The control system of a car engine contains a certain mathematical model, where output values are calculated based on measurements of input values. For example, how long the injectors open depends on the amount of air and many other variables. But besides them, there are also constants, that is, characteristics of the fuel system that are written in memory and cannot be controlled. One of them is the fuel pressure in the rail, or more precisely, its difference between the injector inlets and outlets.
Why do you need a fuel pressure regulator?
Fuel is supplied to the injectors from the tank by pumping it with an electric fuel pump located there. Its capabilities are redundant, that is, they are designed for maximum consumption in the heaviest mode plus a significant margin for deterioration of characteristics over time during long-term operation.
But the pump cannot constantly pump to the full power of its changing capabilities; the pressure must be limited and stabilized. For this purpose, fuel pressure regulators (FPR) are used.
They can be installed either directly in the pump module or on the fuel rail that supplies the injection nozzles. In this case, you have to dump the excess through the drain line (return) back into the tank.
Signs of device malfunction
The valve is operated at an intense rhythm. Long-term loads affect its performance. It is necessary to promptly identify the symptom of a malfunction of the fuel pressure regulator in order to replace it. Failures and malfunctions are determined in most cases by indirect signs. Such factors include the following phenomena:
- fuel consumption increases;
- the power characteristics of the internal combustion engine are deteriorating;
- the power plant loses stability at idle;
- dips occur or jerks appear when switching speed modes;
- the car responds inadequately to pressing the gas pedal.
Checking the fuel pressure regulator often begins with determining the quality of the springs. As the device is used, their hardness decreases. This phenomenon negatively affects performance, in particular, the valve opens earlier than the operating cycle requires.
The result of a drop in rigidity is that fuel is sent to the tank in larger quantities than intended by the designers. At the same time, the pressure in the system decreases, and the engine loses efficiency and power. If there is a design possibility, then the weak spring is replaced.
We recommend: Spacers to increase ground clearance: what are they for?
The low quality of domestic fuel also has a negative impact on the functioning. As a result, the membrane becomes clogged, after which it cannot close partially or completely. As a result, the fuel pressure in the system also drops, which leads to negative phenomena.
You can get rid of mechanical blockages by cleaning. This is carried out if the design of the device allows. It is worth considering that repairing the fuel pressure regulator does not always save users. This happens when there is significant wear or wear on the valve as a whole or its individual parts. It is not always possible to restore the element to full operation.
There are cases when the RTD becomes jammed. In this case, the engine simply stalls, and at the same time fuel begins to flow from poorly sealed joints. Here, repairs are unpromising; all that remains is a complete replacement of the unit with a new one. If this happens, then it is worth changing the gas station or not refueling at dubious gas stations in advance; it is also worth checking the functionality of the fuel filter, which has failed to be properly cleaned.
Partial loss of valve functionality often occurs. In such a situation, the engine operates jerkily, which the driver feels very well while operating the car. Sometimes passengers feel them too. Timely cleaning of passages will be relevant, restoring the product’s functionality .
An electronic device is less sensitive to the quality of gasoline. It is also little influenced by mechanical factors. However, it is not without its shortcomings, weaknesses and characteristic vulnerabilities. But if you avoid situations with low-quality fuel, you can largely avoid loss of regulator functionality.
Device
The regulator can be mechanical or electronic. In the second case, this is a classic control system with a pressure sensor and feedback. But a simple mechanical one is no less reliable, and cheaper.
On the subject: How to find out the fuel consumption of a car by mileage (per 100 km)
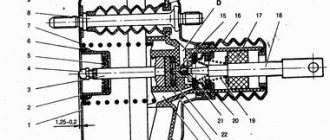
The regulator installed on the ramp consists of:
- two cavities, one contains fuel, the other contains air vacuum from the intake manifold;
- elastic diaphragm separating the cavities;
- spring-loaded control valve connected to a diaphragm;
- housing with return fittings and a vacuum hose from the intake manifold.
Sometimes the RTD contains a mesh filter for coarse purification of passing gasoline. The entire regulator is installed on the ramp and communicates with its internal cavity.
Design Features
The gasoline pressure regulator is one of the few elements of the system that is not controlled from an electronic unit. This unit is completely mechanical and its operation is based on pressure differences. Although in systems without recirculation, the sensor is triggered by the ECU. Since they do not occur often, we will not consider such nodes further.
It is worth noting that the RTD does not operate in strictly specified values, it adapts to the operating mode of the engine. That is, if necessary, it increases or decreases the pressure in the system to ensure optimal mixture formation.
Structurally, this element is very simple and consists of a housing on which fittings and leads are located for connection to the power system. Inside, this housing is divided by a membrane into two chambers - fuel and vacuum.
There are outlets suitable for the fuel cavity - one is used to supply fuel to the chamber, and the second leads to the line for draining gasoline into the tank (return). But the second channel is closed by a valve, which is connected to the membrane.
A spring is installed on the side of the vacuum cavity, which acts on the membrane, ensuring that the drain channel is closed by the valve. This chamber is connected to the intake manifold by means of a fitting via a tube.
