Below is a list of engines installed on the VAZ 2114 throughout the history of production.
- 1.5 liter 8 valve engine;
- 1.6 liter 8 valve engine;
- 1.6 liter 16 valve engine;
All engines have similar roots back to the distant 80s, namely with the 2108 engines. It was the eight engine that became the progenitor of all engines installed on modern VAZs.
This engine was distinguished by its reliability and maintainability.
Let's take a closer look at each of the engines.
Motor 2114: characteristics and features
Let's start with the fact that the VAZ 2114 engine, an 8-valve injector, was created on the basis of the unit that was installed on the VAZ 2108. This engine was taken as the basis, since the engine on the G8, which was popular at one time, turned out to be quite successful, simple and reliable.
We also note that early versions had only a relatively simple BC, but since 2007 the motors received a full-fledged ECU, which began to control engine operation based on data received from numerous ECM sensors.
Considering the similarity of these power units, the performance of the different versions does not differ much. For example, if we consider VAZ 2114 engines, then the main characteristics of the engines are as follows:
Petrol engine VAZ 2111 injector
- Working volume: 1.5 liters;
- Number of cylinders: 4;
- Number of valves per cylinder: 8;
- Power: 77 hp;
- Fuel consumption: 8.2l/100 km.
Gasoline engine VAZ 21114 injector:
• Working volume: 1.6 liters; • Number of cylinders: 4; • Number of valves per cylinder: 8; • Power: 81.6 hp; • Fuel consumption: 7.6l/100 km.
Petrol engine VAZ 21124 injector:
- Working volume: 1.6 liters;
- Number of cylinders: 4;
- Number of valves per cylinder: 16;
- Power: 89.1 hp;
- Fuel consumption: 7.0l/100 km.
Also, to increase service life, you need to regularly service the internal combustion engine, and also know what kind of oil to pour into the engine. You also need to follow the operating instructions. This approach makes it possible to ensure that the engine in a VAZ 2114 can easily travel about 200 thousand km. and more without major repairs.
DESIGN FEATURES
The engine we are considering has a cast cylinder block, the oil supply holes in which are machined, and the holes for antifreeze are made during the casting process. The engine cylinders are also machined inside the monolithic structure.
At the bottom of the structure there are supports for the main bearings, the covers on which are an irreplaceable part of the engine - they are adjusted to size at the stage of manufacturing the supports, and it is impossible to find two covers of the same size.
Inside the supports there are inserts made of a steel-aluminum alloy, and inside the third support there are half rings that prevent axial displacement of the crankshaft.
The pistons of the VAZ 2114 engine are aluminum, with cast steel rings, the connecting rod is steel. The cylinder block of the fourteenth is placed on a metal tray, on top of which a vibration-damping lining is laid.
Owners of the fourteenth are advised to check the integrity of this lining from time to time, since when it wears out, the sump, which is a hollow container for storing oil, can be damaged when driving over uneven surfaces due to the pressure of the cylinder block.
The crankshaft, located under the cylinder block, is equipped with a mount for the flywheel. The lightweight flywheel on the VAZ 2114 has a special mark, through which its correct location on the crankshaft flange is selected - it must be placed strictly perpendicular to the connecting rod journal of cylinder No. 4.
Disassembly and assembly of the engine on VAZ 2113, 2114, 2115 cars
Remove the pipe and gasket.
Using a 10mm wrench, unscrew the six bolts securing the crankshaft rear oil seal holder.
Remove the holder and gasket.
Using a 14mm socket, unscrew the nuts securing the connecting rod cover (the connecting rod must be at BDC).
Remove the connecting rod cover.
Remove the lower connecting rod bearing shell from the cover.
We rest the wooden handle of the hammer against the connector of the lower head of the connecting rod and push the piston and connecting rod out of the cylinder.
Remove the upper bearing shell from the connecting rod head a.
Similarly, we remove the pistons with connecting rods from other cylinders. We clamp the connecting rod in a vice with soft metal pads.
Remove the oil scraper ring expander.
On the VAZ-21083 engine, the piston pin is inserted into the upper head of the connecting rod with interference.
We press out the pin by hitting the mandrel with a hammer, holding the connecting rod hanging or placing the piston in a wooden support with a cylindrical recess for the piston skirt and a hole for the pin.
Remove the piston from the connecting rod.
The VAZ-2111 engine uses floating-type piston rings that rotate freely in the piston bosses and connecting rod bushing. To disassemble the piston and connecting rod, clamp the connecting rod in a vice with soft metal pads. Use a screwdriver to pry up the piston pin retaining ring and remove it from the piston ring groove.
