Basics of the design and operation of a hydraulic compensator
The negative side of the design approach is the capriciousness of the system. Very often the hydraulic compensators on the Priora 16 valves knock and the reasons for this phenomenon are unknown to the inexperienced owner. The situation becomes clearer after studying the features of the compensatory mechanism.
Configuration
The idea of automatic regulation of thermal clearances can be implemented in two versions: a conventional hydraulic pusher and a hydraulic support. The latter is used in gas distribution modules with rocker arms. On the Lada Priora in the sixteen-valve version, the intake and exhaust are equipped with individual camshafts. The optimal solution for this arrangement is the use of a hydraulic pusher.
The Priorov hydraulic compensator on the 126 engine consists of the following parts:
- A plunger pair, including a cylindrical cage and a piston with a ball valve.
- The outer housing is a pusher.
- System of grooves and holes for oil supply.
Principle of operation
The oil composition enters the internal cavity of the piston and, overcoming the resistance of the spring, pushes the ball away to fill the closed cylinder. When filling the liner, oil pushes the piston out and the hydraulic tappet rests against the cam. Next, the ball valve is locked and the assembly unit works like a regular pusher on motors with an adjustable valve mechanism.
Knock of hydraulic compensators on Lada Priora: diagnostics and troubleshooting
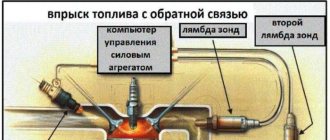
Lada Priora is equipped with a VAZ 21126 engine with an automatic gas distribution mechanism adjustment system. The gap between the camshaft cam and the valve stem is selected by a hydraulic tappet, the successful operation of which is ensured by the engine oil system. The mechanism allows you to avoid making various types of adjustments in the timing belt, reduces fuel consumption and increases the efficiency of the power plant. Fundamentals of the design and operation of a hydraulic compensator
Basics of the design and operation of a hydraulic compensator
Configuration
The idea of automatic regulation of thermal clearances can be implemented in two versions: a conventional hydraulic pusher and a hydraulic support. The latter is used in gas distribution modules with rocker arms. On the Lada Priora in the sixteen-valve version, the intake and exhaust are equipped with individual camshafts. The optimal solution for this arrangement is the use of a hydraulic pusher.
The Priorov hydraulic compensator on the 126 engine consists of the following parts:
- A plunger pair, including a cylindrical cage and a piston with a ball valve.
- The outer housing is a pusher.
- System of grooves and holes for oil supply.
Principle of operation
The oil composition enters the internal cavity of the piston and, overcoming the resistance of the spring, pushes the ball away to fill the closed cylinder. When filling the liner, oil pushes the piston out and the hydraulic tappet rests against the cam. Next, the ball valve is locked and the assembly unit works like a regular pusher on motors with an adjustable valve mechanism.
Why do hydraulic compensators knock on a Lada Priora with 16 valves both hot and cold or causes of noise
Successful operation of the hydraulic compensator (HC) is possible only with a constant supply of oil under pressure. The oil emulsion drainage prevention system allows you to eliminate knocking during startup. It is implemented in the form of a ball valve that closes the oil channel in the cylinder head after stopping the engine.
How the main guns knock
Some owners of Lada Priora have heard about problems with hydraulic pushers, but are not aware of the acoustic nature of the malfunction. It is not difficult to determine whether the modules are rattling: the sound will be similar to the operation of a diesel power plant. Indeed, the clatter can be compared to a running fuel injection pump of a diesel engine or a modern gasoline unit.
Tapping on cold
On the new motor, the hydraulic modules operate silently. This is explained by its ideal condition and confirms the quality choice of lubricant by the manufacturer. Deviations from factory recommendations or mediocre vehicle care require not only decoking of the piston rings in the future, but also a search for the factors that caused the piston ring to knock.
What causes the hydraulic compensators to knock on the Lada Priora 16 valves or the reasons for the knocking when cold can be the following:
- Contaminated or poor-quality oil emulsion.
- Unsuitable oil viscosity. Deviations in viscosity characteristics lead to the inability to push fluid through a small network of channels, which causes oil starvation in hydraulic compensators.
- Clogged oil system holes. A decrease in the flow area leads to a decrease in pressure in the chambers of the hydraulic module.
