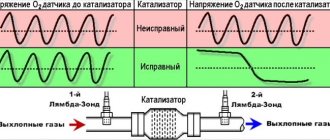
How to check the lambda probe and signs of malfunction? Will a Bosch universal fit?
- The car jerks when you drive at low speeds - 1 answer
First of all, when the lambda fails and malfunctions, several tangible consequences appear in the car’s behavior:
- Increased fuel consumption
- Unstable operation of the car engine (jerks)
- The operation of the catalyst is disrupted (toxicity increases)
Then, to check the lambda probe, you can first unscrew it and carry out a visual check (just as a visual check of the spark plugs can tell you a lot).
Several types of lambdas are installed on cars; the sensors can have one, 2, 3, 4, even five wires, but it is worth remembering that in any of the options, one of them is a signal (often black), and the rest are intended for heater (usually they are white).
What and how can you check the lambda?
To check, you will need a digital voltmeter (preferably an analog voltmeter, since its “sampling” time is much shorter than that of a digital one) and an oscilloscope, if possible, the measurements will be more accurate. Before checking, you should warm up the car since lambda operates correctly at temperatures above 300C°.
First we look for the heating wire:
We start the engine, do not disconnect the lambda connector. We connect the negative probe of the voltmeter (ordinary gauge) to the car body. We “poke” the positive probe on each wire contact and observe the voltmeter reading. When the positive wire of the heater is detected, the voltmeter should show a constant 12 V. Next, using the negative probe of the voltmeter, we try to find the negative wire of the heater. We connect to the remaining contacts of the sensor connector. If a negative contact is detected, the voltmeter will again show 12 V. The remaining wires are signal wires.
Checking the lambda probe with a tester:
We take an electronic constant voltage millivoltmeter and connect it in parallel with the LZ (“+” “-” to the LZ, - to ground), and the lambda probe must be connected to the controller.
When the engine warms up (5-10 minutes), then you need to look at the voltmeter needle. It should periodically move between 0.2 and 0.8 V (i.e. 200 and 800 mV, and if less than 8 cycles occur in 10 seconds, it’s time to change the LZ. Also replace if the voltage “stands” at 0 .45 V.
When the voltage is always 0.2 or 0.9 V, then there is something wrong with the injection - the mixture is too lean or too rich. Since the oxygen sensor voltage should change all the time and jump from ≈0.2 to 0.9V.
There is another quick way to check the lambda probe . You should do this:
Carefully pierce the positive contact of the tester (black lambda wire), the other contact to ground. With the engine running, the readings should range from 0.1 to 0.9V. Constant readings (for example, 0.2 all the time) or readings that go beyond this range, or fluctuations with a smaller amplitude indicate a malfunction of the probe.
- all the time 0.1 - little oxygen
- all the time 0.9 - a lot of oxygen
- The probe is fine, the problem is something else.
If you have the time and desire to bother, you can conduct several tests on a rich and lean mixture and additionally check the lambda probe sensor .
- Disconnect the oxygen sensor from the block and connect it to a digital voltmeter. Start the car and, by pressing the gas pedal, increase the engine speed to 2500 rpm. Using a device for enriching the fuel mixture, reduce the speed to 200 per minute.
- If your vehicle is equipped with an electronically controlled fuel system, remove the vacuum tube from the fuel pressure regulator. Look at the voltmeter reading. If the instrument needle approaches the 0.9 V mark, it means the lambda probe is in working condition. A malfunction of the sensor is indicated by the lack of response from the voltmeter, and its readings are less than 0.8 V.
- Do a lean mixture test. To do this, take a vacuum tube and provoke an air leak. If the oxygen sensor is working properly, the digital voltmeter reading will be 0.2 V or lower.
- Check the operation of the lambda probe in dynamics. To do this, connect the sensor to the connector of the fuel supply system, and install a voltmeter parallel to it. Increase engine speed to 1500 rpm. The voltmeter readings with a working sensor should be at the level of 0.5 V. Another value indicates a failure of the lambda probe.
Hyundai Accent “silver” › Logbook › Still alive or no longer alive? Lambda probe sensor.