Principle of operation
To fix the pressure between the injector inlets and outlets, it is necessary to add to its value in the ramp a negative vacuum in the manifold, where the injector nozzles exit. And since the vacuum depth changes depending on the load and the degree of throttle opening, the difference must be monitored continuously, stabilizing the difference.
Only then will the injectors operate at their standard performance levels, and the composition of the mixture will not require deep and frequent correction.
As the vacuum at the RTD vacuum pipe increases, the valve will open slightly, releasing additional portions of gasoline into the return line, stabilizing the dependence on the state of the atmosphere in the manifold. This is an additional correction.
The main regulation occurs thanks to a spring that presses the valve. The main characteristic of the RDT – stabilized pressure – is standardized according to its rigidity. The work follows the same principle: if the pump presses too much, then the hydraulic resistance of the valve decreases, and more fuel is drained back into the tank.
Operating principle of RTD
The valve design and operating principle depend on the type of fuel system of a particular vehicle. There are 3 ways to supply gasoline from the tank to the injectors:
- The pump together with the regulator is installed inside the tank; fuel is supplied to the engine through one line.
- Gasoline is supplied through one tube and returned through another. The fuel system check valve is located on the distribution rail.
- The circuit without a mechanical regulator provides for electronic control of the fuel pump directly. The system contains a special sensor that registers pressure; the pump performance is regulated by the controller.
In the first case, the return flow is very short, since the valve and electric pump are interlocked into a single unit. The RTD, located immediately after the supercharger, dumps excess gasoline into the tank, and the required pressure is maintained throughout the supply line.
Reference. The first scheme with a regulator inside the gas tank has been implemented on all Russian-made VAZ cars.
The second option is used in most foreign cars. A valve built into the fuel rail allows excess fuel to flow into the return line leading to the tank. That is, 2 gasoline pipes are laid to the power unit.
There is no point in considering the third circuit - instead of a regulator, there is a sensor whose functionality is checked using a computer connected to the diagnostic connector.
We recommend: Thermostat: principle of operation, types, device, photo, video.
A simple fuel pressure valve installed in the fuel pump unit consists of the following elements:
- cylindrical body with pipes for connecting the supply and return lines;
- a membrane connected to a locking rod;
- valve seat;
- spring.
The amount of pressure in the supply line depends on the elasticity of the spring . While most of the fuel goes into the cylinders (high load on the engine), it keeps the membrane and valve stem closed. When the crankshaft speed and gasoline consumption decrease, the pressure in the network increases, the spring compresses and the membrane opens the valve. The fuel begins to be discharged into the return line, and from there into the gas tank.
The fuel pressure regulator installed in the rail operates on a similar principle, but reacts faster to changes in load and gasoline consumption. This is facilitated by connecting an additional pipe of the element to the intake manifold. The higher the crankshaft speed and the vacuum on the spring side, the stronger the membrane presses the rod and closes the passage of fuel into the return line. When the load decreases and the speed drops, the vacuum decreases and the rod releases - the return flow opens and excess gasoline begins to be discharged into the tank.
Signs and symptoms of a malfunctioning RTD
Depending on the nature of the malfunction, the pressure can either increase or decrease. Accordingly, the mixture entering the cylinders becomes richer or leaner.
The control unit is trying to adjust the composition, but its capabilities are limited. Combustion is disrupted, the engine begins to work intermittently, flashes disappear, traction worsens, and consumption increases. And in any case, the mixture is lean or enriched. It burns equally badly.
The role of the fuel regulator in the car system
At different engine operating modes, it is necessary to create the appropriate fuel pressure in the fuel system. To implement this task in practice, a special pressure regulator is used. It is used in injection engines, where the correct operation of the engine depends on the accuracy of the injection parameters.
When the governor is faulty, the engine runs unevenly, acceleration times are increased, and in some cases power can be significantly reduced. So, for example, if the amount of air coming from the manifold remains unchanged, and there is more fuel than necessary, the air-fuel mixture will not ignite or will not burn completely.
We recommend: Replacing the crankshaft oil seal Lada 2107 (VAZ 2107)
Even if in this mode the electronic control unit shortens the injector opening interval, it will not be possible to completely compensate for the excess fuel pressure. This will lead to interruptions in engine operation and an increase in the amount of unburned fuel in the exhaust, which can prematurely damage the catalytic converter or particulate filter.
How to check the device for functionality
To check, the pressure in the rail is measured. It is equipped with a valve to which a test pressure gauge can be connected. The device will show whether the value is within the normal range or not. And the specific fault of the regulator will be indicated by the nature of the reaction of the readings to opening the throttle valve and turning off the return line, for which it is enough to pinch or plug its flexible hose.
Removing the vacuum hose from the RTD fitting will also demonstrate the adequacy of the pressure response. If the engine was running at minimum speed, that is, the vacuum was high, then the disappearance of vacuum should cause an increase in pressure in the ramp. If not, the regulator is not working properly.