- Low pressure in the main oil line. Usually the oil pressure light comes on along with this.
- Jamming of the plunger mechanism due to the presence of a large layer of carbon deposits on the surfaces of the assembly unit.
- Wear of plunger pair parts. Defects in the ball valve or on the mating surfaces lead to fluid leaks from the sub-plunger space.
Knock of hydraulic compensators
We talked about these engine knocks in a separate article.
By the way, a knocking noise from the front right can be caused by a “tired” engine mount.
Keywords: Lada Granta engine | Lada Priora engine | Lada Kalina engine | Lada Largus engine | 4x4 engine | Lada Vesta engine | lada xray engine | Niva engine | universal article
2
Found an error? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter..
- Chevrolet Niva will be sold only in LADA centers
- Review of Lada Vesta Exclusive with photos and videos (new sedan equipment)
- How to remove roof rails on Lada Vesta SW / SW Cross
- How to install wireless phone charging in a Lada car
Why are hydraulic compensators knocking on a Priora with 16 valves?
A knocking sound during operation of parts appears when the supply of emulsion to the plunger is reduced and the pusher does not move evenly. The causes of the characteristic sound can be the following factors:
- Wear or low quality lubricant. The correct operation of the mechanism depends on engine oil. The technical clearances in the plunger are minimal, which requires the use of a high-quality consumable.
- Clogged fluid lines.
- Natural aging of parts. Main engines are designed for 100,000 km. Moreover, if the machine is operated in difficult conditions, the service life is reduced by 15-20%.
How to eliminate the knocking of hydraulic compensators on a Priora: how to remove the sound
Hydraulic compensators are fundamental elements of the Priora engine, which automatically adjust the valves. In their absence, the valves would need adjustment after every 30 thousand mileage (depending on driving style and other criteria). If they start knocking, then this does not always indicate a malfunction.
If there is a knock, what should I do?
When you hear a knock, you need to check the elements for serviceability. To do this, we perform the following steps:
- Checking the ball valve. If there is significant wear, the hydraulic valve will have to be replaced.
- If the plungers are worn out, the part is also beyond repair. In this case, the hydraulic compensators will have to be changed.
- If the internal cavity of the pusher is dirty, the part must be washed and then lubricated with a good oil composition.
If the hydraulic compensators are worn out or clogged, then knocking starts when the engine is cool. At high speeds they usually subside.
By the way, knock
may not disappear even after installing the latest
hydraulic compensators
. This is a temporary phenomenon, and when the parts rub in, the sounds will disappear. If the knocking starts after an oil change, the reason may be poor fuel or a worn out filter.
Why do hydraulic compensators knock on a Priora when it’s cold?
The reasons for knocking parts on a cold engine can be several factors:
- The viscosity of the lubricant is incorrectly selected. Thick oil does not pass through small channels, which causes dry friction.
- Worn or contaminated lubricant. The presence of solid impurities, soot or soot makes it difficult for the mixture to flow freely.
- Low pressure inside the lines, pump malfunction.
- Jamming of the plunger mechanism due to sludge formation or misalignment of surfaces.
- Wear of the main body. Fatigue of the spring, shell on the check valve ball.
Why do hydraulic compensators knock when cold on the Lada Priora and what to do?
In order for hydraulic compensators to consistently perform their duties, they need a regular supply of lubricant under a certain pressure and in the required volume. For these purposes, the cylinder head has a special channel with a check ball valve. It is needed to prevent the viscous substance from draining from the channels after the engine has stalled. This process also involves channels located in the lower part of the bearing housing, through which oil is supplied to the camshaft journals.
If all the mandatory conditions for the correct operation of the elements are not met, it is natural that after some time they will fail and require replacement.
Knocking when cold
It appears immediately after starting the engine (cold) and continues until it warms up to a certain temperature (40-50 degrees). This noise occurs both due to the presence of air in the hydraulic compensators (hydraulic pushers), and when thick (still cold) engine oil does not pass through narrowed (due to contamination) oil channels or due to a deteriorated oil filter. The unpleasant sound continues for a particularly long time in the cold season, when the oil takes longer than usual to liquefy to the desired consistency. In order to eliminate this problem in this situation, it is necessary to clean the oil channels or replace the oil filter.
