On Russian cars, since the introduction of Euro-3 environmental standards (and on foreign cars even earlier), self-diagnosis of misfires was introduced into the algorithms of engine control systems. This was caused not only by tightening requirements for hydrocarbon emissions into the atmosphere, but also by a logical desire to preserve the life of the catalyst. Every time the cylinder, having collected a portion of the working mixture during the intake stroke, cannot burn it, all the fuel and free oxygen from the mixture enters the hot catalyst, where they are either further oxidized, increasing the temperature of the catalyst (the risk of “sintering” of the honeycomb), or gasoline accumulates, at one “wonderful” moment, exploding with a characteristic bang, the force of which is enough to destroy the catalyst.
What does P0300 mean?
In most cars the engine has 4-6 cylinders. A spark plug fires sequentially in each cylinder, igniting the fuel mixture. Energy is then released from the fuel to drive the crankshaft, which must rotate smoothly as the vehicle moves.
If misfire occurs in more than one cylinder, this will result in an increase or decrease in the number of revolutions (RPM) of the crankshaft. If the crankshaft speed increases or decreases by 2 percent or more, P0300 will remain in the PCM (automatic transmission control module) memory.
If the RPM increases or decreases by 2 to 10 percent, the Check Engine Light will illuminate on your vehicle's dashboard. If the deviation percentage exceeds 10 percent, the Check Engine light will flash, indicating a more serious problem is present. The P0300 code indicates that multiple engine cylinders are misfiring randomly.
Causes of error P0300
- Worn or damaged spark plugs
- Worn or damaged spark plug wires and/or ignition coils
- Damage to the distributor cap (if equipped)
- Worn or damaged ignition distributor runner (if equipped)
- Fuel injector damage
- Clogged pipes or valve of the exhaust gas recirculation system
- Incorrect ignition timing setting
- Vacuum leak
- Low fuel pressure
- Damage to the cylinder head gasket
- Distributor cap wear
- Camshaft position sensor malfunction
- Malfunction of the crankshaft position sensor
- Air flow sensor malfunction
- Oxygen sensor malfunction
- Throttle Position Sensor Malfunction
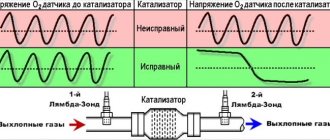
- Malfunction of the catalytic converter
- PCM malfunction
How does a mechanic diagnose a P0300 code?
When diagnosing this error code, a mechanic will do the following:
- Reads all data and error codes stored in the PCM memory using an OBD-II scanner
- Clear error codes from the PCM memory and test drive the vehicle to see if P0300 appears again
- Determines which cylinders are misfiring
- Check the wires connecting the ignition coils to the spark plugs for wear and damage
- Check spark plugs for wear and damage
- Check the ignition coils, as well as wires and connectors for corrosion and damage
- If necessary, replace spark plugs, ignition coils, as well as related wires and connectors
- If the P0300 code appears again after replacing the above components, check the fuel injector and fuel delivery system
- Check the ignition distributor cap and slider for wear and damage
- If there are other error codes stored in the P0300 code, the PCM will clear any existing errors and test drive the vehicle again to determine if the P0300 error code appears again.
- If the P0300 error appears again, check the compression in the cylinders.
- If the P0300 code persists, the problem may be a faulty PCM. In this case, the module may need to be replaced or reprogrammed.
Common errors when diagnosing code P0300
The most common mistake when diagnosing a P0300 code is to rule out a failed cylinder, fuel injector, or PCM.
It is also a mistake to not look at other error codes that appear along with the P0300 code. If you do not resolve all present errors, this may cause the P0300 code to appear again.
Misfire in a VAZ Priora cylinder, signs, causes
Unstable engine operation and shaking at idle, loss of power and increased fuel consumption, the appearance of a “Check” error on the instrument panel, jerking of the car and other troubles can be caused by a misfire in the engine cylinder.
There is nothing wrong with this, because if the engine runs but does not pull, it means that not everything is so critical.
Next, we will talk about how to properly diagnose a car and identify the cause of the malfunction.
Main causes of misfire
There can be many reasons for the problem; even professional mechanics spend more than one hour to identify its source.
