires full compliance with the installation technology, in particular the tightening of fasteners.
Replacing the cylinder head gasket on a VAZ 2109
At the end of the operational period or if the integrity of the cylinder head gasket is damaged, the element must be replaced.
The main sign of a malfunction or gasket wear is the formation of coolant and oil leaks at the junction of the engine block and the cylinder head.
Cylinder head seals
To change the gasket, you will need to dismantle the assembly, get rid of the worn cylinder head gasket and reassemble the structure in the reverse order, following the recommendations regarding the tightening torques of the cylinder head bolts. We will tell you about all this in more detail.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=pW9OyNFXEcU
- Disconnect the wiring from the coolant temperature sensor and emergency oil pressure sensor.
- Remove the thermostat, just remember to drain the coolant first.
- Remove the air filter housing. There is no need to remove the carburetor, because it will not interfere with replacing the gasket.
- Disconnect the exhaust pipe from the exhaust manifold.
- Remove the camshaft drive gear after first setting the piston of the first cylinder to the TDC position. Now you can remove the protective casing of the camshaft drive belt, loosen the gear fixing bolts, securing the gear from turning.
- Remove the camshaft drive belt. Then you can completely unscrew the mounting bolts and remove the gear.
- Press the latch to disconnect the wiring block from the ignition distributor.
- Similarly, turn off the central high voltage.
- Loosen the clamps to remove the fuel supply hose from the fuel pump.
- Disconnect the throttle and air damper drive rods from the carburetor.
- Disconnect the power supply from the solenoid valve.
- Remove the vacuum booster hose from the intake pipe fitting.
- Disconnect the tube from the vacuum ignition corrector.
- Loosen the tension on the clamps to remove the interior heating hoses from the pipes.
- Remove the cylinder head. Using a socket with an extension, the mounting bolts are unscrewed.
- Rock the head a little jerkily, then remove the element.
- Remove the old gasket, clean it of any remaining rubber seal and other contaminants. Wipe dry thoroughly, after which you can reassemble.
- Before assembly, check whether the length of the cylinder head bolts is within the normal range. Ideally, their length is 135.5 millimeters. If the bolts have lengthened during use, then all bolts will have to be replaced.
Replacement procedure
Reassembling the unit if you strictly follow the instructions for dismantling work will not pose any particular problems.
An incredibly important aspect of replacing the cylinder head gasket and all other activities associated with removing the head is the correct adjustment and tightening of the bolts.
Tightening the bolts is done strictly with a torque wrench, which will allow you to control the tension torque.
Here are some guidelines for using this specialized wrench and checking the current tension condition:
- Place the holder in the zero position. This will indicate that now the key data is equal to the moment of the original position;
- Look at the torque tool readings as you begin to tighten the bolts;
- Rotate the holder, monitor the indicators;
- If the torque does not change, the fastener may be stretchable, which is normal. This is exactly what should happen;
- If the torque increases rapidly, bolt movement should be achieved. That is, the stretch of the holder is small, it needs to be stabilized.
How to Correctly Tighten a Cylinder Head Without a Special Wrench
Golden rules of tightening
To properly reassemble the cylinder head, you need to adhere to the golden rules:
- Strictly follow the tightening torque data corresponding to the VAZ 2109;
- Make adjustments only using a torque wrench. Other tools do not allow you to get the desired result;
- To install the cylinder head, use only serviceable bolts that meet the requirements of your engine installed on the VAZ 2109;
- Before work, make sure that the holders are in good condition.
Checking the bolts
Tightening diagram
In addition to observing the required tightening torques for the cylinder head mounting bolts, one more rule must be observed here.
Returning the bolts to their places is carried out strictly according to the diagram below.
Tightening sequence
Next, do the work according to the table, and you will do everything right.
Tightening is performed in four circles, following the sequence of work with the mounting bolts indicated in the diagram.
