The new type of rechargeable batteries practically do not require any maintenance or monitoring; most of them are maintenance-free and disposable. However, there are still those among car enthusiasts who still use serviceable batteries, which have a number of advantages, but require more attention from the motorist.
In this article I want to tell you how to check the electrolyte level in the battery at home, without resorting to any outside help.
As I already said, there are maintenance and maintenance-free batteries. With maintenance-free ones, I think everything is clear, they do not require control from the driver, all you need to do is make sure that the battery is always charged and charge it if necessary.
Relevant: Rules for operating the battery. How to properly charge a car battery?
As for the batteries being maintained, they should be given more attention; for example, it is necessary to monitor the density of the electrolyte, as well as its level in the battery banks.
How to disassemble the battery to add electrolyte
Algorithm of actions required to add water to the electrolytic solution of a maintenance-free power source:
- Remove the sticker located on the top cover of the power source housing.
- Under the label there is a plastic strip that needs to be pryed off from the side with a flat-head screwdriver. Pull the element upwards; plugs of the battery cans are attached to the parts of the batteries on the lid. Centra power supplies have a similar design. Then the owner can begin to determine the level and density of the electrolyte, as well as replace the solution.
- If the plate cannot be removed (for example, on Varta or Bosch products), then you need to visually determine the location of the filler necks of the cans.
- Pierce the lid with a thin awl, then perform circular movements associated with lowering the blade down. Piercing is performed until the tip of the awl begins to contact the battery electrodes.
- Place a mark on the tip to determine the distance from the cover to the top edge of the plates.
- Pull the awl out of the hole and then measure the resulting gap. Since the liquid level should be located 12-15 mm above the upper edge of the electrodes, the owner can calculate the value of the gap between the surface of the electrolyte and the plane of the housing cover.
- To fill the water, use a medical syringe with a volume of 10-15 cm³, equipped with an elongated needle. Then you need to cut the needle to the previously measured distance; the plastic spout should not fall into the holes made.
- Fill the jars with water until the required level is reached. Checking whether the reservoir is full is done by lifting the syringe plunger. If air is drawn into the tank, water continues to be added.
- After filling the cans, you need to rock the body of the power source in different directions, which will allow you to evenly distribute the water in the solution. Shaking the product is prohibited due to the risk of slag getting between the plates. Wait 20-30 minutes, and then carry out a control level measurement. If the volume has dropped, then an additional portion of water is introduced.
- Seal the holes with sealant; the factory label will not stick to the original place. Charge the power supply and then test the performance of the product. It should be taken into account that the technique provides a temporary restoration of battery characteristics.
Bad advice
The Internet is full of advisors who give ridiculous solutions to problems, and there are several myths floating around. Under no circumstances should you adhere to them, because such advice can kill the battery.
Here are some of them:
- Use snow instead of distillate. Snow is not distilled water. Adding it to the electrolyte causes breakdown.
- If lead precipitation occurs, pour out the electrolyte, rinse the jar with water and fill with a new substance. This was practiced in the last century. Modern battery banks have tightly spaced electrodes on which separator bags are stretched. It is impossible to pump out liquid with lead sediment from such jars. The pieces will not pass through the electrodes.
- Some sites sell so-called modifiers. According to the manufacturers, the products easily clean the electrolyte and extend the life of the battery. But these devices are the same as technologies that reduce fuel consumption. They do not work.
Specialist support
Lack of access to banks does not mean that the battery cannot be serviced. The service center technicians will test it and, if necessary, try to restore it. This is not a difficult operation, but no doubt requires a lot of time and practice. Do not underestimate the low level of electrolyte in the battery, even when it seems that it is slightly below normal. However, this greatly affects the performance of the battery; only professionals know how much electrolyte a 60-volt battery needs, so they can be trusted with this capricious part of the car, which often brings surprises.
What should a car owner do when it turns out that the battery requires charging? To do this, you need to remember some rules:
- Firstly, first disconnect the negative and then the positive poles.
- Secondly, when dismantling, do not tilt the battery to reduce the risk of electrolyte leakage.
- When connecting the battery to the charger, it is recommended to charge it in a well-ventilated area because hydrogen and oxygen are released during the charging process.
We recommend: Charging a Bosch s4 silver car battery
As a rule, it takes several hours to charge; to avoid overcharging, it is better to use a rectifier that will automatically adjust the charging process and time.
Car dealerships sell batteries that do not require maintenance. The expression "no maintenance" means that this device has less electrolyte loss compared to a traditional acid battery.
Often, inexperienced owners of passenger cars install a battery with a capacity higher than that recommended by the manufacturer. For example, instead of the recommended 6 st-55, they install 6 st-75, knowing how much electrolyte is in the battery 75, but do not understand that it is too large and will obviously not be fully charged, therefore it will wear out faster than its smaller counterpart.