In the same way, remove the second retaining ring. Use a mandrel to push out the piston pin and remove the piston from the upper head of the connecting rod.
Using a 17mm socket, unscrew the ten bolts securing the crankshaft main bearing caps.
Remove the lower main bearing shell from the cover.
We take out the crankshaft.
We remove the thrust half rings from the grooves of the middle main bearing support.
We remove the upper crankshaft main bearing shells from the supports in the cylinder block.
We assemble the engine in reverse order. We install liners in the main bearing caps without grooves on the inner surface. We install liners with grooves in the first, second, fourth and fifth supports of the cylinder block, and in the third bed - a liner without grooves (the same as in the cover).
Lubricate the bearings with engine oil and place the crankshaft in the supports. We insert thrust half-rings lubricated with engine oil into the grooves of the third main bearing support. The surfaces of the half rings with anti-friction coating (grooves are made on them) should face the cheeks of the crankshaft. Marks on the main bearing caps
We install the main bearing caps in accordance with the marks (see figure) marked on their outer surface (the caps are counted from the timing belt drive side). In this case, the locks of the upper and lower shells of each main bearing must be located on the same side.
The classes of piston diameters and holes for the piston pin, as well as the piston weight group, are marked on its bottom.
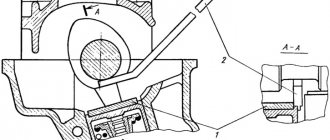
When assembling rod and piston group, it is necessary that the piston pin, lubricated with engine oil, enters the piston hole with pressing force from the thumb and does not fall out of the piston when the pin is in a vertical position. To press the pin into the upper head of the connecting rod of the VAZ-21083 engine, we mount the pin on a universal mandrel (see figure). Size A is calculated using the formula:
A = 0.5 x (D – B – C + E) mm, where D is the piston diameter, B is the length of the pin, C is the distance between the bosses, E is the width of the connecting rod head. We do not tighten screw 7, because When heated by the connecting rod, the pin lengthens and the screw may jam. To assemble the pistons with connecting rods, heat the connecting rod on an electric stove or in a muffle furnace (up to 240°C). We clamp the heated connecting rod in a vice. We assemble the piston with a pin and a heated connecting rod quickly, because Once the connecting rod has cooled, it will not be possible to change the position of the piston pin.
We put the piston on the connecting rod, ensuring that the holes in the upper head of the connecting rod and the piston bosses match. We insert the mandrel with the finger into the hole in the piston boss and push it into the connecting rod head. In this case, the piston must be pressed by the boss against the connecting rod head in the direction of pressing the pin. We install the rings on the pistons and position them as follows: we orient the lock of the upper compression ring at an angle of about 45° to the piston pin axis; the lock of the lower compression ring is at an angle of 180° to the axis of the lock of the upper ring; The oil scraper ring lock is at an angle of 90° to the axis of the upper compression ring lock. We install the lower compression ring with the groove (“scraper”) down. If the ring is marked “TOP” or “TOP”, place the ring with the mark facing up. When installing the oil scraper ring, place the expander lock on the side opposite to the ring lock. Before installing the parts, lubricate the cylinders, pistons with rings and connecting rod bearings with engine oil.
When installing pistons into cylinders, the arrow on the piston bottom must face toward the timing drive.
Before installing the piston and connecting rod into the cylinder, we compress the piston rings with an adjustable mandrel.
Using the wooden handle of the hammer against the bottom of the piston, we push it into the cylinder.
We install the connecting rod cover with the liner and tighten the cover fastening nuts to the prescribed torque (see Tightening torques for threaded connections). We install the other pistons in the same way. When installing the connecting rod cap, the numbers on the connecting rod and cap must be on the same side.
Further assembly is carried out in the reverse order of disassembly.
Pressing the pin into the upper head of the connecting rod
1 – mandrel; 2 – adjusting nut; 3 – piston; 4 – piston pin; 5 – guide sleeve; 6 – connecting rod; 7 – screw.
Source
Engine diagram and structure
General view of the engine
Before we begin to consider the issue of the engine design and description of the characteristics, it is necessary to consider the design of the components and parts that are located directly in the main power unit and outside.
Diagram and design of the Samara-2 engine
Also, it’s worth looking at a cross-section of the VAZ-2114 engine:
Cross section of the Samara engine
Characteristics of an 8-valve engine
Many motorists remember how at the end of the 90s of the 20th century and the beginning of the 2000s, the VAZ 2108-09, which was also called “Samara,” was popular on the roads of the CIS. These cars became legendary in that era. Due to the high popularity, the AvtoVAZ plant decided to resume production of these models with some modifications.