The main reasons for misfire in cylinders 1, 2, 3, 4 can be:
- The ignition coil or module has failed;
- Inoperative fuel injector, clogged due to low-quality gasoline;
- Incorrect spark plug gap, which can lead to poor sparking;
- The spark plugs are flooded or carbon deposits have formed on them;
- Breakage of high-voltage wires, increased resistance (non-standard ones are installed), oiliness of contact points;
- A high-voltage wire has fallen off (often happens on Lada Kalina and Granta);
- On an 8-valve engine, the timing belt may jump (during replacement, an error was made due to marks or as a result of excessive wear);
- On a 16-valve engine, the hydraulic compensators are not working correctly;
- Air leak (can be anywhere);
- The compression in the engine cylinders has dropped or is different (applies to cars with high mileage);
- Low pressure in the fuel rail as a result of reduced fuel pump performance.
Diagnostics using a computer
If your car is equipped with a modern control unit, then this greatly simplifies troubleshooting; otherwise, you will have to use time-tested old-fashioned methods.
By connecting the computer to the car, you can find out in which cylinder, 1, 2, 3 or 4, and for what reason there are misfires, for example, the ignition coil or one of the injectors has failed.
But in any case, before going to a car service center, you need to check the condition of the spark plugs, injectors, high-voltage wires, how the exhaust system works, and whether there is smoke from the exhaust pipe.
Many car owners cannot afford instruments for car diagnostics, these include scanners (software and portable), motor testers, oscilloscopes, gas analyzers and other devices, and you need to be able to use them, read error codes, and so on. Although if you look into it, there is nothing complicated there.
The scanner is connected to a special connector, which can be located in different places in each car model, but it has one function: diagnostics.
Next, error codes are read from the control unit and decrypted.
For example, VAZ 2110, 2114, 2115, Lada Kalina, Priora, Granta cars have the following error codes that are characteristic of misfire:
- P0300 - a large number of misfires;
- P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304 – misfires in cylinders 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively;
- P0300 - a large number of misfires in a random order;
- P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304 – misfires were detected in 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively;
- P0363 – see point 4 + fuel supply to problem cylinders is stopped;
- P1301, P1302, P1303, P1304 – respectively, misfires dangerous for the catalytic converter were detected in cylinders 1, 2, 3, 4;
- P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304 – detection of misfires affecting the toxicity of exhaust gases;
- P0363, P1301, P1302, P1303, P1304 – the same as in point 7, but affecting the catalyst;
- P0351, P0352, P0353, P0354 – open circuit in the ignition coil in the control circuit 1 (1-4), 2 (2-3), 3, 4;
- P2301 P2303 P2305 P2307 - short to on-board network in the coil in the control circuit of cylinders 1 (1-4), 2 (2-3), 3, 4;
- P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204 – respectively, open circuit for controlling injectors 1,2,3,4;
- P0261, P0264, P0267, P0270 - short circuit of the injector control wires to the body, respectively, in the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th center;
- P0262, P0265, P0268, P0271 – the same as point 12, but only to the on-board network;
- P1500 – electric fuel pump relay, wire break.
What repairs can fix the P0300 code?
- Replacing faulty spark plugs
- Replacing worn or damaged spark plug wires and/or ignition coils
- Repair or replace clogged EGR pipes and/or valve
- Repairing Vacuum Leaks
- Repairing or replacing a damaged cylinder head gasket
- Replacing a faulty camshaft position sensor
- Replacing a faulty crankshaft position sensor
- Replacing a faulty air flow sensor
- Replacing a faulty oxygen sensor
- Replacing a faulty throttle position sensor
- Replacing a faulty fuel injector
- Replacing a faulty catalytic converter
- Elimination of all present errors
- Replacing the ignition distributor cap and slider (if equipped), as well as wires, spark plugs and ignition coils
- If necessary, repair faulty internal engine components
- Engine replacement (if cylinder is damaged)
- Replacing a faulty PCM
Additional comments for troubleshooting P0300
It should be noted that the cause of the P0300 code is not always worn or damaged spark plugs and wires. Sometimes the problem may lie in other components of the system. Before starting repairs, it is necessary to perform a thorough diagnosis and consider all possible causes of the error.
It is also necessary to eliminate all present errors. Every time after repair work is performed, you should clear the error code from the PCM memory and test drive the vehicle to find out if the P0300 error code appears again. This will help determine if the problem is resolved.
It is important to make sure that the spark plug has the correct gap. To do this, you need to use a gap gauge.
If the spark plug is not properly gapped, it can cause the cylinders to misfire. Typically, car manufacturers provide spark plug specifications. These characteristics can be found on a label under the hood of the car or obtained from any auto parts store for your car.