How to handle the battery
In order for the electric current storage device to serve for a long time, it is necessary to follow some recommendations from specialists:
- In winter, before starting the engine, turn off all unnecessary electrical appliances (radio, lights, fans).
- Do not load the power source by rotating the starter for a long time. Perform short intervals of up to five seconds and allow it to rest for about half a minute between individual samples.
- Remember to press the clutch during this action, this will significantly facilitate the rotation of the engine crankshaft.
- When driving a car in city mode, sometimes it is worth taking a longer trip so that the battery has a chance to fully charge.
Correct charging
It is not normal when the car cannot be started without outside help. The energy balance of the vehicle must be constant. The battery should be charged properly while the engine is running, and the generator should produce as much current as the car consumes. However, in practice this is not always the case. Therefore, the same battery in one car works without problems even for 8 years, but in another, already in the second winter season, it often fails the driver. This is because the battery, firstly, does not tolerate constant incomplete charging, and secondly, current is used uneconomically, for example, music, light while parked.
We recommend: Characteristics of the 6ST-55 battery
Nothing harms a battery more than frequent and prolonged discharges, undercharging or overcharging. In all these cases, the cause may be too little or too much charging current. This is easy to check in a workshop and simple to fix. Take care of your battery by following the recommendations of professionals:
- Do not approach with fire while charging, there is a danger of a flash of released hydrogen.
- You cannot connect the poles with a piece of metal.
- Leaving a car without recharging the storage device for a period of more than two months is risky.
- Securely attach the battery to the car body.
- It is prohibited to overload the device by charging with too much current or voltage.
- Operate the starter with too much current consumption.
Do not put the terminals on the battery by hitting it from above. It is necessary to unscrew the screw, straighten the seat on the cable with a screwdriver, and carefully place it on the electrode.
Why check electrolyte content?
When operating the car in any conditions, the water contained in the electrolyte still evaporates. At the same time, in addition to a decrease in the liquid level, its density increases, which negatively affects the performance and durability of the battery.
In addition, by checking the level of the solution, you can monitor its cleanliness. The presence of impurities in the electrolyte negatively affects the performance and durability of the battery.
Advantages and disadvantages
Classic perm has its positive and negative sides.
Advantages of the procedure:
- Hair remains curly for a long time.
- The hairstyle acquires the desired volume.
- If previously the strands were oily at the roots, then after the procedure they become drier.
The disadvantages of the procedure include:
- Inability to dye strands for a long time.
- Aggressive effect of the drug on the hair structure.
- The need for careful care with nourishing and restorative agents.
- Severe dryness of strands.
The disadvantages of perm include the presence of contraindications.
This procedure is not recommended in the following cases:
- pregnancy;
- lactation;
- tendency to allergic reactions;
- severe hair damage;
- illness and fever;
- menstruation;
- taking potent medications.
The listed contraindications also apply to biowaves. But compared to perm, the number of disadvantages mentioned above is reduced, since the aggressive effect on the hair is reduced. It will no longer be possible to “burn” them.
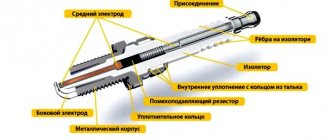
What's inside the battery
There are six compartments, or “jars,” arranged in a specific sequence inside a car’s battery. Each compartment has lead plates with positive and negative charges. The “can” is hermetically sealed, and its contact with other elements occurs through a common polar connection.
The voltage level in each battery compartment is 2, maximum 2.1 volts. All elements are connected to each other in a serial electrochemical circuit, having a total output voltage of 12 volts.
Due to the fact that each “can” is filled with a special chemical compound that has a liquid consistency, a car battery has the ability to accumulate and release an electric charge. This liquid is called “electrolyte”, and such simple theoretical knowledge from the field of physics and chemistry will help you understand how to check the density of the battery (more precisely, the electrolyte) correctly.
What is an electrolyte and its role in a battery?
To start the engines of modern cars, acid batteries are used, which are filled with a special solution that conducts electric current. It consists of sulfuric acid dissolved in pure distilled water. Ready-made electrolyte is offered by some automotive stores with a density of 1.29 g/cc. see Previously, ready-to-use batteries were offered, as well as dry-charged batteries that needed to be prepared for operation in a certain way.
To do this, you should adhere to the following algorithm:
- First, the battery needs to be filled;
- let the plates soak for an hour;
- recharge it with a current not exceeding 1/10 of the battery capacity;
- the voltage at the terminals during charging should be approximately 13.6-14.4 volts.
Electrolytic fluid plays an important role in the operation of a car battery.