Consequences of incorrect cylinder head installation
Correct tightening of the cylinder head is very important, since the performance of the motor directly depends on it. The cylinder head acts as a cylinder cover, and any violations in its fit affect the processes occurring inside the power unit.
Insufficient tightening of the head leads to a drop in compression due to loss of tightness at the junction of the cylinder head with the cylinder block, burnout of the gasket, breakthrough of working gases from the cylinders and their entry into the channels of the lubrication or cooling systems, penetration of technical fluids into the combustion chambers, which in turn is negative affects the functioning of the power unit and can cause very serious damage.
Excessive tightening also does not bring anything good; in this case, damage to the head often occurs - cracks appear, or fasteners are destroyed - bolts break, threads break, etc.
Uneven or incorrect tightening often causes warping of the head, due to which gaps appear at the junction of it with the block, which leads to the same consequences as insufficient tightening.
Part Features
The cylinder head is a structurally quite complex part. It is a massive plate in which there are channels for the circulation of fluids of the lubrication and cooling system, and technological holes - spark plugs, for injectors (in diesel engines), mounting holes.
Also on top of the cylinder head there is a so-called “bed” of the camshaft - a seat for its installation.
Despite its massiveness, the block head is a fragile part due to the voids inside, so excessive tightening force often leads to cracks in the walls and bridges.
For the manufacture of cylinder head, two types of metals are used - aluminum (the most common) and cast iron.
To secure the latter, steel bolts or studs with nuts are used. For example, the head of the UAZ 31519 block is secured with studs.
The difference in the materials used to make the head and its fasteners has one negative factor - different thermal expansion of the components when heated, especially for aluminum cylinder heads.
Uneven tightening of fasteners (nuts, studs, etc.) during thermal expansion leads to the appearance of excessive stress in the metal structure, resulting in warping of the head.
In what cases is it necessary to tighten the block?
It becomes necessary to tighten the bolts if the cylinder head was removed to change the gasket or repair some components. Also, some car owners recommend tightening after a certain period of operation of the car or after a certain mileage of the VAZ 2110. It is important to know that before installing the head it is always recommended to install a new gasket.
Reinstalling an old one, even if it is in good condition, may not give the desired result. A new gasket is inexpensive and for VAZ 2110 cars they are sold in almost all car stores. You also need to know that the bolts that secure the cylinder head wear out over time and, under constant stress, can even stretch to some extent. Re-installation of bolts is permissible, but only when their length is no more than 9.5 centimeters.
Bolt tightening conditions
When installing the cylinder head, it is important to comply with the tightening technology, which includes a number of criteria:
- Tightening order;
- An effort;
- Condition of fasteners (for example, studs with nuts);
Each engine has its own tightening order, which must be followed to ensure uniform tightening of the head to the block and to prevent the occurrence of stress on any surface areas. For example, on a VAZ 2105 it looks like this.
Force is another important factor for the correct fastening of this engine element. Attracting the plate is carried out in several approaches (their number differs on different motors), each of which is performed with its own force.
The cylinder head fasteners are tightened with quite a lot of force, which leads to them being pulled out. Therefore, on many engines, bolts cannot be reused; they must be replaced. But there are also motors for which replacement of fasteners is not necessary and their re-installation is possible.
General rules for performing work, methods used
There are a number of general rules that must be followed when installing the block head:
- It is important to strictly observe the tightening torque. For these purposes, a special tool is used - a torque wrench. It is not recommended to perform this operation with regular keys;
- The head bolts must be pulled smoothly, jerking is not allowed. Since the tightening force on the last approaches is significant, extending the wrench arm with a pipe can simplify the procedure and ensure smooth, uniform tightening;
- Before installing the bolts, you need to carefully inspect the condition of the threads on them. There should be no dirt or foreign particles on the coils.
- The threads of fasteners should be lubricated with engine oil before tightening. But you should not pour grease into the holes for the bolts (especially for “blind” holes), since in the future it will not allow the fasteners to be fully tightened.