The process of replacing hydraulic compensators on a 16-valve valve
Hydraulic compensators produced by AvtoVAZ
So, if the diagnostics showed that the hydraulic compensators are out of order, then we replace them. Of course, first of all, you need to buy new ones. Now, consider the sequential replacement process:
- We dismantle the upper protective cover.
Fastening bolts are marked with an arrow
- We remove the receiver.
Removing the receiver from the car
- Now, it is necessary to dismantle the ignition module.
We unscrew the fastenings and dismantle the ignition model
- Disconnect the crankcase ventilation hose.
Unscrew the clamp and remove the crankcase ventilation hose
- Using a 10mm wrench, we dismantle the injector wiring harness bracket.
Using a wrench, unscrew the fastenings of the wiring harness.
- We dismantle the valve cover.
Removing the valve cover
- Now, you need to carry out diagnostics and press on the drifts.
The principle of operation and diagnostics of hydraulic compensators
- Next, we dismantle the camshaft pulleys.
We jam the camshafts and remove them
- Disconnect the oil pressure sensor wires.
Removing the oil pressure sensor
- Remove the bolts that secure the camshaft bearing housing.
Unscrew the camshaft mounting bolts
- We dismantle the rear support of the power unit.
Unscrew the rear engine mount
- Now, you need to remove the camshaft bearing housing.
We take out the bearing housing
- The spark plug wells need to be removed from the housing. Inspect them for the presence of oil.
- We dismantle the camshafts assembled with oil seals.
Removing the camshafts
- Remove the plugs that are located on the head and camshaft housing.
We take out the block head plugs
- We remove the hydraulic compensator from the cylinder head.
We take out the hydraulic compensators
- Lubricate the bearing journals and cams.
- We install new hydraulic compensators.
- We carry out the assembly in the reverse order, observing the order and tightening torque of the cylinder head.
If the replacement is correct, then after assembly and the first start of the engine, nothing should knock. If the knock remains, you need to disassemble everything again and carry out diagnostics, and then fix the problem.
Selection of hydraulic compensators
The choice of any spare part must be taken quite seriously. Hydraulic compensators are no exception. Let's consider possible options for installing them on the VAZ-2112 series:
- 2112-1007300 is the original catalog number of hydraulic compensators for the VAZ-2112. The cost is 3300 rubles . Manufactured by AvtoVAZ.
- Herzog HL0 7300 – an analogue substitute for the original part, which can be used for installation on a car. The price is 2700 rubles.
Hydraulic compensators manufactured by Herzog
- Master-sport 2112-1007300-SET/16/-MS is one of the options for replacing the original hydraulic compensator made in the Russian Federation. Certified and recommended for installation.
We recommend: Do-it-yourself removal and installation of the exhaust manifold
Replacing hydraulic compensators
To do this, first purchase a set of hydraulic compensators. Even if only one hydraulic valve is knocking, you will have to change them all. To do this you will need:
- Set of keys and sockets;
- Screwdriver Set;
- Set of hydraulic compensators;
- Head cover gasket;
- Camshaft seals;
- Sealant.
Before starting work, you need to disconnect the terminals from the battery. Then you need to remove the wires from the ignition coils and disconnect the injector wires. Then you need to disconnect the exhaust hose of the crankcase ventilation system from the head cover. Next, this hose can simply be moved to the side or completely removed by disconnecting it from the ventilation pipe located on the crankcase.
The next step is to remove the oil dipstick mounting bracket and remove it from the engine along with the dipstick. Next, you need to unscrew the nuts and bolts securing the intake manifold to the cylinder head, after which the intake manifold is removed from the power unit.
At the front of the engine, you need to unscrew the bolts securing the upper and lower timing belt casings and remove them. Then you should loosen the tension roller and remove the belt from the camshaft gears.
Replacing spare parts
The camshaft gears also need to be removed by first unscrewing the bolts that secure them. The gears must be removed from the shafts carefully so as not to lose the keys. After removing the gears, you need to remove the rear timing belt cover.
Next, the bots securing the block head cover are unscrewed. The cover often sits very tightly in place, so it is quite possible that you will have to carefully pry it off with a screwdriver from different sides. After removing the cover, you will have access to the camshaft bearing housing, which is also removed from the engine.
After dismantling the bearing housing, the camshafts can be removed from the head. Before removing them, the shafts must be marked so that they cannot be mixed up during assembly. When the camshafts are removed, access to the hydraulic compensators will appear.