I was puzzled by the increased gasoline consumption. I traveled 500 km to Belarus and spent 45 liters, consumption was 9 liters and that was on the highway. Well, I already realized that something was wrong. Having checked all the sensors in principle and ringing them, it turned out that the lambda probe sensor (hereinafter referred to as the oxygen sensor simply DC) reacts very inadequately. I will describe everything further and in detail.
My car uses a 4-wire DC, 2 white sensor heaters, black for signal, gray for sensor ground.
Lambda probe: check.
To check the functionality of the oxygen sensor, you will need: the factory instructions, which will tell you where the lambda probe is located, and a digital voltmeter. These are the main supporting tools. The engine should be warmed up while testing the device. 1. Next, we check the resistance on the wires of the DC heaters. At the required 2-10 ohms I have
It already seems like something is wrong. Okay, let's move on, I'll post a video on measuring voltage. We take the negative from the car body (I even tried and took the battery from the negative) and connect the plus to the black wire and set the voltage. This is what happened: Attempt No. 1
Upd: Small mini instructions. To check the oxygen sensor (lambda probe), connect the negative lead of the multimeter probe to the engine body. Identify the pins on the oxygen sensor. As I already said, there can be from one to four wires. Connect the positive lead of the multimeter probe to the signal wire of the oxygen sensor. Warm up the engine to normal temperature. Accelerate the engine to 2500-3000 rpm for 3 minutes to warm up the oxygen sensor. Run the engine at higher speeds and check that the oxygen sensor turns on. The voltage on the sensor should be from 0.2 to 1 volt and turn on at a frequency of 8-10 times every 10 seconds. If the voltage is approximately 0.45 volts and does not change, then the oxygen sensor simply does not work. Using a tester, check for battery voltage at the oxygen sensor heater power supply. If there is no voltage, check the wires going to the relay or to the ignition switch. Also check the ground connection of the lambda probe heater. — When the oxygen sensor is working and warmed up, the voltage at the signal pin should change from 0.2 to 1 volt with a frequency of 8-10 times in 10 seconds (1 Hz) at an engine speed of 2500 rpm. — When the throttle valve is opened sharply, the multimeter should show a voltage of 1 volt. — When closing the throttle suddenly, show the voltage near zero. At this point, the lambda probe testing procedure can be considered complete.
From all of the above, I still suspect that the sensor is dead. I'm waiting for your opinions and comments. M.b. There are specialists among us who will advise you. Or post your measurements, we will compare, preferably with photos and video recording)))
Upd: a small example - tap of sensor survivability and dying.
How does a lambda probe work?
The principle of operation of the oxygen sensor is to monitor the amount of air (oxygen) in the exhaust gases. Why oxygen? Because it has been scientifically proven that complete combustion of the fuel mixture occurs at a rigid fuel to air ratio of 1:14.7 . To assess this ratio, the composition of the mixture, the concept of “excess air coefficient” was introduced, which is defined as the ratio of air entering the cylinders to the amount of air contained in the optimal air-fuel mixture, which is usually denoted by the Greek letter “λ” (lambda). The formula is as follows: if “λ” is equal to “1” - the mixture is lean.
Due to the constant deterioration of the environment throughout the world, the requirements for harmful CO emissions are constantly becoming more stringent, so almost all modern engines are equipped with oxygen sensors, catalysts and other systems aimed at making the exhaust less toxic. The control unit regulates the fuel supply through the injectors and also monitors the correct operation of the lambda probe. In the event of a malfunction, a report in the form of an error will be recorded in the appropriate log, and the driver will see the hated “Check Engine” inscription on the instrument panel.
How to check the serviceability of the lambda probe will be discussed in my article today. You will learn about the signs of malfunction, the causes, and how to check the oxygen sensor at home.
Oxygen sensors come in various types, among which there are one-, two-, three-, and also four-wire ones, it all depends on the configuration (presence of a heater and power supply circuit). Almost all modern lambdas are heated.
First, let's talk about why the lambda probe fails. The reasons may be the following:
- Excessive lead content in fuel;
- Antifreeze gets inside the sensor;
- Violation of the tightness of the sensor housing during cleaning or as a result of exposure to chemicals. substances;
- Severe overheating of the sensor housing due to the use of unsuitable (low-quality) fuel.