Despite the fact that each engine has its own characteristics of tightening the cylinder head, the general technology of this operation is the same. In general, two methods are used to tighten fasteners:
- In several approaches, bringing the tightening force to the required value;
- Tightening the fasteners to a certain force (in one or more approaches), and then tightening the bolts twice to a certain angle.
The tightening method is selected based on the type of bolts.
The first method is used when using non-stretching bolts (these are not used now, but they can be found on old cars). But often this type of fasteners requires tightening after a certain period of engine operation in order to compensate for the shrinkage of the cylinder head gasket. But such fasteners are allowed for reuse, and more than once.
The second method of tightening the block is relevant for most modern cars. And all due to the use of tensile bolts (the so-called TTY type).
Such fasteners, due to elastic deformation, are able to compensate for thermal expansion of the head and shrinkage of the gasket, but for this they need to be put into deformation mode (in fact, just stretched a little).
To do this, it is necessary to tighten the bolts twice to a certain angle. On some cars this angle is 45 degrees, on others it is 90 degrees.
But after the elements are put into elastic deformation mode, they will no longer be able to return to their original state, and therefore their reuse is not allowed due to the high probability of destruction.
General procedure
Although tightening the cylinder head has many nuances and features, the general technology of the operation is not complicated, it is only important to comply with the conditions.
The general algorithm of work is as follows:
- We study the documentation (tightening order and force);
- We prepare the tool;
- We inspect and wipe the surfaces of the block and head, clean the mounting holes (with a rag or compressed air);
- We lay the gasket;
- We put the block head in place (the correct placement of the gasket and head is ensured by guide bushings);
- Lubricate the threads of the fasteners;
- We install the latter in the holes and tighten them by hand;
- We specify the drawing scheme, the number of approaches and the force of each of them, as well as the time of breaks between approaches (all this is indicated in the documentation);
- We make the first approach, observing the tightening order (for convenience, you can mark the bolts according to the order with a marker). In the photo is a VAZ 2103;
- We carry out all subsequent approaches.
Some vehicles additionally require re-tightening of fasteners after a certain period of vehicle operation. This information must be indicated in the technical documentation.
Some nuances
The tightening torque is one of the main factors for the normal fit of the block head. But this criterion is influenced not only by the applied force, but also by the fasteners themselves:
- General condition of the bolts – new or used;
- Presence of lubricant on the threaded part;
- Thread condition.
The type of power plant (petrol, diesel), as well as the number of valves, does not affect the cylinder head tightening technology. But this does not mean that the force and tightening procedure are identical for all motors, and before seating the head, you should definitely study the conditions for performing the operation and all its features.
Common Mistakes
Despite the fact that automakers clearly indicate the procedure and nuances of tightening the cylinder head, many car enthusiasts make mistakes when assembling the engine. The most common of them are:
- Pouring oil into the mounting holes to lubricate the threads (the liquid is incompressible, so poured oil will not allow the head to be properly tightened);
- Over-tightening (exceeding tightening forces leads to damage to the cylinder head and the fasteners themselves);
- The use of damaged or inappropriate keys (the edges of the bolt heads may be torn off, after which it will be problematic to tighten or unscrew them normally);
- Use of unsuitable bolts as replacements (fasteners from different engines may differ in length, thread spacing, head height and diameter);
Features of the work performed using the example of some cars
To prove the proposition that each power plant has its own characteristics of tightening the cylinder head, let’s consider the nuances of performing work on specific models.
VAZ-2112 16 valves
A number of modifications of the VAZ-2112 were equipped with two types of 16-valve power plants (factory indexes - 21120 and 21124). These two motors, despite some design features, have identical head tightening technology.
These units use 93mm long tension bolts. In this case, reuse of fasteners is allowed, but under one condition - if their length does not exceed 95 mm (if it is longer, they should be replaced). 10 bolts are used to secure the head.
Tightening is carried out in three approaches:
- The bolts are tightened according to the order with a force of 2 kg/m;
- Turning 90 degrees;
- Repeated tightening to 90 degrees.