To find out which of the hydraulics is knocking, it is enough to apply force to each. If at least one of them moves easily in its socket even with slight pressure, it means that it is knocking and therefore must be replaced. To remove hydraulic compensators from their sockets, you can use a magnet.
Before installing new hydraulics, their surface must be lubricated with engine oil. The engine is assembled in the same sequence in which it was disassembled. Before installing the camshafts, the seals on them must be replaced. The head cover gasket should also be replaced, and before installing it, the seat should be coated with sealant.
If, after the replacement has been completed, the hydraulic compensators still knock, it means that the problem is not in them, but in the head of the cylinder block itself. It is quite possible that the hydraulics are knocking because they are not getting enough oil, due to clogged oil channels in the head. To troubleshoot the problem, you will most likely need to remove the head from the power unit.
READ VAZ 2107 knocking in the front suspension
For your information
- New hydraulic compensators can also tap. This usually happens after capitalization and is observed within a short period of time after the first start-up. It is not a malfunction if it does not recur during subsequent starts.
- If the hydraulic modules knock after changing the oil, the reason is the quality of the lubricant or the filter.
- The knocking of hydraulic pushers during startup should not be considered a malfunction. Over a long period of parking, the oil is drained from the working chambers and at the beginning of work the containers are filled.
Sample recommendations for repairs
Let the malfunction be caused by the reason indicated under number 1 or 2. Then the compensator must be replaced, and there can be no other options. If we talk about “reason 3”, it is usually recommended to clean the compensator, but this will require dismantling.
Four types of hydraulic compensator modules
It’s better to immediately replace the faulty module without disassembling it. The diameter of the module body does not exceed 10-15 mm, and repairs will be difficult.
If the noise of the compensators appears at high speeds, a conclusion is drawn about foaming of the oil (see above). The cause of the malfunction is then looked for like this:
- Check the oil level on a cold engine;
- If necessary, add oil or drain excess. The last step is simple to perform: instead of the dipstick, a tube from a dropper is installed, and the liquid itself is drawn out with a “pear”;
- Start the engine, gradually increase the speed;
- If the noise effect appears again, it is concluded that air enters the lubrication system through damaged parts.
Replacing hydraulic compensators on a Priora (16 valves)
For work, prepare the following tools:
- flat-head, Phillips-head screwdriver;
- socket wrenches;
- You may need a cylinder head gasket; replacing it will allow you to be safe from the fact that the spark plugs may flood the spark plugs with oil;
- sealant;
- magnet - for convenience.
- Stop the car with the handbrake. Lift the hood.
- Loosen the clamp securing the crankcase ventilation hose (main circuit).
- Disconnect the hose from the cylinder head fitting. Cover the fitting with rags to prevent any objects from getting inside.
- Remove the bracket for the wires of the injectors and ignition coils, having first unscrewed the bolts with the “10” head.
- Disconnect the throttle assembly wiring harness from the cylinder head, having first removed the fastenings with the same head.
- Let's move on to the cylinder block cover. All fifteen screws will have to be unscrewed. To do this, use the E-8 head. Please note that it is additionally secured with sealant.
- Therefore, use a plastic screwdriver to carefully pry the cover in places where there are visible gaps, and then lift it. At this point, evaluate the camshaft lobe wear. It should not be covered with chips or other signs of mechanical damage.
- Now you can check the faulty hydraulic compensators. Avoid damaging the valves of the gas distribution mechanism; handle them carefully.
- Remove the faulty hydraulics with a magnet and put new ones in their place, securing them in a level position.
- Along the way, you should inspect all parts, assessing the degree of wear. This will help to find the reasons for the wear of the hydraulics or the consequence - something that has worn out faster due to their improper operation.
- Replace sequentially. Do not forget to coat the cylinder head cover with sealant to ensure maximum adherence to the body.
- Reassemble the components in reverse order, check the operation of the new hydraulic tappets by starting the engine.
How hydraulic compensators knock: video
What to do if hydraulic lifters are knocking on Lada cars
Have you encountered any unusual engine noise? Perhaps it's the hydraulic compensators knocking. This problem occurs most often on Priora, but knocking also appears on other Lada cars (for example, Granta, Kalina, Largus Niva 4x4, Vesta or XRAY). Let's figure out why such a knock appears in the engine and how to deal with it.