Signs of a malfunctioning oxygen sensor:
- Jerking while moving;
- Increased fuel consumption;
- Problems with the catalyst;
- Unstable engine speed;
- High exhaust toxicity.
You can check the lambda probe in different ways, using:
- Oscilloscope;
- Multimeter;
- And also a voltmeter.
Causes of failure and their symptoms
Although during normal operation the service life of the sensor is determined by a mileage of 60,000-80,000 kilometers (according to the “manual”), it can be damaged ahead of time if:
- Periodically and constantly use leaded or low-quality fuel (the lead contained in gasoline is dangerous);
- When installing a lambda probe, use a sealant that is not heat-resistant or contains silicone;
- For some reason (incorrectly adjusted ignition timing, interruptions in it, “rich” air-fuel mixture) the sensor overheats;
- “Flooding” the engine through repeated and unsuccessful attempts to start it (the danger of igniting fuel in the exhaust system with subsequent detonation);
- Oil and coolant will get into the exhaust system (poor condition of the valve stem seals (see Replacing valve stem seals) and “breakdown” of the cylinder head gasket);
- The exhaust system is depressurized;
- There will be an open, short to ground, or even poor contact in the sensor output circuit.
Well, since in the event of a lambda probe failure, the electronic control unit contains average readings, according to which the air-fuel mixture will be formed (different from the ideal ratio). We will be able to “read” information about the failure of the oxygen sensor based on the following signs of engine operation:
- Fuel consumption is significantly increased;
- The car's dynamics have deteriorated;
- At low speeds (idling), the engine is unstable;
- Increased heating of the sensor itself, which is accompanied by crackling of the exhaust pipe after stopping the engine.
And, of course:
- The “CHECK” warning light on the instrument panel lights up.
Attention! In most cases, the failure of the oxygen sensor is not detected by the on-board electronics, except in cases where there is a break in the heating circuit. Therefore, if the mileage of your car is more than 100,000 kilometers, then replacing the lambda is a resolved issue, since its price is much lower than the costs that will appear with the increased appetite of the car.
How to check a lambda probe using an ohmmeter
As a rule, in all operating manuals, checking the oxygen sensor comes down to using a multimeter to measure the voltage that the sensor produces under different engine operating modes.
Checking the lambda on different cars can differ significantly due to the differences in the sensors themselves. This verification method is described using the example of checking a lambda probe manufactured by BOSCH.
Most often, the “weak link” in a lambda probe is the filament circuit; usually problems arise with it. A little less common is a malfunction of the tip, which reduces sensitivity. In order to understand whether the filament coil is intact or not, it is necessary to perform a “ringing”; for this you can use an ohmmeter. The electrodes of the device are connected to the clamps of the two white wires of the sensor - contacts 3-4 of the connector (sometimes - white and brown wires), and are first disconnected from the power supply. The resistance of the spiral should not be less than 5 ohms.
As for the sensitivity of the tip, it can deteriorate as a result of the plaque that I described above. If the plaque I talked about is there, then the oxygen sensor needs to be changed. To check the thermoelectric parameters of the sensor, connect the voltmeter electrodes to contacts 1-2 of the connector, or to the terminals of the black and gray lambda wires. The test itself must be performed with the engine warm and running.
Replacing a lambda probe on a VAZ 2114
Content:
A lambda probe, or simply an oxygen sensor, is a device located on the exhaust manifold of the power unit. It is used to estimate the amount of free oxygen in the exhaust. Today we will get acquainted with this meter in more detail, consider the principle of its operation on a car, understand the signs of malfunctions and tell you how the device can be replaced on your own.
Appearance of the device
Design
Regardless of the name, lambda probe or oxygen sensor, its essence does not change.
The basis of the device is a ceramic solid electrolyte, the material for which is zirconium dioxide. It is additionally coated with yttrium oxide. But that's not all. There is a coating on top of the ceramic element. It is made from conductive platinum electrodes.
The operating principle is similar to galvanic cells. When the DC is installed on the engine exhaust manifold, due to the influence of the exhaust gas flow, it heats up to approximately 300-400 degrees Celsius.