The drawing diagram is shown below.
Between the 2nd and 3rd approaches you need to take a 20-minute break.
Since these engines use tensile bolts, additional tightening is not required during vehicle operation.
VAZ-2107
On the VAZ-2107, all installed modifications of power units are 8-valve.
The block head is attached to them with 11 bolts, 10 of which are main, and 1 is an auxiliary side bolt (installed in the side protrusion).
On this car, tightening fasteners is also performed in three approaches:
- 10 main bolts are tightened in order with a force of 3.5-4.0 kg/m;
- The same bolts reach with a torque of 11.5-12.0 kg/m;
- The auxiliary is tightened with a force of 3.5-4.0 kg/m.
Additional tightening of the cylinder head is not required when operating the VAZ-2107.
"Samara", 10th family, Priora
On models of the Samara family (2108-21099), as well as VAZ 2110-2112 with 8-valve units, tightening is already performed in 4 approaches:
- Tightening with a force of 2.0 kg/m;
- Reaching with a moment of 7.5-8.5 kg/m;
- Turn 90 degrees;
- Repeated rotation by 90 degrees.
The break between points 3 and 4 is 20 minutes.
As for the VAZ of the “tenth” family, which are equipped with 16-valve engines, their tightening technology is the same as that of the VAZ-2112 (described above).
The same applies to the Lada Priora; on 8-valve units, a method with 4 approaches is used (VAZ 2108-21099), and on 16-valve units, 3 approaches are used (VAZ 2112 with a 16-valve engine).
"Volga"
On ZMZ-406 engines installed on the Volga, according to the automaker’s technical documentation, tightening the engine block head bolts is carried out in two approaches:
- With a force of 4.0-6.0 kg/m;
- With a moment of 13.0-14.5 kg/m.
But many car owners of this car note that this technology does not allow the cylinder head to be properly tightened, so they use techniques with a large number of approaches.
A common method is the cross method, performed in 4 stages and with the following efforts:
Subsequent tightening of the bolts is not required when operating on this engine.
Cylinder block for VAZ 2110: we repair it ourselves
VAZ 2110 car engine
It's no secret that the main component of any car is the engine. And its main component is the cylinder block. How well all the parts of the VAZ 2110 cylinder block are working depends on the operation of the entire unit and the safety of driving the car. The article suggests getting acquainted with the procedure for performing repair work on a cylinder block with your own hands.
Features of VAZ 2110 car engines
Manufacturers produce engines for the VAZ 2110 in two modifications:
- In one VAZ 2110 cylinder block, 16 valves together with the gearbox form a power unit. This is a four-stroke and four-cylinder engine, running on gasoline, in-line, located transversely in the engine compartment. The design has sixteen valves and two camshafts. The cylinders operate in this order: 1-3-4-2, the countdown begins from the crankshaft pulley. Phased distributor injection provides power to the system. The controller controls the engine. Most devices are equipped with an exhaust gas converter.
- In another design - a VAZ 2110 cylinder block with 8 valves. Unlike the first type of device, the engine has eight valves, one camshaft. Carburetor power system.
General features of nodes:
- All cylinder blocks are made by casting, the material is special low-alloy cast iron.
- The cylinder diameters have five accuracy classes, which are divided every 0.01 millimeters. And they are designated by the letters A, B, C, D, E. On the lower plane of the cylinder block, its class is stamped.
- It is possible to repair pistons with cylinder bores, which can be increased in diameter by 0.8 or 0.4 millimeters.
- The main bearing caps are not replaceable and must be processed together with the cylinder block. They can be distinguished by the marks on the outer surface.
Diagnostics of the technical condition of the VAZ 2110 cylinder block
Before checking the parts of the assembly, it must be thoroughly washed and the oil channels cleaned. To do this, all elements must be blown and dried with compressed air:
- The cylinder block for the VAZ 2110 is visually inspected for cracks in the supports and other places. They are not allowed.