Supply system
The air filter is located in the front part of the engine and is equipped with rubber retaining elements. If it becomes necessary to replace them, the corrugation is located on the same parallel with the center line of the car. The main function of the throttle pipe is determined by dosing the air flow entering the intake pipe. The air entering the engine is adjusted thanks to the throttle valve, which is connected to the accelerator pedal. The throttle pipe consists of two components: the throttle position sensor and the idle speed control.
Crankshaft device
The crankshaft consists of flat machined plates with counterweights (the so-called “cheeks”), which are connected to each other by “necks”. Counterweights are needed to dampen the reciprocating movements of the pistons and stabilize the rotation of the shaft.
Some modern engines use balancer shafts with an offset center of gravity and driven by the crankshaft for additional stabilization. They rotate in different directions, helping to balance the movements of the pistons.
Crank mechanism with an additional block of balancers
In V-twin and W-twin engines, connecting rods from opposing cylinders press against interconnected journals. This allows for more uniform operation of the engine and reduces its dimensions. In in-line engines, each connecting rod is mounted on a separate journal with balancers.
Crank mechanism of an inline four-cylinder engine with standard journals and balancers V6 engine crankshaft with a split adjacent connecting rod journal
The crankshaft journals are cylindrical in shape with a ground surface. The main journals are located along the axis of the shaft, and the “crank journals” are located along the axis of the connecting rods. The rubbing pairs of the crankshaft are usually mounted on plain bearings. To prevent longitudinal displacement of the shaft, support bearings are provided, they are also called crankshaft half rings.
The crankshaft is located in the cylinder block in the reciprocal seats of the “crankshaft bed”. On the crankshaft there is a shank for fastening the timing sprocket, generator pulley and water pump. On the back of the shaft there is a flange for fastening the flywheel. A rolling bearing is installed in the flange, and the gearbox input shaft fits into it. Inside the crankshafts there are channels for forced lubrication of the journal liners, connecting rods and cylinder-piston group. The design of crankshafts depends on the layout of the cylinders and their number. Drive gears for various equipment, such as an oil pump, can be installed on the crankshaft.
Crankshaft device
Motor maintenance
When the design and main technical characteristics inherent in the VAZ 2114 engine have been reviewed, it is necessary to consider maintenance and provide answers to questions that motorists are increasingly asking.
Maintenance
If you believe the plant, the manufacturer, the VAZ 2114 engine must be serviced every 12-15 thousand kilometers. It depends on what marking the motor is installed on the vehicle. Maintenance scheme for all engines installed on the “fourteenth” model:
- At the first maintenance, the oil, oil filter and air filter element are replaced, as well as the functionality of all systems is checked.
- The second maintenance is done after 12,000 km. In this case, it is necessary to change the oil and oil filter element.
- Third maintenance – 25,000 km, replacing not only the oil, but also the air filter, and ongoing repair of faults.
- After 45,000 km, it is necessary to replace the timing belt and roller so that the VAZ 2114 engine does not have to be overhauled.
Subsequent maintenance is carried out in accordance with 2 and 3 maintenance.
Frequently asked questions and their answers
The process of repairing a VAZ 2114 engine.
Many car enthusiasts on forums ask the same questions. Let's try to classify all of them, and also give answers according to factory standards and recommendations.
What kind of oil should be poured into the VAZ 2114 engine?
If you rely on the manufacturer’s data, then different oil is poured into the VAZ 2114 engine, depending on the type. So, what kind of oil should you put in the VAZ 2114? If you take it for an 8 valve engine, then ideally it would be suitable with the 10W-40 marking. If it is a 16 valve engine - 5W-30. In any case, the oil for the VAZ 2114 should be semi-synthetic.
What is the operating temperature of the engine?
Based on the manufacturer's data, the operating temperature of the motor for engines installed on models 2113-2115 is 87-103 degrees Celsius. After 105 degrees the electric fan turns on.
Where is the engine number on the VAZ 2114?
The engine number is quite easy to find. It is located on the gearbox side, near the thermostat. The engine number always has a pad on the cylinder block, which is located in a visible place.
What is the resource of ICE 2114?
The service life of the VAZ 2114 engine is 150 thousand km for an eight-valve power unit and 180,000 km for a 16-valve power unit. To extend the service life, you need to know what oil to pour into the engine, as well as service it on time. Although driving style and careful operation of the car play an important role.