When heated, the zirconium electrolyte acquires the necessary conductivity, thereby ensuring optimal performance of the sensor.
It is important to install a lambda probe. The DC is positioned so that one electrode receives outside air, and the second breathes a mixture of exhaust gases. When the amount of oxygen changes on one of the electrodes, a potential difference occurs. It is transmitted to the electronic engine control unit via a signal. This allows the ECU to adjust the fuel supply through the fuel injection system.
If you look at the question from a scientific point of view, lambda is the ratio of the actual amount of air to the required, that is, necessary.
Indicators
Lambda indicators may vary, but the car requires certain, optimal parameters.
| Index | Peculiarity |
| Lambda equals one | Theoretically, this is the optimal air ratio, at which the actual amount is equal to the required |
| Lambda is greater than one | Indicates that the air-fuel mixture is lean and therefore the engine is not operating optimally. |
| Lambda is less than one | Under such circumstances, the mixture turns out to be rich and there is an excess of fuel. Because of this, there is a lack of oxygen necessary to burn such an amount of gasoline |
If we talk directly about ideal conditions for the VAZ 2114 and its engines, then the lambda should have a ratio of 14.7 to 1. In other words, the mixture needs to be lean. This is due to the need for a sufficient amount of oxygen on the catalyst to burn CH and CO.
For domestic cars, a modern DC is used, which functions as a threshold element.
How does he work
We have already noted that the DC begins to work only after heating to a certain temperature - 350 degrees Celsius. Because of this, the first variations of the probe were installed in close proximity to the exhaust manifold.
Over time, the sensor was improved, a heating element was built in, which made it possible to quickly bring it to operating parameters. Because of this, the location of the probe in the exhaust system has lost its significance.
If you study the design of the device, it will include several main components.
- Ceramic tips with protective screens and sampling holes. On the one hand, they serve to take in exhaust, and on the other, outside air. These elements are contained in a middle element inside a ceramic insulator. They are the main working components of the recreation center. These are electrodes from which readings of potentials and their differences are taken.
- Conductive heating element. It should be looked for inside the tips.
- Electrical signal current collector. This component is located in the middle part of the DC.
- In addition to the sensitive elements of the tips, all other components of the DC are located inside a metal case equipped with a thread. It is necessary in order to fix the device on the receiving pipe body.
- Modern recreation centers are equipped with wires and a sealing collar. They are called four-wire lambda probes.
- Two white wires are the contacts of the heating system.
- The black wire is the signal wire.
- Black and white striped wiring - grounding.
The other end of the wire, using a plug box, connects the device to the on-board computer. He receives information from the DC about the current state of the air-fuel mixture. Moreover, at idle speed, a request from the ECU to the DC is sent twice per second, and with increasing speed even more often. Depending on the information received, the electronic control unit adjusts the amount of fuel supplied to the engine, creating a rich or lean mixture.
The ECU always strives to ensure that the lambda ratio is as close as possible to the ideal - 14.7:1.
Functionality check
Before replacing the device, you should check its current condition.
You can check the DC using a measuring device:
- The normal lower signal level is from 0.1 to 0.2V;
- Upper - from 0.8 to 0.9V.
The manufacturer guarantees high performance of the device. As practice shows, if the lambda probe was manufactured strictly in accordance with GOST, the first signs of its malfunction may appear no earlier than after 80 thousand kilometers. On average, the “life” of a recreation center is 160 thousand kilometers.
DK is in its place
But the instruction manual attached to the VAZ 2114 states that the DC should be changed after every 80 thousand kilometers. This is due to a decrease in sensitivity, which deteriorates the quality of the air-fuel mixture supplied to the combustion chamber.
How does DC affect engine performance?
In fact, the lambda probe has a very serious impact on the efficient and correct operation of the power unit. DC allows you to maintain optimal characteristics of the fuel and air mixture. If the DC is working properly, then:
- The engine operates correctly, is stable, and there are no vibrations;
- When you sharply press the accelerator pedal, the engine power quickly adjusts, changing the quality of the mixture depending on the engine speed. Due to this, jerking does not occur, the engine does not tremble;
- The maximum amount of burned exhaust is released into the surrounding atmosphere due to the correct operation of the catalyst, which burns the remaining harmful substances in the exhaust pipe. This causes less harm to nature.