Cylinder block VAZ 2110
- If you suspect that coolant has entered the crankcase, you need to check the tightness of the unit on a special stand. In this case, the holes located on the jacket intended for cooling the cylinder block assembly are plugged, and water at room temperature is pumped into it under a pressure of 3 kgf/cm. There should be no water leakage from the structure.
- If oil gets into the coolant, then, without completely disassembling the engine, check for the formation of cracks in the block in those areas where the oil channels are located. To do this, the liquid is drained from the cooling system, the cylinder head of the VAZ 2110 is removed, the cooling jacket of the assembly is filled with water and compressed air is supplied to the oil channel located vertically. If air bubbles appear, the entire cylinder block must be replaced.
- The surfaces of the block head are carefully inspected for cracks. If they are detected, the cylinder head of the VAZ 2110 is replaced.
- Using a set of feeler gauges and a ruler, the mating plane of the head and the block is checked. The ruler must be installed diagonally on the plane, then in the transverse and longitudinal directions. The deviation from flatness should be no more than 0.1 millimeter.
Performing the operation without a torque wrench
Since the force is precisely indicated on all of these vehicles, it is impossible to do without a torque wrench when seating the cylinder head. But on some cars it is quite possible to do without it and use ordinary wrenches and an extension socket to tighten it.
Let us immediately note that performing work without special equipment. The tool is allowed only on “old” engines (Moskvich, VAZ of the first models).
A feature of tightening the cylinder head without a torque wrench is the need to “feel” the force applied. Otherwise, the general method of work is the same as using special equipment. tool:
- We tighten all the bolts by hand;
- We do the 1st approach, applying medium force (we try to pull all the bolts with the same force, smoothly and without jerking). Be sure to follow the tightening order;
- We carry out the second approach, increasing the force (in order to more accurately “feel” the force, the key with an increased shoulder should be pulled “toward” rather than pushed “away”);
- We do the third approach with high force (turn until the bolt stops).
One of the options for tightening without a torque wrench is to double tighten the fasteners after completing the 2nd approach.
Since not everyone can “feel” the applied force without the skills, it is better not to use the method without a torque wrench, because the consequences of improperly tightening the cylinder head are quite serious and can lead to very serious damage.
Therefore, before engine repairs involving removing the cylinder head, you should stock up on a special tool, especially since it will not be superfluous and there will always be a use for it.
Tightening process and diagram (on an 8-valve car)
As we have already said, the procedure for tightening the cylinder head bolts on an 8-valve and a sixteen-valve unit is very similar. The tightening torque is the same in both cases, but the bolts are unscrewed and then tightened according to a completely different pattern. It is important to thoroughly clean the contacting surfaces before installing a new or old VAZ 2110 cylinder head. It is highly undesirable to do this with sandpaper, a file or other hard objects that can damage these surfaces.
Rough cleaning of the surface can lead to depressurization of the cylinder block system with ensuing dangerous consequences. For this purpose, special liquids are sold in the store. They are applied to a surface that may have remnants of an old gasket or other contaminants and are left to dry for some time. After some time, they are carefully removed and the surface remains perfectly clean.
Required Tools
Key for tightening to the required torque
- rod compass;
- surface treatment liquid;
- knob;
- new gasket;
Cylinder head gasket - new bolts;
- rags.
Stages
After installing the head, you can proceed to tightening the bolts.
- Insert all bolts into their respective slots. Important! There should be no rust on the bolts and sockets; if there is any, be sure to remove it using special liquids. You can also lubricate them to make them screw in easier.
- We begin to tighten the bolts in four circles strictly according to the diagram for the VAZ 2110 using a torque wrench.
The diagram according to which the tightening takes place
At this point, the process of tightening the GB cylinders can be considered completed, as you yourself have seen, nothing is difficult, and having completed the work once, the next time you can do it all literally with your eyes closed. The video we offer will help you better understand the process.