Do valves bend on VAZ 2114 engines?
Of course, like in any other engine, the VAZ 2114 has a valve mechanism that bends. This often happens due to overheating, when the head bends. The valves can also bend if the timing belt breaks.
What to do if the engine does not develop power and the speed drops?
In this case, it is worth carrying out a comprehensive diagnosis of the power unit. The issue may lie either in the inoperability of one of the sensors or in the mechanics. You can find the fault on your own or with the help of professionals at a car service center.
Engine malfunctions and repairs
Disassembled VAZ 2114 engine.
The fault diagram of the 2114 motor and its modifications is quite typical. Typically, the most common ones are floating speed, tripping, pump failure, as well as others that car owners are familiar with in detail. Where certain faults are located can be determined by carrying out diagnostic work.
After 150,000 km, the engine will need a bulkhead (overhaul). Every car enthusiast can repair his engine on his own, but many do not take risks and turn to a car service center.
For the VAZ 2114, repairs are carried out by analogy with the 2108 engine, since they are quite similar. In order to replace the timing belt, you will have to fix the camshafts. The set of replacement operations includes changing the timing belt, a roller or two, as well as adjusting the valves.
To replace the water pump, you will have to fix the camshafts, just like to change the timing belt. Because the belt also passes through the pump, and therefore the process is quite complicated.
Engine tuning
Tuning version of the VAZ 2114 engine.
Tuning the VAZ 2114 engine is carried out typically for the entire series of power units installed on 2113-2115. As you know, there are two options for modifying the engine: mechanical and chip tuning. The modification scheme is quite simple, the mechanics are done first, and then the electronics. But many car enthusiasts only carry out chip tuning to reduce consumption, since the price of fuel is too high.
Chip tuning of the VAZ 2114 is carried out using special equipment and is aimed at increasing power or reducing fuel consumption. This type of work should be entrusted to professionals, since only they have the necessary skills and knowledge.
As for mechanical modifications, the scheme is standard. In case of complete modification of the motor, it must be completely disassembled. It is necessary to gain full access to the interior of the power unit. Next, the process of boring-honing and installation of new spare parts with light weight is carried out.
Installed turbine on a VAZ 2114 engine
After assembly, it is recommended to install a tuning version of the cooling and exhaust system, since combustion will occur with the release of more heat than before. Standard oil will not be suitable for the VAZ 2114 engine after tuning, so it is recommended that the modification process be done by professionals.
Types of repairs
Depending on what fuel the VAZ-2114 engine runs on, major overhauls are distinguished:
- A unit operating on gasoline.
- Diesel engine.
From the one who carries out the work, major repairs happen:
- Independent.
- Auto service specialist.
- A private craftsman who works in his garage.
Major repairs are identified according to urgency:
Design
All modifications of the engine installed on the VAZ 2114 have a block cast from cast iron and a fuel injection system. Despite the design solutions used to improve dynamic and environmental performance, the design of the VAZ 2114 engine has retained its simplicity and reasonable maintenance cost.
Operation and resource availability
An oil change should be done every 9-11 thousand km.
Regardless of the modification, 3.2 liters will be required to change the oil. Recommended viscosity: 5W-30, 10W-40, 5W-40, 15W-40. According to the manufacturer, the engine life is 150 thousand km. (200 thousand km for Priora motor). Practice has shown that with proper maintenance, the engine can cover up to 250 thousand km.
Failure to comply with maintenance standards and improper tuning of the VAZ 2114 engine significantly reduces its service life.
Features and Disadvantages
- after a timing belt breaks, the valves remain unharmed;
- Regular adjustment of valve clearances is required;
- wear of cooling system components;
- oil leaks from under the valve cover;
- oil leakage from under the ignition distributor and fuel pump;
- poor fastening of the exhaust manifold (solved by replacing steel nuts with brass ones);
- unreliability of early injection systems.
- A broken timing belt does not deform the valve;
- the need for periodic valve adjustment;
- increased noise and vibration load.
- Thanks to the holes on the pistons, even with moderate sports shafts, if the timing belt breaks, the valves do not bend;
- Every 15 thousand km you need to tighten the timing belt.
- a broken timing belt leads to bending of the valves (the problem can be solved by installing plug-free pistons.
Popular faults
Due to the imperfect quality of the unit and the large number of low-quality spare parts, the motor and attachments require increased attention.