Inside the case of a modern battery there are lead plates of different polarities. The positive grids are coated with lead dioxide, and the negative grids are simply lead in powder form. To increase strength and ductility, antimony was previously included in their composition. Calcium and silver are used to alloy the lattices of modern units. This significantly reduces water consumption during operation.
During the operation of the battery, chemical reactions occur when the atoms of the porous lead plates interact with a solution of sulfuric acid. When charging, the lead atoms are released from the electrons of the sulfuric acid. The electrolyte density increases. Battery discharge is accompanied by lead binding and a decrease in density.
Battery device
The degree of charge is determined by the density of the electrolyte. Depending on the ambient temperature, the norm is 1.24-1.27 g/cc.
Today we offer serviced, low-maintenance and maintenance-free batteries. Only the first two varieties have access to the electrolyte.
Required electrolyte level in the battery
If you have a serviceable battery, you will need to regularly monitor the level of the chemical solution in it.
When it drops, add clean water. The liquid capacity also depends on the volume of the battery:
These figures are quite arbitrary, as they may differ - it all depends on the battery model, manufacturing method and manufacturer.
It is important to consider one point regarding the level of the solution: it should be 10-15 mm higher than the plates, that is, cover them completely.
The final stage of working with the battery
At the final stage, you need to screw the plugs into place. You should first clean the inside of them. It is not advisable to allow liquid to overflow. Spilled drops must be removed with a rag so as not to touch the electrolyte with your hands, because it contains some acid.
You need to wipe away streaks using movements away from the holes. If the battery was under the hood at this time, then it is necessary to prevent drops from getting on other parts and the engine. Having completed wiping, you need to throw the rags in the trash, and pour the container with water in which you rinsed the rag down the drain so as not to splash acid particles on clothes and objects.
Reasons for changes in fluid volume
Due to the way the battery operates, the level and density of the electrolyte decreases over time. This happens almost always, even in maintenance-free batteries. In most cases, the density increases over time, because sulfuric acid is not subject to evaporation or hydrolysis, unlike water. Essentially, the water level in the electrolyte changes.
This happens for the following reasons:
- Leakage through cracks in the housing. Diagnostics is simple - if the place where the battery was located is filled with electrolyte or there are smudges, then the housing is damaged. In this case, the density usually does not change; if you solder or seal the crack, you can continue to use the battery. But more often they prefer to replace the battery.
- Leakage when turned over. The battery cover has holes for the release of water vapor and gases and plugs for checking the level and density of the electrolyte. Some electrolyte may leak through them. This happens when dismantling the battery or when traveling on rough off-road conditions. The density should not change.
- Natural evaporation of water. Intense evaporation occurs if the battery is used at high temperatures - in the heat of summer or if the battery is close to heated engine parts. Only water evaporates from the electrolyte and the density in this situation inevitably increases.
- Hydrolysis of water. If you charge the battery with strong currents, or when overcharging, part of the energy is spent on hydrolysis of water. This is decomposition into gaseous hydrogen and oxygen - “gurgling” or even boiling is observed in the battery banks. The density will increase as hydrolysis decomposes the water and the acid will remain intact.
A low level negatively affects the performance characteristics of the battery - concentrated acid easily corrodes lead and its salts settle on the plates and bottom, sulfating the battery and shorting the banks. To extend battery life, you need to periodically monitor the density and level of electrolyte.
Low level - why it’s dangerous
It is dangerous for many reasons, I will try to explain it simply and quickly:
- If the level drops, it means the water is evaporating. The density of sulfuric acid increases (since it does not go anywhere). This has a very negative effect on the plates themselves; they simply begin to deteriorate faster.
- If the acid concentration is high, this can lead to an accelerated sulfation process of the plates
- The upper part of the plates is exposed - and this also negatively affects them when charging. They simply warm up and can crumble.
- If there is not enough electrolyte (the plates are exposed), the battery capacity drops accordingly, meaning you simply won’t start the car.
From my own experience, I will say that batteries with bare plates do not last long; as a rule, they crumble or become sulfated within 3 to 6 months of use. Therefore, it is very important to add liquid to the required values!
Determination of electrolytic fluid in a battery
There are two types of energy sources commonly used in the automotive industry today:
- Maintenance-free devices are enclosed in a sealed housing that completely prevents access from the outside. They, as a rule, exhaust their resource and must be replaced. You cannot restore their functionality on your own. The only thing the owner of such a battery can do is charge it as needed.
- Maintained - require constant attention and monitoring. It is necessary to regularly monitor the level of the electrolyte solution, as well as its density and the condition of the plates.
How to find out the electrolyte level
Electrolytic liquid can change its volume as it is stored and used. How can you check the electrolyte level in a battery? There are several options, each of which can be used in a specific situation:
- According to special marks applied to the body. Some energy sources have two horizontal lines parallel to each other on the outer surface of the housing in its upper part. The bottom one is marked “min” - shows the minimum possible level of the electrolyte solution. The top one has the inscription “max” - the maximum permissible limit of the liquid medium.