Controller operation in different modes
Operating principle of RTD
If we take a simplified look at the operating principle, it is quite simple. The pump pumps fuel into the ramp, from which it also enters the fuel chamber of the regulator. As soon as the pressure force exceeds the spring stiffness, the membrane begins to move towards the vacuum cavity, dragging the valve with it. As a result, the drain channel opens and part of the gasoline flows into the tank, while the pressure in the ramp drops. Because of this, the spring returns the valve with the membrane to its place, and the return channel closes.
But as already mentioned, the RTD adapts to the operating mode of the motor. And it does this due to the vacuum in the intake manifold. The greater this vacuum, the stronger its effect on the membrane. Essentially, the vacuum created creates an opposing force against the spring.
In reality, everything looks like this: to operate the engine at idle speed, an increase in the amount of fuel is not necessary, and therefore no increased pressure is required.
In this operating mode, the throttle valve is closed, so there is not enough air in the intake manifold and a vacuum is created. And since the vacuum chamber is connected to the manifold by a pipe, a vacuum is created in it. Under the influence of vacuum, the membrane presses on the spring, so less gasoline pressure is needed to open the valve.
Under load, when the throttle valve is open, there is practically no vacuum, which is why the membrane does not participate in creating force on the spring, so more pressure is required. Thus, this element functions in the power system depending on the operating mode of the motor.
Video: Fuel pressure regulator. It doesn't drive well, it doesn't start well.
How to clean an RTD
The regulator cannot be repaired; if it malfunctions, it is replaced with a new one; the price of the part is low. But sometimes it is possible to restore functionality by cleaning the built-in mesh filter. To do this, the regulator is dismantled and washed with carburetor cleaner, followed by purging.
The operation can be repeated for better results. It is also possible to use an ultrasonic bath with a solvent, which is used to clean injectors, where similar problems arise due to dirty fuel.
There is no particular point in these procedures, especially if the part has already served a lot. The cost of time and money is quite comparable to the price of a new RTD, despite the fact that the valve in the old one is already worn out, the diaphragm is aged, and caustic cleaning compounds can cause final failure.
Signs of regulator malfunction
Prolonged operation of the vehicle, without inspection and minor repairs, causes a more serious malfunction in the operation of its systems. As for the fuel pressure regulator, most often after a certain period of time its spring begins to sag, which accordingly does not create the required force and the fuel returns back to the tank. In turn, this process helps to reduce the pressure in the fuel rail and leads to a loss of engine power.
Moreover, this is not the only problem that may arise. Very often, when idling, engines stall, losing power, and when changing gears, the car refuses to accelerate. Also, often, when jerking occurs (while driving), the engine seems to choke, not responding to the gas pedal. Another reliable sign of a breakdown in the fuel pressure regulator is a sharp increase in fuel consumption and, believe me, you definitely won’t miss this indicator.
We recommend: How to clean the air conditioner in your car yourself
Simply put, there are the following possible indicators of a fuel pressure regulator failure:
uneven operation of the motor;
stopping idling;
a sharp increase (or decrease) in crankshaft rotation speed;
loss of engine power;
complete or partial lack of response to the gas pedal;
poor vehicle acceleration when changing gears;
frequent jerks during movement;
rapid increase in fuel consumption.
If you notice at least one of the described factors, it is worth checking whether everything is in order with the fuel pressure regulator.
Among the types of its breakdowns, the main ones are:
weak valve holding the required pressure,
the fuel begins to move freely throughout the system, thereby reducing its pressure, and ultimately returns to the tank. As a result, when the speed increases, the engine lacks fuel and its power drops significantly;
complete blockage of the regulator or limited fuel supply.
Leads to the engine stopping while the car is moving, and fuel begins to pour out of all accessible cracks;
valve malfunction
(they say “the valve is sticking”) happen due to pressure changes, which results in the car “jerking.”
But the most common problems with the fuel pressure regulator, nevertheless, are expressed in mechanical damage to its parts or their clogging. In addition, often the reason lies in the wear and tear of the materials used to create the mechanism, and even after eliminating the problem that has arisen, you will no longer be able to achieve the original standard indicators.
Also, there are some other subjective reasons that affect the proper operation of the pressure regulator - low-quality fuel (diluted with water), prolonged absence of vehicle operation, valve malfunction. We called them subjective because problems can be avoided through each driver’s responsible attitude towards his car, including timely repairs and quality service.
Instructions for replacing the fuel pressure regulator using the example of an Audi A6 C5
Access to the regulator on these machines is easy; it is installed on the fuel rail of the injectors.
- Remove the decorative plastic cover from the top of the engine by unscrewing the twist latches counterclockwise.
- Use a screwdriver to pry up and remove the retaining spring bracket on the regulator body.
- The vacuum hose is disconnected from the regulator fitting.
- The residual pressure in the rail can be relieved in various ways by letting the engine run with the fuel pump turned off, pressing on the spool of the pressure gauge valve on the rail, or simply disconnecting the halves of the regulator housing. In the last two cases, you need to use a rag to absorb the escaping gasoline.
- With the lock removed, the regulator is simply removed from the body, after which it can be washed, replaced with a new one, and everything reassembled in the reverse order.
Before installation, it is recommended to lubricate the rubber O-rings so as not to damage them when immersed in the socket.