Main problems and possible causes:
- Unstable idling of the VAZ 2114, the engine stalls after starting. Cause – Coking of the idle speed controller (IAC), throttle position sensor, vacuum seal “drizzle”, unreliable signals from the mass air flow sensor;
- Starting has deteriorated, the engine is running rough - the reason may be: incorrect valve adjustment, lack of compression in one of the cylinders (the valve may have burned out), wear of the valve springs, air leaks (check the connections of the hoses and pipes going after the mass air flow sensor and to the vacuum valve, valve hose purging of the absorber, tight fit of the injectors to the cylinder head), malfunction of the ignition module, spark plugs do not produce a spark, inoperability of high-voltage wires, incorrect valve timing (the timing belt may have slipped a few teeth);
- The VAZ 2114 engine has lost throttle response and does not pull. The breakdown is possible due to a malfunction of the ignition module (symptoms appear when the engine is warm), a clogged catalyst, the fuel pump does not create the required pressure, a dirty air filter, air leaks, carbon deposits on the spark plugs, lack of compression;
- Extraneous knocking, noise and vibration of the VAZ 2114 engine. Failure may occur because valve clearances need adjustment, sagging valve springs, sagging seats, wear on the main bearings of the crankshaft or connecting rod bearings (it is possible that the pistons themselves are knocking), hydraulic compensators, wear on the engine mounts (pillows);
- Does not show the engine temperature of the VAZ 2114. Occurs due to a malfunction of the coolant temperature sensor (the sensor screwed into the cylinder head is responsible for the readings on the instrument panel), open circuit, oxidation of contacts, a malfunction in the indicator on the dashboard;
- The engine is heating up. Thermostat failure (liquid circulates only in the engine cooling jacket). When buying a thermostat, look in the instructions for what engine operating temperature it is designed for (for the engines in question this is 95-103 degrees); Damage to the water pump impeller, malfunction of the fan switch sensor, or the fan itself does not work.
How to repair the cylinder head of a VAZ-2114 8 valves with your own hands
The power plant of a car is a rather complex device, consisting of many mechanisms and systems that interact with each other.
The basis of any engine is the cylinder block and its upper part - the cylinder head. Structurally, it was not possible to connect these two parts without placing a gasket between them to ensure tightness between these elements of the power plant, as well as to ensure the connection of the channels of the lubrication and cooling systems so that the working fluids do not mix and do not penetrate the cylinders. At the same time, the gasket must perform its functions under very difficult conditions - high pressure, significant temperature, exposure to oil and coolant.
Any cylinder head (cylinder head) gasket consists of many layers, including sheet steel, cardboard, fiber, and cork. All these layers are well compressed and covered with a layer of sealing substance.
Despite the material the gasket is made of, there is always the possibility of its breakdown. And if you do not pay attention to such a malfunction in a timely manner, it can lead to significant damage to the power plant and major repairs with the replacement of the cylinder-piston group or cylinder block.
Improved dynamic performance
To improve the dynamic characteristics of the VAZ 2114 engine on a budget, you can do the following:
- modify the intake and exhaust, namely install a larger throttle valve, an intake receiver and an exhaust without a 4-2-1 catalyst, popularly called a “spider”;
- split gear for phase adjustment;
- non-standard camshafts;
- if you have an 8-valve engine, the best solution would be to replace the cylinder head with a 16-valve one;
- modification of the cylinder head of varying complexity can increase the maximum power to 120 hp. With. without loss of resource.
Tuning can go as far as installing turbocharging, nitrous oxide injection and other means that significantly increase power, but all of them are quite expensive and reduce engine life.
When modifying, do not forget that all procedures must be supplemented with appropriate software for the control unit, otherwise your tuning may adversely affect the operation of the motor.
Engine tuning
For naturally aspirated engines, the following type of tuning is usually used:
- receiver complete with 54 mm throttle body at the inlet;
- straight-through spider 4/2/1 at the outlet;
- camshaft Nuzhdin 10.93 or Dynamics 118 instead of the factory equipment.
The dynamics of the internal combustion engine will improve, the power will increase to 85 - 90 hp. With. Next is just lightening the crankshaft, modifying the intake manifold and milling the cylinder head.
For 16 valve engines, tuning has the same principles, since chipping it does not make sense. To achieve 120 l. With. You can increase the damper to 56 mm, use a direct-flow type exhaust, Nuzhdin 8.85 or Stolnikov 8.9 280 camshaft.
Thus, only one engine, modification 21126, bends the valves on the VAZ 2114. All other engines are considered safe and provide a real service life of about 270,000 km.