The hydraulic compensator (also known as hydraulic pusher) is a cylindrical shape that is located between the camshaft and the valves. They perform two functions: transmitting force from the camshaft to the valves and eliminating gaps in their drive.
Diagram of operation of the hydraulic pusher in the valve mechanism of the VAZ-21126 engine: 1 – valve; 2 – check valve spring; 3 – check valve; 4 – cylinder head; 5 – camshaft cam; 6 – pusher; 7 – plunger; 8 – plunger spring; 9 – sleeve; 10 – check valve body; A, B – hydraulic pusher cavities; B – oil channel.
Checking hydraulic compensators
Check the condition of the spring and measure the gaps between the valve stems and guide bushings. If necessary, eliminate increased gaps. Then:
- Turn the crankshaft so that the valve that is knocking begins to open slightly.
- Turn the spring a little and the valve will turn with it.
- Start the engine. If the knocking noise persists, repeat steps 1 and 2.
- If the knocking of the valves remains, then the hydraulic compensator is faulty.
Causes of knocking hydraulic compensators
- Engine knocking when starting. If the extraneous noise disappears a few seconds after starting the engine, this is not a sign of a malfunction.
- There is a knocking sound from hydraulic compensators on a cold and warm engine, the noise disappears when the speed increases. The check valve ball may be worn out and the hydraulic compensator will have to be replaced. It is also possible that the hydraulic compensator mechanism may become dirty; cleaning the parts will help.
- The knocking noise only occurs when the engine is warm. Wear and, as a consequence, the appearance of increased gaps between the plunger and the hydraulic compensator sleeve. You will have to change the hydraulic compensator.
- Engine knocking at high speeds. The cause may be too much or too little engine oil. Bring the engine oil level to normal. It is also possible that the oil receiver may be damaged, in which case the faulty parts should be replaced.
- The valves are constantly knocking. The reason may be a gap between the pusher and the camshaft cam. Cleaning or replacing faulty parts will help.
Analogues on the market
Only its close relative, Suprotek, stands out on the auto chemical market. It is difficult to explain what such advertising is connected with, but the experience of using a similar product leaves much to be desired. The only thing that Suprotek benefits from is a detailed description of the composition and rules of application. Nothing can be said about the composition. To do this, you need to look at the security certificate. But any aldehyde resins included in the composition capture molecules of sulfur, zinc, magnesium and phosphorus, which has a beneficial effect on the aggressive stability of the cylinder block.
Main types of faults
We answer the question of how to check hydraulic compensators for functionality. It can be noted that there are four reasons for the occurrence of malfunctions:
- Increasing the size of the gaps in the areas indicated by the arrows in the photo below. Gaps are formed between the plunger and the plunger bushing. The result will be increased oil leakage. The compensator simply will not have time to “select” the thermal gap;
- In rare cases, the check valve does not close tightly. Which, at a minimum, makes it impossible to create sufficient pressure generated between the sleeve and the plunger;
- The bushing should move freely relative to the plunger. In the areas indicated in photo 3, a blockage may appear, and then the plunger pair jams;
- Clogged engine oil passages are another reason why compensators stop working.
Points 1-3 are illustrated in the photo:
Diagnostics and repair
Why do hydraulic lifters knock on the Lada Priora and what to do in this case
First of all, it is worth determining which specific hydraulic pusher is not working correctly, and whether they are the cause of the unpleasant sound. This can be done using acoustic diagnostics or by turning off the engine cylinders alternately. For this, it is advisable to contact a car service or do it yourself. However, trying out repair methods yourself can be more expensive than calling an experienced engine specialist.
Then you need to check the oil pressure in the engine system for compliance with the standards. If it is lower than necessary, then the oil pump or filter may need to be replaced.
Often the cause of incorrect operation of the mechanism is engine oil, which was chosen incorrectly or is present in insufficient quantities. It is necessary to change it to another brand, change its viscosity or add special additives to it that eliminate the knocking of hydraulic pushers.
Sometimes you may notice that oil appears in one of the spark plug wells when the engine is running under heavy load. You need to pull it out with a syringe and clean the spark plugs. Then, to create the required pressure in the system, under the cover of the hydraulic compensators and heads, you need to apply sealant, which was “greedy” when assembling the car at the manufacturer.