- By visual inspection. It allows you to determine the approximate amount of liquid content. In the absence of tags and other available means, it is enough to simply unscrew the plugs on the top cover of the case, while installing the device on a flat horizontal surface. Looking inside, especially if there is good lighting, you can understand by the following criteria whether the solution is enough or not:
- the plates are completely hidden by the liquid medium, there are no leaks on the outside of the case - the level is normal;
- the electrodes are visible (they are level or above the surface of the liquid) – topping up is required.
- By performing simple measurements. The electrolyte level in the battery can be checked using:
- Hydrometer device. It will allow you to find out the density of the liquid in each jar, which will make it possible to draw a conclusion about its quantity. We lower it into each hole one by one, draw up the solution using a bulb and look at the readings. If the value is higher than normal, then the level is insufficient.
- Available means: a transparent juice tube or the same body of a ballpoint pen. We lower the tube into the hole in place of the unscrewed cap until it rests against the top edge of the jar. We pinch the end remaining on the surface with a finger, thus blocking the flow of air into it. Holding your finger, remove the tube and measure the height of the column of liquid trapped inside it. At a normal electrolyte level, its value should be in the range from 11 to 15 mm.
Low battery electrolyte level
How can you tell if your battery has low electrolyte levels? This is very eloquently evidenced by:
- significant increase in density;
- the appearance of plates above the surface of the liquid medium.
There may be several reasons for this:
- Evaporation of distilled water is the most common factor in volume reduction in the summer. As is known, too high outdoor temperatures provoke evaporation processes. And when using the battery during this period, it is very hot under the hood.
- Liquid boiling over due to a malfunction of the temperature relay-regulator.
- As a result of battery discharge, some of the acid is consumed for electrochemical reactions.
A decrease in the electrolyte level below normal in the battery leads to very serious consequences:
- firstly, a solution of increased concentration promotes accelerated destruction of the plate material;
- secondly, that part of the electrode surface that is located above the liquid boundary undergoes sulfation.
In both cases, the outcome is the same: rapid loss of capacity and premature failure of the energy source. This means it will need to be replaced. Where is the guarantee that the new battery will not lose its functionality just as quickly?
Option one is to learn how to properly operate and maintain the battery, and first of all, maintain the liquid component at normal levels.
What should be the electrolyte level in the battery? The norm is when the electrolyte solution is 1–1.5 centimeters above the electrode plates, completely covering them when the car is moving.
Moreover, the electrolyte level must be the same in each jar - this is very important for reliable battery operation.
Methods for determining the level in a maintenance-free power supply
Conventionally, batteries can be divided into two types: serviced and maintenance-free. In the latter case, the design does not provide access to the compartments and manufacturers do not recommend opening the case yourself. Otherwise, you will break the seal, and you will hardly be able to seal the plastic case properly. Such manipulation will lead to the fact that the battery will have to be thrown away. In a maintenance-free battery, the amount of electrolytic mixture can be determined in two ways.
By control marks
On the body of such batteries there are “min” and “max” marks placed on an oval eye made of transparent material. The electrolyte level should be between these marks. If it is lower, it means that some of the distilled water has evaporated or flowed out through the safety valves. This usually happens due to improper charging or after the service life has expired.
By indicators
Modern models of imported and domestic batteries can be equipped with indicators. People call them “magic eyes”. The indicator changes color depending on the amount of charge and the density of the electrolytic mixture. To check the solution level in your car battery, follow these steps:
- using a clean rag, thoroughly wipe away the dirt and dust near the indicator;
- lightly tap the indicator with your finger - this will remove oxygen bubbles and you will be able to see it better;
- look at the color that appears on the indicator.
Green indicates that the level is normal, the charge is maximum. White – you need to connect the charger. Red – increased acidity of the solution, that is, the amount of water has decreased.
Inspect the battery housing.
The concept and principle of operation of the battery
How to replace the electrolyte in a battery, which today is practically not dismountable and monolithic. We’ll share the advice a little later, but now a little about the battery. Monoblock batteries are sold in specialized stores or markets, unlike those that could be bought 10 years ago.
Therefore, this type of product can be classified as conditionally repairable. How the device works
: Thanks to the current generated by the generator and with the help of chemical reactions of the electrolyte with the lead plates, electricity is accumulated, which is used to start the engine. Especially when the question concerns the resuscitation of an old battery, replacing the electrolyte is inevitable.