How to ensure optimal operation of the DC
So that you do not have to change your DC in the very near future, follow simple recommendations. They will allow you to maintain the sensor in optimal conditions and guarantee efficient operation.
- Use gasoline of the quality and brand recommended by the manufacturer for your car. In this case, for the VAZ 2114.
- If you plan to use fuel additives, make sure that their use is approved and that the quality matches the instructions on the packaging.
- Never use sealants to secure the sensor.
- If the engine is difficult to start, do not repeat a large number of starting attempts in a short period of time.
- When checking the condition of the cylinders, do not turn off the spark plugs.
- Avoid overheating the exhaust system, since the DC has a temperature limit of 950 degrees Celsius.
- Do not treat lambda zone tips with aggressive chemicals.
- Make sure that the connection between the pipe and the DC is always sealed.
Symptoms of a problem
Now regarding the signs of malfunction. There may be several of them. Therefore, carefully monitor the behavior of your VAZ 2114. If you detect one of the signs, immediately take appropriate measures.
Location of the recreation center
- When gas is low, the power unit begins to operate unstably, may stall, and floating speeds appear;
- The dynamic parameters of the machine have deteriorated significantly;
- Under normal conditions, fuel consumption levels increase excessively;
- A cracking sound is observed in the catalyst zone after the engine is turned off;
- You can hear the characteristic smell of spoiled eggs. Such stench is caused by the ingress of a large volume of gasoline into the catalyst, which is not burned.
If you need to replace the DC, check whether such a probe is installed on your car. On earlier versions of the VAZ 2114, single-wire sensors were installed, and then four-wire sensors appeared. Their price ranges from 1200-3000 rubles, depending on the type of recreation center.
If, when removing the device, you find that there is carbon deposits on the device, but the measuring device shows a slight deviation from the norm, it is not necessary to change the DC. You just need to get rid of the carbon deposits.
To do this, heat the sensor very much and then cool it quickly. This will allow the carbon deposits to crack and fall off. All that remains is to lightly wipe the device with a brush.
What if without a recreation center?
Many people ask whether it is possible to disable the recreation center and how this is done. We categorically cannot recommend doing this, since it leads to serious negative consequences:
- The engine will begin to operate unstably and incorrectly;
- Fuel consumption will increase;
- The composition of the exhaust will deteriorate significantly;
- You will need to reflash the on-board computer.
Therefore, if you find problems with the lambda probe, take the necessary measures to eliminate them. It's not difficult to do it yourself.
luxvaz.ru
How to check a lambda probe using a voltmeter
In order to check the oxygen sensor with a voltmeter, you need to start the engine and increase the engine speed to 3 thousand, then check the readings of the device at a maximum of 2 V. The voltmeter should show a voltage of about 0.55 V. Your task in this case is to either increase or decrease the speed . The voltmeter should show up to 0.8-1 V or drop to 0.4 V and below. If the data changes dynamically, the lambda is most likely working. If there are no vibrations or they are insignificant, most likely the probe is faulty and requires replacement.
How to check the oxygen sensor for a lean mixture?
To check whether the mixture is rich or lean, you need to take a vacuum tube and simulate an air leak. If the oxygen sensor is working properly, the voltmeter will show 0.2 W or lower.
To more accurately check the functionality and serviceability of the oxygen sensor, you will need an oscilloscope.
I recommend watching a video on how to check the lambda probe
Information on how to test an oxygen sensor yourself will help you determine whether it is faulty. Do not rush to waste time and money on replacing the element, as the problem may not be in this sensor at all. The lambda probe detects the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases and converts this data into a voltage signal. It is necessary for the electronic engine control unit to form an optimal mixture of fuel and air.
If the sensor signal is outside normal operating parameters, the car computer stores a fault code in memory and the Check Engine light on the instrument panel lights up, warning the driver of the problem.