Hydraulic pushers do not need any adjustment, since they themselves are able to adapt to the operating mode of the mechanisms.
Sequence of actions on Lada Priora
- Both terminals are removed from the battery.
- The wires on the injectors and on the ignition coil are disconnected, the cable is removed from the throttle, the air filter and all other wires that prevent access to the engine intake manifold are removed.
- Before removing the manifold, you will have to remove the belt from the generator, then unscrew its mounting bolt. After this, the generator can be moved to the side and you can get to one of the intake manifold mounting bolts (there is no other way to get to this bolt).
- The next step is to remove the ramp and fuel injectors (if the car has air conditioning, you will also have to remove its hoses so that they do not interfere).
- All other manifold mounting bolts are unscrewed, after which it is removed.
The valve cover is unscrewed with a 12 mm socket wrench.
- Now you can remove the valve cover, timing pulleys and camshafts.
Removing a previously unscrewed valve cover
- Since we now have access to the hydraulic compensators, all that remains is to replace them with new ones (we should also change the seals on the camshafts and the sealant on the valve cover).
After removing the cover, the camshafts are removed
Worn hydraulic compensators are removed from their sockets
- After this, the above components are reassembled. The instructions below are suitable for cars with 16 valves.
We recommend: Silent locks for VAZ 2107: how to install it yourself?
Replacing hydraulic compensators on a VAZ-2112 is not so easy, but you can do it yourself. Of course, this will require time and effort. The choice of product should also be taken quite seriously, because the resource of use depends on the quality.
Which hydraulic compensator is making the knocking noise?
To determine which hydraulic compensator is making a knock (usually their number is equal to the number of valves in your engine), they use a diagnostic method “by ear”, using a technological version of such a medical device as a phonendoscope - you have almost certainly seen it on your therapist’s neck.
It is this device that allows the master to say exactly where the source of the knocking lies, although real professionals, of course, will determine this without any phonendoscope.
After diagnosing the knocking part, you need to remove the hydraulic compensator, thoroughly clean it, then install it in place and start the engine again.
If the knocking noise persists, the hydraulic compensator is considered to be out of order, and the service will replace it.
If the knocking continues after replacement, the reason most likely lies in the quality of the oil used, or in other engine components. The latter is unlikely, since diagnosing a sound source using a phonendoscope is an accurate procedure and, as a rule, does not cause failures.
Types of hydraulic compensators
Depending on the design and location, there are several types:
- Hydraulic pusher. Due to its simplicity and reliability, it is most widespread, especially on motors from foreign manufacturers;
- Hydro support. It is placed where the impulse from the eccentric does not go directly, but through the lever;
- Hydraulic support for installation in levers and rocker arms. A modernized version of the hydraulic support. Mounted directly into one of the parts in the gas distribution system;
- Roller hydraulic pusher. The working part is the roller. Otherwise it functions the same as the other representatives.
( 1 rating, average 4 out of 5 )
Malfunctions and their causes
As mentioned above, the design of hydraulic compensators is extremely simple. But even such simple parts fail. There are three main signs that indicate that something is wrong with the hydraulic compensators:
- While the engine is running, a quick knocking noise is clearly audible.
- Engine power drops significantly, especially at high speeds.
- The engine runs rough, even at idle.
If any of these signs are observed, then it’s time to change the hydraulic compensators. The main problem with these parts is that they are extremely sensitive to the quality of the engine oil. Sometimes it doesn’t even get to the point of replacing hydraulic compensators. The car owner simply drains the old oil, fills in new oil (after flushing the engine) and the knocking disappears. If the problem does not go away, it means that there is mechanical wear of the hydraulic compensators (usually this occurs due to the so-called metal fatigue).
How to get rid of the knocking of hydraulic compensators with your own hands
Increased engine noise may indicate the presence of serious malfunctions, which can lead to complete inoperability of the unit.
The knocking of hydraulic compensators when cold does not belong to this category, but if this part is not adjusted, the engine will consume more fuel, develop less power and the comfort of driving the car will sharply decrease. The wear of the piston group will also increase due to incorrectly selected gaps in the gas distribution system.
This article will tell you in detail how to eliminate the knocking of hydraulic compensators, as well as how to do this work efficiently and with minimal time and financial costs.