How to check the electrolyte and measure its density
Before checking the electrolyte in the battery, clean its surface from dirt and dust so that when removing the covers from the battery compartments, they do not get inside . Take a thin glass tube, its diameter can be from 4 to 5 millimeters. Now you need to lower the tube into the compartment all the way, so that it touches its bottom. The hole can be closed using your finger (remember to protect yourself first by wearing technical gloves!).
Remove the tube from the jar: a small amount of electrolytic liquid should fall into it. Focus on its height - how much space it takes up in the tube. If the height of the liquid is 10-15 millimeters, the density is within normal limits, and when the level is higher or lower, the density must be adjusted.
Before you begin adjusting the density, you need to make accurate measurements of it - in each battery compartment separately, since they do not communicate with each other. Be sure to charge the battery before taking measurements, otherwise the results may be incorrect. In addition, shortly before the process, the battery should be left for 3-4 hours in a room at room temperature (from 20°C, maybe a little higher). After all, a chemical liquid is directly dependent on the temperature factor.
To measure the level of electrolyte density, a simple instrument such as a hydrometer is used. It is also sometimes called a more complex word - densimeter. But essentially it's the same thing. The hydrometer consists of a tip, which is alternately lowered into the battery compartments, a flask, a rubber bulb for sucking out liquid and a measurement scale, which is located inside the flask.
The verification algorithm will be as follows:
- wipe the tip dry with a clean cloth;
- lower it into the battery compartment;
- Use a rubber bulb to scoop out a small amount of liquid;
- monitor the “behavior” of the electrolyte: when it stops moving, measure the density on the scale;
- pour the liquid back into the “jar”.
As you can see, the technique for taking readings is very simple. The main thing is to remember to protect your hands with gloves.
Electrolyte replacement
After all cleaning and preparation procedures, it is necessary to begin filling the electrolyte. To do this you will need the following tools:
- watering can;
- latex gloves;
- the electrolyte solution itself.
You also need a hydrometer to pre-check the density. It should be 1.28 g per cubic centimeter. If everything corresponds to the norm, then you need to gradually begin to fill the reservoirs with electrolyte, noting in advance the required amount of liquid for each of them.
Advice! If there is sulfate deposits on the electrodes, then special additives can be added to the electrolyte to remove it.
The reservoirs are filled evenly and gradually; excess liquid can be removed with a rubber bulb and wiped with a cloth or napkin.
The filling process is quite simple and does not require special preparation. Here you just need to measure the density of the substance and gradually fill empty jars with it. If necessary, special additives are added to protect the electrodes.
After filling, do not immediately put the battery into operation. It is necessary to wait about two days until the additive substances are completely dissolved, as well as until all the air leaves the housing. Only after this can you begin the charging and testing stage, analyzing the result of the work done.
Battery check
After two days, you can start charging the battery. This is done using a special device with a voltage of 12V. It is necessary to remove the protective plugs and connect the charger to the battery. After this, the cyclic charging process begins, which operates in accordance with the “charge-discharge” scheme.
Advice! The charging current should not exceed 0.1 ampere. This is the optimal indicator for the first time.
The procedure is carried out until the device is fully charged. The test is carried out with a simple voltmeter, determining the voltage of each section or terminals. At each section the voltage should not be less than 2.4 V, and at the terminals - not less than 13 V.
As a result, you can significantly improve the technical performance of the old battery. Replacing the electrolyte often returns the characteristics to the original ones. If the reason is not in the liquid, but in the plates themselves, then any resuscitation procedures are useless. It is necessary to purchase a new battery, because the old one is already dead.
For a more detailed analysis, it is recommended to watch this video. Refilling a new battery is described here, the principle of which is practically no different from replacing the electrolyte. This will allow you to avoid mistakes in the final steps and get the device into working condition:
- How to charge a car battery with a charger
- How to replace the electrolyte in a car battery
- How long does it take to charge a car battery?
- What current to charge a car battery with: 60, 70, 100 Ah
How long does it take and how to charge it correctly?
After keeping the battery in which distilled water and electrolyte were mixed for 3 hours, it must be charged.
The correct way to charge the battery after adding water is as follows:
- Prepare the battery for charging:
- cleaning the terminals from oxides in order to ensure strong contact;
- cleaning the surface of the case from any remaining traces after filling the battery;
- removing the plugs and lids on each jar to once again ensure that the electrolyte level in each jar is normal;
- To avoid burns, you need to wear gloves, and it is advisable to wear safety glasses.
- Determine charging method. There are three main ways:
- DC charging is a fairly effective method, but difficult to implement;
- charging under constant voltage is a much simpler method, but less effective; the battery charge after completion does not exceed 80% of the nominal one;
- combined - special expensive equipment is required here, but the battery owner does not expend any additional effort.
- Charge the battery.
DC charging is a very effective way to charge your battery as much as possible. In this case, it takes a long time and constant monitoring of the charging process, but the result will be excellent.