If you suspect that the oxygen sensor in your car is faulty or diagnostics have shown problems with it, do not rush to change the lambda probe. The computer simply reports where the problem was found. And the real culprit could even be a damaged vacuum hose. Because of this problem, the oxygen sensor “sees” too much oxygen in the exhaust gases. Another option is damage to the electrical connector of the lambda probe, preventing it from working properly. In both cases, the control unit will report a sensor malfunction.
Therefore, before replacing the lambda probe, you should definitely check its functionality. Today you will learn how to check the lambda probe with your own hands. Only after confirming the diagnosis can you go in search of a new part.
FAULTS - CAUSES AND SIGNS
The VAZ 2114 lambda probe has a certain service life - on average, the device can operate for 80-160 thousand km (calculated by the mileage of the car). But depending on various factors, it may fail earlier. This happens for the following reasons:
- Poor quality gasoline;
- There is a waste of oil in the engine, because of this, oil deposits form on the sensor (coking occurs);
- If the ignition fails, popping noises occur in the muffler, destroying the oxygen sensor on the VAZ;
- External influences - impact from an accident, liquids or oil entering the contacts of the device.
What may be signs of a malfunction of the VAZ 2114 oxygen sensor:
- Fuel consumption increases;
- The CheckEngine engine diagnostic lamp lights up on the instrument panel inside the car;
- Difficulties during acceleration of the car, loss of power;
- Engine adjustments, popping noises in the intake manifold and muffler.
But these same signs may indicate other malfunctions, and there are many reasons for this. For example:
- The air flow sensor does not work;
- Non-functional spark plug;
- High-voltage wires are pierced to ground;
- Weak compression in the engine cylinders;
- Problems with the ignition module.
Article on the topic: How to remove the front and rear bumpers on a VAZ 2110
Connecting a multimeter to the oxygen sensor before testing
To diagnose the oxygen sensor, it is recommended to use a professional multimeter (it allows you to get the most accurate results), but a regular tester will do.
Before performing a lambda probe test, you must first locate it. On many older vehicles, the sensor was installed on or near the exhaust manifold. Modern cars often use two sensors - one installed in the exhaust manifold area, and the second after the catalyst. Make sure which sensor you need to check.
Reading Oxygen Sensor Signals
Start the engine and check the sensor voltage signals with a tester. When checking the lambda probe with a multimeter, the voltage on the device display should constantly change within the range of 0.10-0.90 Volts. This is a sign of normal sensor operation.
If you only see a low or high voltage signal on the screen, there is clearly a problem. To verify that the sensor is operating correctly, perform the following two tests.
Checking the reaction of the oxygen sensor to a lean fuel mixture
- Disconnect the hose from the crankcase ventilation valve that goes to the intake manifold. As a result, more air will flow into the engine. You can find the valve using your vehicle's owner's manual.
- Check the digital multimeter readings. Such actions should result in a signal of about 0.20 V being displayed. If the reaction is different or the numbers on the screen change only after a while (not immediately), the sensor is not working correctly.
- Connect the hose to the crankcase ventilation valve.
Checking the reaction of the oxygen sensor to a rich fuel mixture
- Disconnect the pipe that connects the engine throttle body and the air filter housing.
- Block the hole leading to the engine with a clean rag. This will reduce the amount of air that enters the engine.
- Check the tester readings. The oxygen sensor should produce a signal of about 0.80 V. If the lambda probe responds differently or takes a very long time to respond, it is faulty.
- Connect the air duct to the air filter housing and stop the engine.
If such diagnostics show that the oxygen sensor is functioning properly, the problem may lie in other components of the power unit. The engine may have a vacuum leak (air leak – https://avtopub.com/kak-najti-podsos-vozduxa-v-dvigatele-i-ustranit-ego/), problems in the ignition system, etc. If the lambda probe did not respond to your actions or reacted too late or incorrectly, it will have to be replaced.
See our article about what happens if you turn off the lambda probe in a car. Is it possible to drive without it? Read the link – https://avtopub.com/chem-grozit-otklyuchenie-datchika-kisloroda-v-avtomobile/
Now you can accurately determine whether the oxygen sensor is really faulty or whether it’s not the problem at all. This simple check will help you save money and time and get your car back to life faster.