Why do misfires occur in the VAZ 2114 cylinders?
There are probably no drivers, especially those with extensive driving experience, who are unaware of such a problem as misfire in cylinders 1 and 4 of the VAZ 2114. This is expressed in the fact that the car jerks and cannot move. In a word, a very unpleasant problem.
Previously, all units had 4 cylinders, and if problems arose with one, then the engine, as they said, began to “triple” and function on 3 cylinders.
VAZ car cylinder block
Nowadays, the situation is somewhat different because the units produced today can even have twelve cylinders. Of course, the phrase “troubling the engine” is no longer relevant, but it still remains and is mentioned when the operation of one of the cylinders is disrupted.
What causes misfires
The occurrence of misfires on a VAZ 2114 is a real problem that can become a prerequisite for more serious consequences. The car not only jerks, jumps and cannot work at full power. But it also starts with great difficulty; when driving, characteristic popping noises are heard, which occur due to detonation of the combustible mixture in the problem cylinder.
Checking the operation of the cylinders on a VAZ 2114 using computer diagnostics helps to detect many errors. If error P0301 lights up, then this indicates problems in the first one, if P0302 means misfires were detected in the second one.
Code 0302 - errors in the second cylinder
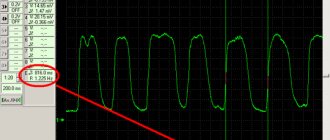
The VAZ 2114 electronic control unit continuously monitors the operation of the power unit through sensors. In this case, the rotation speed of the sensor on the crankshaft and the cylinders involved in a certain period of time is estimated. When a misfire occurs, the crankshaft rotation speed slows down slightly and this is determined by the computer. Modern electronics, if a miss is detected and the specified interval is exceeded, turns off the problematic cylinder. It simply will not receive fuel.
The cylinder can be turned on after a certain time, or after the engine is restarted. No more than 2 cylinders can be turned off at the same time. This is enough to get to the service station and keep the catalyst intact. On early versions of controllers, errors very often occurred when misfires were detected when driving on a bad road. However, now on the VAZ 2114 this problem has been completely solved after installing a road quality sensor.
VAZ 2114 car engine
The difficulty in identifying this malfunction lies in the fact that the misfire is not constant, but appears periodically. It often happens that in cold weather (until the engine is warmed up) it “troubles”, but after warming up, it starts working normally. This occurs due to wear of the cylinders, because after warming up, the metal parts expand and compression is restored.
Often, at idle speed, the VAZ 2114 power unit functions perfectly, but when the load increases, it throttles and functions with noticeable interruptions.
The problem is a burnt-out gasket, as a result of which, when the pressure in the combustion chamber increases, a leak appears.
The combustion chamber
It happens that the VAZ 2114 engine coughs a little, and then its operation returns to normal. In this case, nothing definite can be recommended, because a complete check of the power unit is required. There may be various reasons.
Fault diagnosis
The ignition of a VAZ 2114 is diagnosed according to the following scheme: the power plant check light lights up on the panel; during testing, error P0300 may light up. This means:
- problems in the first - P0301;
- problems in the second - P0302;
- problems in the third - P0303;
- problems in the fourth - P0304, etc. Error code 0304 - error in the fourth
There are many factors that cause the air-fuel mixture to not ignite, and they are different.
Basic faults
Due to the extensive accumulated experience in repairing this malfunction, we can identify common factors that are inherent to any units. Common reasons that can lead to misfires in the ignition system:
- First of all, the problem may lie in the candles.
Increased or decreased clearance, carbon deposits. Low quality candles. Candle with soot - Wiring problem. Mechanical damage. Oily contact.
- Damage to the module itself or the ignition coil.
- Due to poor quality fuel, the injectors may become clogged.
- Compression in the cylinder is broken.
Compression dropped - Incorrect adjustment of the gas distribution mechanism.
- Air leakage into the fuel system due to various factors. Damage to the intake manifold, wear of the injector rings.
- For various reasons, the gap between the cylinder and the piston has decreased.
These are the main factors that are most common.
On cars without a computer, checking and identifying the cause occurs by trying different options.
Once the cause is identified, we move on to repairs. For these works you will need the help of a specialist.
Loading …
"The engine is troit"
Source: https://avtozam.com/vaz/2114/propuski-zazhiganiya-v-tsilindrah/