It is possible to charge the battery to almost 100%. The time it takes to recharge is about 10 hours.
Charging under constant voltage is much easier to perform. Just set the voltage to 14.4 V and wait. This charging method will require almost a day and will charge the battery to almost 80% of its nominal value.
Charging in a combined way is carried out using a special device. “Smart” equipment will independently perform the entire range of actions to check the battery charge level, start the charging process and automatically supply the required voltage at the right time.
It prevents water from boiling away from the electrolyte and excessive current supply. The equipment is expensive. With such recharging, it will take up to 12 hours, depending on the degree of discharge.
The amount of electrolyte in batteries of different capacities
In some cases, it is necessary to completely replace the solution. Trying to find out how much liquid is required based on the level in the jars will not give any result. Unfortunately, manufacturers do not indicate the volume of the compartments, so you have to calculate it based on the battery capacity.
For these cases, we have prepared a table of correspondence between the amount of solution and the parameters declared by the manufacturer; you just need to find these values on the stickers or in the instructions.
Battery type
Electrolyte quantity (liters)
Checking with a load fork
A load plug is a device that represents some kind of electrical load (usually a high-resistance resistor or a refractory coil) with two wires and terminals for connecting the device to the battery, as well as a voltmeter for taking voltage readings.
The verification process is quite simple. It consists of the following steps:
- You need to work at a temperature of +20°С…+25°С (in extreme cases up to +15°С). You should not test a cold battery, as you risk significantly draining it.
- The plug is connected to the battery terminals - the red wire is to the positive terminal, and the black wire is to the negative terminal.
- Using the device, a load with a current of 100...200 Amperes is created (this is an imitation of a switched on starter).
- The load acts on the battery for 5...6 seconds.
Based on the readings of the ammeter and voltmeter, we can talk about the condition of the battery.
| Voltmeter readings, V | Charge percentage, % |
| >10,2 | 100 |
| 9,6 | 75 |
| 9 | 50 |
| 8,4 | 25 |
On a fully charged battery, after applying a load, the voltage should not drop below 10.2 V. If the battery is slightly discharged, then a drop of up to 9 V is allowed (however, in this case it must be charged). And after this, the voltage should be restored almost immediately, and after a few seconds completely.
Sometimes it happens that if the voltage is not restored, then there is a high probability of one of the banks shorting. For example, with minimal load it is necessary for the voltage to recover to 12.4 V (up to 12 V is allowed with a slightly discharged battery). Accordingly, the lower the voltage drops from 10.2 V, the worse the condition of the battery. With this device you can check the battery both upon purchase and already installed in the car, without removing it.
When to charge the battery
Before charging the battery, you must ensure that it is truly discharged. There are several ways to do this:
- Voltage measurement at the terminals. This can be done using a constant voltage voltmeter, in other words, an electronic multimeter or a pointer tester. For standard batteries used in most passenger cars, the standard voltage value is 12 V. In practice, it differs slightly from the nominal value. So, a value equal to 12.7 V tells the car owner that the battery charge level is 100%, and accordingly, there is no need to charge it. If the measured voltage is 12.2 V, then this indicates that the charge level is approximately 50%. And if the voltage drops to 11.6...11.7 V, it means that the battery is almost completely discharged and needs additional charging.
- Measuring the electrolyte density value. However, this verification method is only possible for so-called serviceable batteries, that is, in which it is possible to reach containers with electrolyte (and add it, if necessary). To measure density, a special device is used - a hydrometer. The electrolyte density should be around 1.27 g/cm³. If it is significantly less, it means that the battery should be charged with a charger. In unattended ones there is a special window where 3 stages of density will be displayed.
- Problems starting the engine. One of the reasons why the starter does not turn, and problems arise with starting the engine, is precisely the battery discharge. This is usually accompanied by problems in the operation of other consumers of electricity in the car - lighting, operation of the audio system, and so on.
In a discharged battery, sulfation of its lead plates occurs, which leads to a sharp decrease in its service life, that is, durability.
Serviceable and maintenance-free batteries
Based on the structure of the battery case, they are distinguished into so-called “maintenance” and “maintenance-free” . Nowadays the second type is increasingly predominant, that is, when buying, you practically do not need to monitor it (for beginners this is just a godsend). However, this option also has big disadvantages, for example, if the water evaporates from the cans, then you won’t be able to add it so easily. Many people throw away ( take them to stores ) such batteries and buy new ones, although just add water (to the required level) and it will work for a long time
Maintenance-free battery device
The main drawback of a classic lead-acid battery is increased gas formation during charging - if under normal conditions hydrogen comes out in small bubbles, then when the charging current is exceeded, the process resembles boiling. That’s what they used to say, in fact, “charge until it boils.” The decomposition of water due to electrolysis leads to the fact that the electrolyte level drops over time, and its density increases - this is why batteries of the classical design have plugs to control the density and top up with distilled water.
Although a conventional battery has the longest lifespan of any type when properly maintained, it is not convenient for the average consumer. Therefore, the appearance of batteries capable of operating for a long time without adding water was logical.
The first to appear were the so-called calcium (Ca/Ca) batteries. In them, both plates of each bank are doped with calcium, in contrast to classical batteries, where the plates are stamped from a lead-antimony alloy. As a result, the release of hydrogen has sharply decreased - under normal operating conditions, a calcium battery operates for at least three years without a significant drop in the electrolyte level.
However, calcium batteries have one feature: they tolerate discharge very poorly below 12V, since the positive electrode quickly sulfates and is destroyed. A discharge can “kill” even a new battery, as evidenced by the practice of car dealerships: for example, while Avtoframos installed Ukrainian Ista calcium batteries on cars of the Logan family, long-term parking of the car often led to the need for a warranty replacement of the battery even before it was sold to the client.
Video: Maintenance or maintenance-free battery.
A way out of the situation was the development of hybrid batteries (Ca+) - in them the positive electrode is made of an antimony alloy, their resistance to deep discharge has increased significantly. A further development of maintenance-free batteries was the appearance of AGM and gel batteries - in them the electrolyte is either impregnated with an inert filler (AGM) or thickened with silicon compounds.
The ventilation design of maintenance-free batteries is more complicated than that of classic ones: to catch drops of electrolyte and prevent its spillage when tilted, a labyrinth is introduced into it, often supplemented with check valves. Before starting charging, it is necessary to check its serviceability - the output channel clogged with dirt must be cleaned.
Something else useful for you:
Technical characteristics of the model range
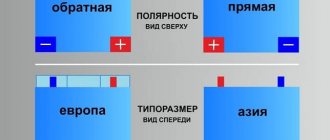
The Akom model range includes batteries of different capacities, starting currents, and different polarities. You can choose a model for both European and Asian cars, both passenger cars and trucks. The full range and characteristics of each line can be found on the official website.
Akom
This launch series includes models for European and Asian passenger cars (Asia), as well as for trucks. The passenger group includes batteries with a capacity of 55 to 100 Ah, cold cranking current from 460 to 870 A. Trucks have a capacity of 140 - 190 Ah, with starting currents of 950 and 1200 A. For Asian cars, batteries with a capacity of 40 to 100 Ah are intended, with cold cranking current from 330 to 790 A.
Akom
| Akom | Capacity | Starting current | Dimensions | Weight |
| European cars | 55 | 460 | 242x175x190 | 14,8 |
| 55 | 520 | 242x175x175 | 15,5 | |
| 60 | 520 | 242x175x190 | 15,5 | |
| 60 | 590 | 242x175x175 | 15,8 | |
| 62 | 540 | 242x175x190 | 16 | |
| 65 | 580 | 242x175x190 | 16,5 | |
| 74 | 700 | 277x175x175 | 18,5 | |
| 75 | 700 | 277x175x195 | 18,5 | |
| 90 | 780 | 353x175x190 | 23,5 | |
| 90 | 870 | 353x175x175 | 23 | |
| 100 | 850 | 353x175x190 | 24,5 | |
| Asian cars | 40 | 330 | 187x127x225 | 9,8 |
| 50 | 420 | 238x129x225 | 12,7 | |
| 65 | 520 | 232x173x225 | 16,1 | |
| 75 | 600 | 260x173x225 | 18,3 | |
| 100 | 700 | 305x173x225 | 21,9 | |
| Trucks | 140 | 950 | 513x189x215 | 40 |
| 190 | 1200 | 513x189x215 | 50 |
Akom EFB
Batteries in this series are new from the manufacturer Akom. They are created using advanced EFB technology and meet all international quality standards. An improved separator and a new plate design almost doubles the service life of the structure. The starting current has also been increased.
The batteries work in all weather conditions. They perfectly withstand the range from -40 to +50 degrees Celsius. They have a double resource. Compared to conventional batteries, they can withstand twice as many full charge-discharge cycles and are not afraid of deep discharge and are resistant to corrosion.
Suitable for modern premium vehicles equipped with a start-stop system and a large amount of electronics.
The batteries presented in this line have capacities from 55 to 100 Ah and cold cranking current from 530 to 930 A.
Akom EFB
| Akom EFB | Capacity | Starting current | Dimensions | Weight |
| Vehicles with Start-Stop system | 55 | 530 | 242x175x190 | 16,2 |
| 60 | 560 | 242x175x190 | 16,6 | |
| 62 | 580 | 242x175x190 | 16,6 | |
| 65 | 650 | 242x175x190 | 18,1 | |
| 75 | 720 | 275x175x190 | 19,8 | |
| 90 | 820 | 353x175x190 | 24,3 | |
| 100 | 930 | 353x175x190 | 25 |
Akom Reactor
Reactor batteries are powerful and have higher inrush currents. Designed for cars literally “studded” with various energy consumers. According to the manufacturer, they have no analogues in Russia.
Capacities range from 55 to 100 Ah, and cold cranking current from 550 to 1000 A.
Akom Reactor
| Akom Reactor | Capacity | Starting current | Dimensions | Weight |
| Cars | 55 | 550 | 242x175x190 | 15 |
| 62 | 620 | 242x175x190 | 16,8 | |
| 75 | 750 | 278x175x190 | 20 | |
| 100 | 1000 | 353x175x190 | 26 |
Akom Ultimatum
Ultimatum batteries are aimed at vehicles with a start-stop system and a large number of energy consumers. Akom Ultimatum is also used on boats, yachts and motorhomes. One of the obvious advantages is resistance to deep discharges.
The capacity of the models presented in the line ranges from 60 to 95 Ah. Starting current – from 550 to 850 A.
Akom Ultimatum
| Akom Ultimatum | Capacity | Starting current | Dimensions | Weight |
| EFB battery for cars with a start-stop system, and the same for boats, yachts and motorhomes | 60 | 550 | 242x175x190 | 16,8 |
| 70 | 640 | 278x175x190 | 19,3 | |
| 95 | 850 | 353x175x190 | 25 |
Akom Bravo
Bravo batteries have an optimal ratio of capacity and starting current. Focused on domestic and foreign vehicles with the usual set of options. Available in direct and reverse polarity. Models for cars and trucks are presented.
Tanks for cars - from 55 to 100 Ah, for trucks - 140 and 190 Ah. Cold cranking currents for the first group are from 430 to 760 A, for the second - 890 and 1100 A.
Akom Bravo
| Akom Bravo | Capacity | Starting current | Dimensions | Weight |
| Cars | 55 | 430 | 242x175x190 | 14,3 |
| 60 | 480 | 242x175x190 | 15 | |
| 74 | 650 | 278x175x190 | 18,2 | |
| 90 | 760 | 353x175x190 | 22 | |
| Trucks | 140 | 890 | 511x183x239 | 38 |
| 190 | 1100 | 524x239x223 | 46 |
What you need to know when working with batteries
When operating or servicing a battery, you must follow simple but mandatory rules:
- When making an electrolyte yourself, you need to pour the acid into water, but in no case vice versa. Water has a lower density and splashes from the surface of the acid.
- If electrolyte gets on the skin, it must be washed off with plenty of water and soap and lubricate the affected area with any cream.
- If the solution gets into your eyes, immediately rinse them first with plenty of water, literally placing your open eye under the stream, then with furatsilin solution (1 tablet per glass of water) and be sure to consult a doctor. Under no circumstances should you wash your eyes with boric acid from a car first aid kit - it is used for completely different cases!
- If acid gets on your clothes or shoes, do not be lazy and immediately wash the area with plenty of soap. If you don't do this, after a few hours the fabric and even tarpaulin leather will crumble into dust.
- Do not charge the battery indoors. During charging, hydrogen and oxygen are released from the cans, which will explode at the first spark no worse than a bomb. Be sure to open the garage door or use the hood. And, of course, do not use matches for illumination and do not smoke.
- Do not turn the battery over during transportation, even if you are taking it for recycling. The section plugs are leaky, and sulfuric acid corrodes almost anything.
Features of battery maintenance
There are certain rules in servicing the starter battery, the violation of which leads to a reduction in its service life. So, what you cannot or are highly discouraged from doing:
- add electrolyte to the jars, you can add water, and then only distilled water;
- there is no particular need to drain the electrolyte from the battery; this action is performed only on dry-charged batteries when refilling them (immediately after purchase) or if all the solution has leaked out of the cans;
- operate a car with contaminated terminal terminals;
- do not allow dirt to get inside the housing.
Of course, you need to try not to let the battery become completely discharged, and if the starter “gets tired” of turning, you should give it a rest for some time.
Video: Battery electrolyte level
Related articles:
- Dry-charged battery - maintenance and operation The battery is the source of electricity in the car - without it it is impossible to start the engine, all consumers run on the battery when the engine is not running and the generator does not […]
- The most important parameters when choosing a new battery Car batteries are produced by various companies; there are many models on the market that differ in size, cost, battery type, capacity, and other characteristics. […]
- Caring for battery terminals - methods, materials used A car battery requires care, even if it is a maintenance-free type: dirt and oxides formed on the body during operation negatively affect the condition of the battery […]